Final report on link level and system level channel models - Winner
Final report on link level and system level channel models - Winner
Final report on link level and system level channel models - Winner
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
WINNER D5.4 v. 1.4<br />
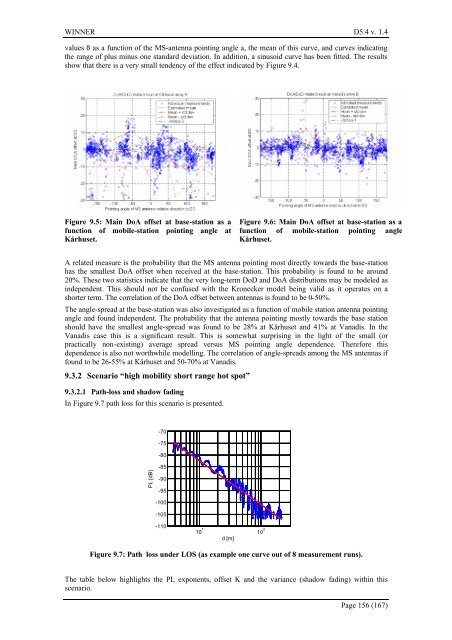
values ß as a functi<strong>on</strong> of the MS-antenna pointing angle a, the mean of this curve, <strong>and</strong> curves indicating<br />
the range of plus minus <strong>on</strong>e st<strong>and</strong>ard deviati<strong>on</strong>. In additi<strong>on</strong>, a sinusoid curve has been fitted. The results<br />
show that there is a very small tendency of the effect indicated by Figure 9.4.<br />
Figure 9.5: Main DoA offset at base-stati<strong>on</strong> as a<br />
functi<strong>on</strong> of mobile-stati<strong>on</strong> pointing angle at<br />
Kårhuset.<br />
Figure 9.6: Main DoA offset at base-stati<strong>on</strong> as a<br />
functi<strong>on</strong> of mobile-stati<strong>on</strong> pointing angle<br />
Kårhuset.<br />
A related measure is the probability that the MS antenna pointing most directly towards the base-stati<strong>on</strong><br />
has the smallest DoA offset when received at the base-stati<strong>on</strong>. This probability is found to be around<br />
20%. These two statistics indicate that the very l<strong>on</strong>g-term DoD <strong>and</strong> DoA distributi<strong>on</strong>s may be modeled as<br />
independent. This should not be c<strong>on</strong>fused with the Kr<strong>on</strong>ecker model being valid as it operates <strong>on</strong> a<br />
shorter term. The correlati<strong>on</strong> of the DoA offset between antennas is found to be 0-50%.<br />
The angle-spread at the base-stati<strong>on</strong> was also investigated as a functi<strong>on</strong> of mobile stati<strong>on</strong> antenna pointing<br />
angle <strong>and</strong> found independent. The probability that the antenna pointing mostly towards the base stati<strong>on</strong><br />
should have the smallest angle-spread was found to be 28% at Kårhuset <strong>and</strong> 41% at Vanadis. In the<br />
Vanadis case this is a significant result. This is somewhat surprising in the light of the small (or<br />
practically n<strong>on</strong>-existing) average spread versus MS pointing angle dependence. Therefore this<br />
dependence is also not worthwhile modelling. The correlati<strong>on</strong> of angle-spreads am<strong>on</strong>g the MS antennas if<br />
found to be 26-55% at Kårhuset <strong>and</strong> 50-70% at Vanadis.<br />
9.3.2 Scenario “high mobility short range hot spot”<br />
9.3.2.1 Path-loss <strong>and</strong> shadow fading<br />
In Figure 9.7 path loss for this scenario is presented.<br />
-70<br />
-75<br />
-80<br />
PL [dB]<br />
-85<br />
-90<br />
-95<br />
-100<br />
-105<br />
-110<br />
10 1 10 2<br />
d [m]<br />
Figure 9.7: Path loss under LOS (as example <strong>on</strong>e curve out of 8 measurement runs).<br />
The table below highlights the PL exp<strong>on</strong>ents, offset K <strong>and</strong> the variance (shadow fading) within this<br />
scenario.<br />
Page 156 (167)