Atlas of the muscle motor points for the lower limb: implications for ...
Atlas of the muscle motor points for the lower limb: implications for ...
Atlas of the muscle motor points for the lower limb: implications for ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2470 Eur J Appl Physiol (2011) 111:2461–2471<br />
positioned over <strong>the</strong> main <strong>motor</strong> point in case <strong>of</strong> monopolar<br />
stimulation.<br />
However, it is not possible to infer from <strong>the</strong> present data<br />
if <strong>the</strong>se electrode configurations or <strong>the</strong> above-mentioned<br />
multichannel stimulation can improve <strong>the</strong> effectiveness <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> electrical stimulation procedures. Fur<strong>the</strong>r studies<br />
comparing <strong>the</strong> electromechanical responses obtained by<br />
different stimulation sites and modalities are required to<br />
resolve elements <strong>of</strong> confusion and controversy and improve<br />
standardization <strong>of</strong> electrical stimulation procedures.<br />
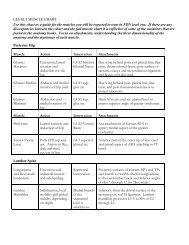
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that <strong>muscle</strong> <strong>motor</strong><br />
<strong>points</strong> can be easily and quickly localized in <strong>the</strong> <strong>lower</strong> <strong>limb</strong><br />
through visual inspection and manual palpation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>muscle</strong> during electrical stimulation and that an interindividual<br />
variability in <strong>the</strong> <strong>motor</strong> point position exists and<br />
may limit <strong>the</strong> usefulness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> anatomic <strong>motor</strong> point<br />
charts, especially <strong>for</strong> posterior thigh and leg <strong>muscle</strong>s.<br />
Acknowledgments Musculoskeletal Images are from <strong>the</strong> University<br />
<strong>of</strong> Washington ‘‘Musculoskeletal <strong>Atlas</strong>: A Musculoskeletal <strong>Atlas</strong> <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> Human Body’’ by Carol Teitz, M.D. and Dan Graney, Ph.D.<br />
Copyright 2003–2004 University <strong>of</strong> Washington. All rights reserved<br />
including all photographs and images. No re-use, re-distribution or<br />
commercial use without prior written permission <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> authors and<br />
<strong>the</strong> University <strong>of</strong> Washington. The authors are grateful to Pr<strong>of</strong>.<br />
R. Merletti (LISiN, Politecnico di Torino, Italy) <strong>for</strong> his careful review<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> final version <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> manuscript and to Dr. D. Antista (School <strong>of</strong><br />
Motor Sciences, Turin, Italy) <strong>for</strong> his valuable assistance in subject<br />
recruitment and evaluation. This study was supported by Regional<br />
Health Administration Project ‘‘Ricerca Sanitaria Finalizzata 2009’’<br />
and by bank foundations ‘‘Compagnia di San Paolo’’ (Project<br />
‘‘Neuromuscular Investigation and Conditioning in Endocrine<br />
Myopathy’’), ‘‘Fondazione Cariplo’’ (Project ‘‘Steroid myopathy:<br />
Molecular, Histopathological, and Electrophysiological Characterization’’)<br />
and ‘‘Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Saluzzo’’.<br />
References<br />
An XC, Lee JH, Im S, Lee MS, Hwang K, Kim HW, Han SH (2010)<br />
Anatomic localization <strong>of</strong> <strong>motor</strong> entry <strong>points</strong> and intramuscular<br />
nerve endings in <strong>the</strong> hamstring <strong>muscle</strong>s. Surg Radiol Anat<br />
32:529–537<br />
Apaydin N, Loukas M, Kendir S, Tubbs RS, Jordan R, Tekdemir I,<br />
Elhan A (2008) The precise localization <strong>of</strong> distal <strong>motor</strong> branches<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> tibial nerve in <strong>the</strong> deep posterior compartment <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> leg.<br />
Surg Radiol Anat 30:291–295<br />
Bax L, Staes F, Verhagen A (2005) Does neuromuscular electrical<br />
stimulation streng<strong>the</strong>n <strong>the</strong> quadriceps femoris? A systematic<br />
review <strong>of</strong> randomised controlled trials. Sports Med 35:191–212<br />
Becker I, Baxter GD, Woodley SJ (2010) The vastus lateralis <strong>muscle</strong>:<br />
an anatomical investigation. Clin Anat 23:575–585<br />
Bergquist AJ, Clair JM, Collins DF (2011) Motor unit recruitment<br />
when neuromuscular electrical stimulation is applied over a<br />
nerve trunk compared to a <strong>muscle</strong> belly: triceps surae. J Appl<br />
Physiol 110:627–637<br />
Bigland-Ritchie B, Jones DA, Woods JJ (1979) Excitation frequency<br />
and <strong>muscle</strong> fatigue: electrical responses during human voluntary<br />
and stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol 64:414–427<br />
Binder-Macleod SA, Snyder-Mackler L (1993) Muscle fatigue:<br />
clinical <strong>implications</strong> <strong>for</strong> fatigue assessment and neuromuscular<br />
electrical stimulation. Phys Ther 73:902–910<br />
Davies PS, Jones PR, Norgan NG (1986) The distribution <strong>of</strong><br />
subcutaneous and internal fat in man. Ann Hum Biol 13:189–192<br />
Gandevia SC (2001) Spinal and supraspinal factors in human <strong>muscle</strong><br />
fatigue. Physiol Rev 81:1725–1789<br />
Gobbo M, Gaffurini P, Bissolotti L, Esposito F, Orizio C (2011)<br />
Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation: influence<br />
<strong>of</strong> electrode positioning and stimulus amplitude settings on<br />
<strong>muscle</strong> response. Eur J Appl Physiol [Epub ahead <strong>of</strong> print]<br />
Gregory CM, Bickel CS (2005) Recruitment patterns in human<br />
skeletal <strong>muscle</strong> during electrical stimulation. Phys Ther 85:358–<br />
364<br />
Hultman E, Sjöholm H, Jäderholm-Ek I, Krynicki J (1983) Evaluation<br />
<strong>of</strong> methods <strong>for</strong> electrical stimulation <strong>of</strong> human skeletal <strong>muscle</strong> in<br />
situ. Pflugers Arch 398:139–141<br />
Jones PR, Davies PS, Norgan NG (1986) Ultrasonic measurements <strong>of</strong><br />
subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness in man. Am J Phys<br />
Anthropol 71:359–363<br />
Karaca P, Hadzić A, Vloka JD (2000) Specific nerve blocks: an<br />
update. Curr Opin Anaes<strong>the</strong>siol 13:549–555<br />
Kim MW, Kim JH, Yang YJ, Ko YJ (2005) Anatomic localization <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>motor</strong> <strong>points</strong> in gastrocnemius and soleus <strong>muscle</strong>s. Am J Phys<br />
Med Rehabil 84:680–683<br />
Lee NG, You JH, Park HD, Myoung HS, Lee SE, Hwang JH, Kim<br />
HS, Kim SS, Lee KJ (2009) The validity and reliability <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>motor</strong> point detection system: a preliminary investigation <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>motor</strong> <strong>points</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> triceps surae <strong>muscle</strong>s. Arch Phys Med<br />
Rehabil 90:348–353<br />
Lee JH, Lee BN, An X, Chung RH, Kwon SO, Han SH (2011) Anatomic<br />
localization <strong>of</strong> <strong>motor</strong> entry point <strong>of</strong> superficial peroneal nerve to<br />
peroneus longus and brevis <strong>muscle</strong>s. Clin Anat 24:232–236<br />
Lefebvre R, Leroux A, Poumarat G, Galtier B, Guillot M, Vanneuville<br />
G, Boucher JP (2006) Vastus medialis: anatomical and<br />
functional considerations and <strong>implications</strong> based upon human<br />
and cadaveric studies. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 29:139–144<br />
Lieb FJ, Perry J (1968) Quadriceps function. An anatomical and<br />
mechanical study using amputated <strong>limb</strong>s. J Bone Joint Surg Am<br />
50:1535–1548<br />
Maffiuletti NA (2010) Physiological and methodological considerations<br />
<strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> neuromuscular electrical stimulation. Eur J<br />
Appl Physiol 110:223–234<br />
Maganaris CN, Baltzopoulos V (1999) Predictability <strong>of</strong> in vivo<br />
changes in pennation angle <strong>of</strong> human tibialis anterior <strong>muscle</strong><br />
from rest to maximum isometric dorsiflexion. Eur J Appl Physiol<br />
Occup Physiol 79:294–297<br />
Malesević NM, Popović LZ, Schwirtlich L, Popović DB (2010)<br />
Distributed low-frequency functional electrical stimulation<br />
delays <strong>muscle</strong> fatigue compared to conventional stimulation.<br />
Muscle Nerve 42:556–562<br />
Merletti R, Knaflitz M, De Luca CJ (1992) Electrically evoked<br />
myoelectric signals. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 19:293–340<br />
Nordander C, Willner J, Hansson GA, Larsson B, Unge J, Granquist<br />
L, Skerfving S (2003) Influence <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> subcutaneous fat layer, as<br />
measured by ultrasound, skinfold calipers and BMI, on <strong>the</strong> EMG<br />
amplitude. Eur J Appl Physiol 89:514–519<br />
Oprandi G, Botter A, Lanfranco F, Merletti R, Minetto MA (2010)<br />
<strong>Atlas</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>muscle</strong> <strong>motor</strong> <strong>points</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>lower</strong> <strong>limb</strong> <strong>muscle</strong>s.<br />
J Sports Med Phys Fitness 50(3 Suppl 1):5<br />
Place N, Casartelli N, Glatthorn JF, Maffiuletti NA (2010) Comparison<br />
<strong>of</strong> quadriceps inactivation between nerve and <strong>muscle</strong><br />
stimulation. Muscle Nerve 42:894–900<br />
Prentice WE (2005) Therapeutic modalities in rehabilitation, 3rd edn.<br />
McGraw-Hill, New York<br />
Reid RW (1920) Motor <strong>points</strong> in relation to <strong>the</strong> surface <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> body.<br />
J Anat 54:271–275<br />
Seidel PM, Seidel GK, Gans BM, Dijkers M (1996) Precise<br />
localization <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>motor</strong> nerve branches to <strong>the</strong> hamstring<br />
123