European Red List of Vascular Plants - European Commission
European Red List of Vascular Plants - European Commission European Red List of Vascular Plants - European Commission
through Africa north and south of the Sahara and more or less throughout the Americas, the only places where it is absent are Australia, New Zealand and islands in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Of the 27 EU countries only seven support fewer than 200 species and the main correlation appears to be that south of Fennoscandia, it is the size of the country that has the greatest influence over the number of aquatic species which a country supports. Of the 395 species assessed, 38 are found in only one country, of which 17 (45%) belong to genera known to have taxonomic problems; Isoetes, Trapa or Zannichellia many of which may, in time, be shown to simply be forms of other taxa; 24 occur in two countries; 307 (approximately three quarters) occur in five or more countries and 197 (approximately half) occur in 20 or more countries. 5.3.2 Endemic species richness Figure 22 shows the distribution of endemic aquatic plant species (e.g. those that are unique to Europe and are found nowhere else in the world). The distribution of endemic plants shows that there is a high rate of endemism in the north and west of the Iberian Peninsula, central and northern France, Belgium and the Netherlands with the UK, Germany and Denmark as well as Ukraine and Russia. Regarding the size of the areas covered by endemic species, the same caveat as in Figure 21 applies. 5.3.3 Distribution of threatened species Of the 26 threatened aquatic plant species, most are found in the Atlantic region, the Iberian Peninsula and other parts of the Mediterranean, with only a few occurring in northern countries. The importance of the Iberian Peninsula for threatened species can be seen in Figure 23. Two threatened species Eryngium viviparum and Thorella verticillato-inundata can be considered to fall within the Atlantic region. Six threatened species are endemic to the Iberian Peninsula: Apium bermejoi, Rorippa valdesbermejoi (Critically Endangered); Isoetes fluitans. Marsilea batardae (Endangered), Allium schmitzii and Pinguicula mundi (Vulnerable). Two threatened species are endemic to the Azores: Isoetes azorica and Marsilea azorica (both Vulnerable), although it has recently been suggested that the latter is in fact M. hirsuta, probably introduced from Australia. Fourteen threatened species can be considered predominantly Mediterranean in distribution, of which four are mainly eastern: Trapa annosa (Extinct, Serbia), Callitriche pulchra, Isoetes heldreichii (Critically Endangered, Greece) and Cyperus cyprius (Vulnerable, Cyprus); six Figure 22. Distribution of endemic aquatic plant species in Europe (excluding species assessed as Not Applicable and Data Deficient) 38
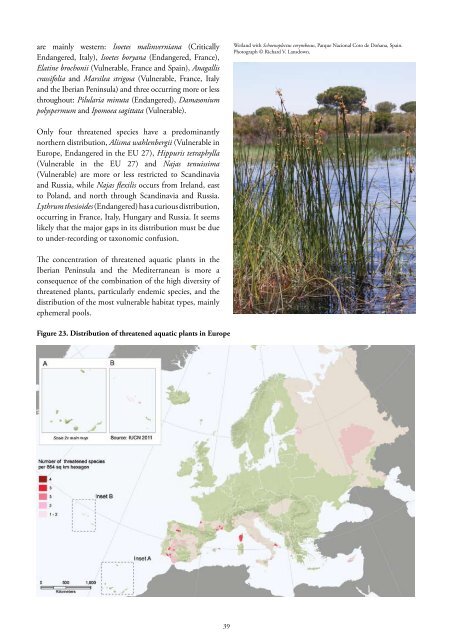
are mainly western: Isoetes malinverniana (Critically Endangered, Italy), Isoetes boryana (Endangered, France), Elatine brochonii (Vulnerable, France and Spain), Anagallis crassifolia and Marsilea strigosa (Vulnerable, France, Italy and the Iberian Peninsula) and three occurring more or less throughout: Pilularia minuta (Endangered), Damasonium polyspermum and Ipomoea sagittata (Vulnerable). Wetland with Schoenoplectus corymbosus, Parque Nacional Coto de Doňana, Spain. Photograph © Richard V. Lansdown. Only four threatened species have a predominantly northern distribution, Alisma wahlenbergii (Vulnerable in Europe, Endangered in the EU 27), Hippuris tetraphylla (Vulnerable in the EU 27) and Najas tenuissima (Vulnerable) are more or less restricted to Scandinavia and Russia, while Najas flexilis occurs from Ireland, east to Poland, and north through Scandinavia and Russia. Lythrum thesioides (Endangered) has a curious distribution, occurring in France, Italy, Hungary and Russia. It seems likely that the major gaps in its distribution must be due to under-recording or taxonomic confusion. The concentration of threatened aquatic plants in the Iberian Peninsula and the Mediterranean is more a consequence of the combination of the high diversity of threatened plants, particularly endemic species, and the distribution of the most vulnerable habitat types, mainly ephemeral pools. Figure 23. Distribution of threatened aquatic plants in Europe 39
- Page 1: European Red List of Vascular Plant
- Page 4 and 5: Published by the European Commissio
- Page 6 and 7: 6. Discussion .....................
- Page 8 and 9: Acknowledgements All of IUCN’s Re
- Page 10 and 11: Andrés Vicente Pérez Latorre Lore
- Page 12 and 13: are declining. But more interesting
- Page 14 and 15: a global “biodiversity hotspot”
- Page 16 and 17: The assessment provides three main
- Page 18 and 19: level, and species complexes have b
- Page 20 and 21: Convention includes 612 European pl
- Page 22 and 23: 3.2 Threat status of policy plants
- Page 24 and 25: Figure 5. Species richness of polic
- Page 26 and 27: Figure 7. Distribution of threatene
- Page 28 and 29: indica aggressively compete for spa
- Page 30 and 31: Today, agricultural production is c
- Page 32 and 33: particularly important to Europe in
- Page 34 and 35: ecause they are wild relatives of a
- Page 36 and 37: Table 6. Threatened and extinct CWR
- Page 38 and 39: It should be noted that the percent
- Page 40 and 41: Figure 14. Species richness of Euro
- Page 42 and 43: threatened species are endemic to t
- Page 44 and 45: with the predicted range in 2055. T
- Page 46 and 47: The following definition was consid
- Page 48 and 49: Near Threatened. One species is Ext
- Page 52 and 53: 5.4 Major threats to aquatic plants
- Page 54 and 55: fertilisation. As a consequence man
- Page 56 and 57: plant species are classed as Extinc
- Page 58 and 59: into water bodies as run-off and ca
- Page 60 and 61: the list are threatened but it also
- Page 62 and 63: in natural populations within defin
- Page 64 and 65: Greater Pasque Flower (Pulsatilla g
- Page 66 and 67: ■■ Raise the profile of CWR as
- Page 68 and 69: References Anderson, S. 2002. Ident
- Page 70 and 71: IPCC. 2007. Fourth Assessment Repor
- Page 72 and 73: identifying_and_protecting_the_worl
- Page 74 and 75: Family Species Red List Status Euro
- Page 76 and 77: Family Species Red List Status Euro
- Page 78 and 79: Family Species Red List Status Euro
- Page 80 and 81: Family Species Red List Status Euro
- Page 82 and 83: Appendix 2. Red List status of sele
- Page 84 and 85: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 86 and 87: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 88 and 89: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 90 and 91: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 92 and 93: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 94 and 95: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 96 and 97: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
- Page 98 and 99: Family Species IUCN Red List Catego
are mainly western: Isoetes malinverniana (Critically<br />
Endangered, Italy), Isoetes boryana (Endangered, France),<br />
Elatine brochonii (Vulnerable, France and Spain), Anagallis<br />
crassifolia and Marsilea strigosa (Vulnerable, France, Italy<br />
and the Iberian Peninsula) and three occurring more or less<br />
throughout: Pilularia minuta (Endangered), Damasonium<br />
polyspermum and Ipomoea sagittata (Vulnerable).<br />
Wetland with Schoenoplectus corymbosus, Parque Nacional Coto de Doňana, Spain.<br />
Photograph © Richard V. Lansdown.<br />
Only four threatened species have a predominantly<br />
northern distribution, Alisma wahlenbergii (Vulnerable in<br />
Europe, Endangered in the EU 27), Hippuris tetraphylla<br />
(Vulnerable in the EU 27) and Najas tenuissima<br />
(Vulnerable) are more or less restricted to Scandinavia<br />
and Russia, while Najas flexilis occurs from Ireland, east<br />
to Poland, and north through Scandinavia and Russia.<br />
Lythrum thesioides (Endangered) has a curious distribution,<br />
occurring in France, Italy, Hungary and Russia. It seems<br />
likely that the major gaps in its distribution must be due<br />
to under-recording or taxonomic confusion.<br />
The concentration <strong>of</strong> threatened aquatic plants in the<br />
Iberian Peninsula and the Mediterranean is more a<br />
consequence <strong>of</strong> the combination <strong>of</strong> the high diversity <strong>of</strong><br />
threatened plants, particularly endemic species, and the<br />
distribution <strong>of</strong> the most vulnerable habitat types, mainly<br />
ephemeral pools.<br />
Figure 23. Distribution <strong>of</strong> threatened aquatic plants in Europe<br />
39