Final report on link level and system level channel models - Winner
Final report on link level and system level channel models - Winner
Final report on link level and system level channel models - Winner
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
WINNER D5.4 v. 1.4<br />
Table 6.6: The three output arguments.<br />
Parameter name Definiti<strong>on</strong> Unit<br />
CHAN<br />
DELAYS<br />
FULLOUTPUT<br />
delays<br />
A 5D-array with dimensi<strong>on</strong>s U x S x N x T x K<br />
A K x N vector of path delay values. Note that delays<br />
are, for compatibility with the INITVALUES, also<br />
included in FULLOUTPUT.<br />
A MATLAB struct with the following elements:<br />
A K x N matrix of path delays. This is identical to the<br />
sec<strong>on</strong>d output argument.<br />
subPathPowers A K x N x M array of subpath powers. -<br />
Aods A K x N x M array of subpath angles of departure degrees<br />
Aoas A K x N x M array of subpath angles of arrival degrees<br />
subpath_phases<br />
A complex-valued K x N x M array giving the final<br />
phases of all subpaths. When polarizati<strong>on</strong> opti<strong>on</strong> is<br />
used, a K x P x N x M array, where P=4. In this case<br />
the sec<strong>on</strong>d dimensi<strong>on</strong> includes the phases for [VV VH<br />
HV HH] polarized comp<strong>on</strong>ents.<br />
sec<br />
sec<br />
degrees<br />
Path_losses A K x 1 vector linear scale<br />
shadow_fading A K x 1 vector linear scale<br />
Delta_t<br />
Xpr<br />
A K x 1 vector defining time sampling interval for all<br />
<strong>link</strong>s.<br />
A K x 2 x N array of cross-polarizati<strong>on</strong> coupling<br />
power ratios. The sec<strong>on</strong>d dimensi<strong>on</strong> is the [V-to-H H-<br />
to-V] coupling ratios.<br />
sec<br />
linear scale<br />
6.3 Guidelines <strong>and</strong> examples <strong>on</strong> performing <strong>system</strong>-<strong>level</strong> simulati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
Chapter 6.1 has provided an overview <strong>on</strong> the c<strong>on</strong>cept of our implementati<strong>on</strong>. In the following, we want to<br />
show how this generic interface can be used to simulate some special types of <strong>system</strong>-<strong>level</strong> situati<strong>on</strong>s.<br />
This can serve as a quick guide <strong>on</strong> how to implement these special cases <strong>and</strong> as proof of the versatility of<br />
our implementati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
6.3.1 H<strong>and</strong>over<br />
A h<strong>and</strong>over situati<strong>on</strong> is characterized by a MS moving from the coverage are of <strong>on</strong>e BS to the coverage<br />
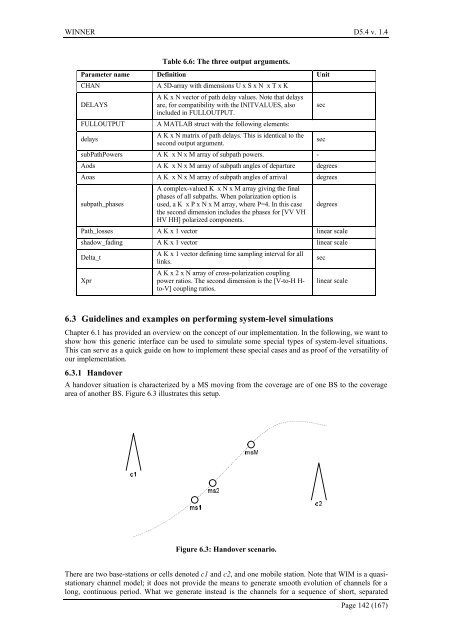
area of another BS. Figure 6.3 illustrates this setup.<br />
Figure 6.3: H<strong>and</strong>over scenario.<br />
There are two base-stati<strong>on</strong>s or cells denoted c1 <strong>and</strong> c2, <strong>and</strong> <strong>on</strong>e mobile stati<strong>on</strong>. Note that WIM is a quasistati<strong>on</strong>ary<br />
<strong>channel</strong> model; it does not provide the means to generate smooth evoluti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>channel</strong>s for a<br />
l<strong>on</strong>g, c<strong>on</strong>tinuous period. What we generate instead is the <strong>channel</strong>s for a sequence of short, separated<br />
Page 142 (167)