WINNER II pdf - Final Report - Cept
WINNER II pdf - Final Report - Cept
WINNER II pdf - Final Report - Cept
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>WINNER</strong> <strong>II</strong> D1.1.2 V1.2<br />
⎡<br />
ρ(d) ∝ ⎢e<br />
⎣<br />
d<br />
− MS<br />
∆<br />
⎤<br />
⎥<br />
⎦<br />
d MS<br />
[ ]<br />
m<br />
ρ(0)<br />
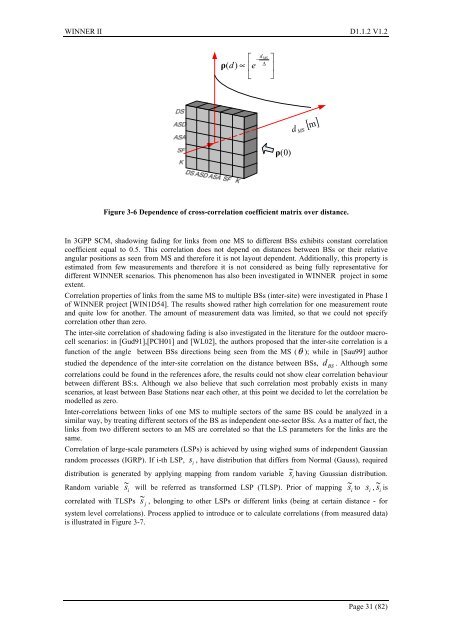
Figure 3-6 Dependence of cross-correlation coefficient matrix over distance.<br />
In 3GPP SCM, shadowing fading for links from one MS to different BSs exhibits constant correlation<br />
coefficient equal to 0.5. This correlation does not depend on distances between BSs or their relative<br />
angular positions as seen from MS and therefore it is not layout dependent. Additionally, this property is<br />
estimated from few measurements and therefore it is not considered as being fully representative for<br />
different <strong>WINNER</strong> scenarios. This phenomenon has also been investigated in <strong>WINNER</strong> project in some<br />
extent.<br />
Correlation properties of links from the same MS to multiple BSs (inter-site) were investigated in Phase I<br />
of <strong>WINNER</strong> project [WIN1D54]. The results showed rather high correlation for one measurement route<br />
and quite low for another. The amount of measurement data was limited, so that we could not specify<br />
correlation other than zero.<br />
The inter-site correlation of shadowing fading is also investigated in the literature for the outdoor macrocell<br />
scenarios: in [Gud91],[PCH01] and [WL02], the authors proposed that the inter-site correlation is a<br />
function of the angle between BSs directions being seen from the MS (θ ); while in [Sau99] author<br />
studied the dependence of the inter-site correlation on the distance between BSs, d . Although some<br />
correlations could be found in the references afore, the results could not show clear correlation behaviour<br />
between different BS:s. Although we also believe that such correlation most probably exists in many<br />
scenarios, at least between Base Stations near each other, at this point we decided to let the correlation be<br />
modelled as zero.<br />
Inter-correlations between links of one MS to multiple sectors of the same BS could be analyzed in a<br />
similar way, by treating different sectors of the BS as independent one-sector BSs. As a matter of fact, the<br />
links from two different sectors to an MS are correlated so that the LS parameters for the links are the<br />
same.<br />
Correlation of large-scale parameters (LSPs) is achieved by using wighed sums of independent Gaussian<br />
random processes (IGRP). If i-th LSP, s , have distribution that differs from Normal (Gauss), required<br />
distribution is generated by applying mapping from random variable<br />
i<br />
BS<br />
s~<br />
i having Gaussian distribution.<br />
Random variable s~<br />
i<br />
will be referred as transformed LSP (TLSP). Prior of mapping s~<br />
i to s<br />
i<br />
, s~<br />
i is<br />
correlated with TLSPs s~<br />
j , belonging to other LSPs or different links (being at certain distance - for<br />
system level correlations). Process applied to introduce or to calculate correlations (from measured data)<br />
is illustrated in Figure 3-7.<br />
Page 31 (82)