3.6M north10.pdf - Dean-O's Toy Box
3.6M north10.pdf - Dean-O's Toy Box
3.6M north10.pdf - Dean-O's Toy Box
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
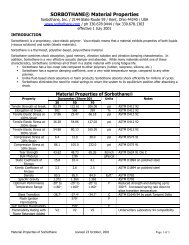
148 High-Power Microwave-Tube Transmitters<br />
Soft-tubs line-type modulstor<br />
Shun_thsrd-lube mcdulstor<br />
(topo!qical descendant of line-type moduhtor)<br />
Figure 10-1. Progression of sofi-tube, line-type moduhtor into shunt-type, hard-tube modus’utor.<br />
combination of screen and anode voltages.<br />
Because of cut-off grid bias, the hard tube can be turned off as well as on.<br />
Tube current, therefore, can be fully controlled by the voltage applied to the<br />
control grid from zero to the maximum. (The maximum curxw-tt is determined<br />
by cathode emissive capability, a factor that varies with cathode area, cathode<br />
material, and cathode temperature.) This feature, then, makes the tube a “proportional<br />
and reciprocal” full-control modulator switch. It is called proportional<br />
and reciprocal because the factors that will reduce current are simply the reverse<br />
of the factors that can increase it. More will be said about hard-tube technology<br />
later.<br />
10.2 Hard-tube modulator topology<br />
Figure 10-1 shows how the replacement of the half-control switch in the linetype<br />
modulator with a full-control switch allows the pulse-forming network to<br />
be replaced with a quasi-infinite energy store. This is now possible because the<br />
time delay of an artificial transmission line is no longer required to externally<br />
turn the switch tube off through commutation. Initiated by a trigger, the pulse<br />
duration in the line-type modulator was set by network constants: the PRF was<br />
limited by the rate of rise of charging voltage across the soft switch tube, while<br />
the pulse-repetition interval (PRI) had to exceed<br />
The pulses of current removed from the hard-tube modulator are now replicas of<br />
the voltage applied to the grid of the hard switch tube. The output voltage V. of<br />
the hard-tube modulator is the inverted replica of the circuit’s switch tube grid<br />
drive voltage. Unlike the line-type modulator, the output-pulse duration and