NURSING CARE PLAN - amoebiasis2 - Nursing Crib
NURSING CARE PLAN - amoebiasis2 - Nursing Crib
NURSING CARE PLAN - amoebiasis2 - Nursing Crib
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>NURSING</strong> <strong>CARE</strong> <strong>PLAN</strong><br />
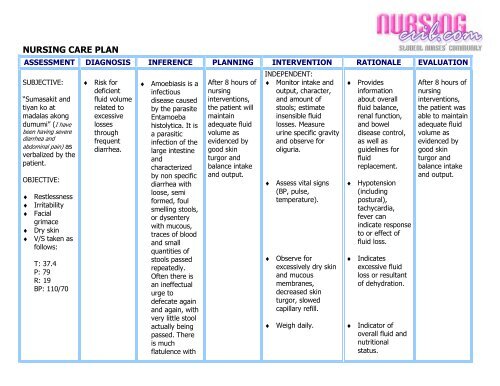
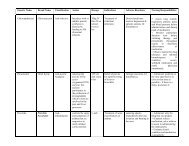
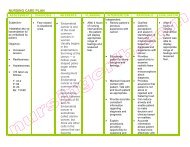
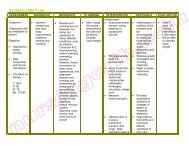
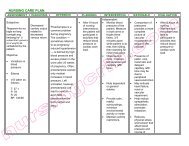
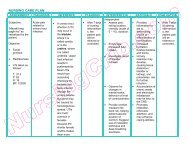
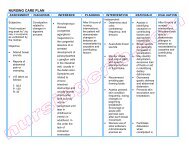
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE <strong>PLAN</strong>NING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION<br />
SUBJECTIVE:<br />
“Sumasakit and<br />
tiyan ko at<br />
madalas akong<br />
dumumi” (I have<br />
been having severe<br />
diarrhea and<br />
abdominal pain) as<br />
verbalized by the<br />
patient.<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
♦ Restlessness<br />
♦ Irritability<br />
♦ Facial<br />
grimace<br />
♦ Dry skin<br />
♦ V/S taken as<br />
follows:<br />
T: 37.4<br />
P: 79<br />
R: 19<br />
BP: 110/70<br />
♦ Risk for<br />
deficient<br />
fluid volume<br />
related to<br />
excessive<br />
losses<br />
through<br />
frequent<br />
diarrhea.<br />
♦ Amoebiasis is a<br />
infectious<br />
disease caused<br />
by the parasite<br />
Entamoeba<br />
histolytica. It is<br />
a parasitic<br />
infection of the<br />
large intestine<br />
and<br />
characterized<br />
by non specific<br />
diarrhea with<br />
loose, semi<br />
formed, foul<br />
smelling stools,<br />
or dysentery<br />
with mucous,<br />
traces of blood<br />
and small<br />
quantities of<br />
stools passed<br />
repeatedly.<br />
Often there is<br />
an ineffectual<br />
urge to<br />
defecate again<br />
and again, with<br />
very little stool<br />
actually being<br />
passed. There<br />
is much<br />
flatulence with<br />
After 8 hours of<br />
nursing<br />
interventions,<br />
the patient will<br />
maintain<br />
adequate fluid<br />
volume as<br />
evidenced by<br />
good skin<br />
turgor and<br />
balance intake<br />
and output.<br />
INDEPENDENT:<br />
♦ Monitor intake and<br />
output, character,<br />
and amount of<br />
stools; estimate<br />
insensible fluid<br />
losses. Measure<br />
urine specific gravity<br />
and observe for<br />
oliguria.<br />
♦ Assess vital signs<br />
(BP, pulse,<br />
temperature).<br />
♦ Observe for<br />
excessively dry skin<br />
and mucous<br />
membranes,<br />
decreased skin<br />
turgor, slowed<br />
capillary refill.<br />
♦ Weigh daily.<br />
♦ Provides<br />
information<br />
about overall<br />
fluid balance,<br />
renal function,<br />
and bowel<br />
disease control,<br />
as well as<br />
guidelines for<br />
fluid<br />
replacement.<br />
♦ Hypotension<br />
(including<br />
postural),<br />
tachycardia,<br />
fever can<br />
indicate response<br />
to or effect of<br />
fluid loss.<br />
♦ Indicates<br />
excessive fluid<br />
loss or resultant<br />
of dehydration.<br />
♦ Indicator of<br />
overall fluid and<br />
nutritional<br />
status.<br />
After 8 hours of<br />
nursing<br />
interventions,<br />
the patient was<br />
able to maintain<br />
adequate fluid<br />
volume as<br />
evidenced by<br />
good skin<br />
turgor and<br />
balance intake<br />
and output.
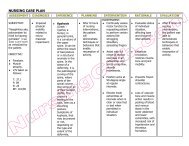
abdominal<br />
cramps. In<br />
severe cases,<br />
the liver and<br />
other organs<br />
may get<br />
affected,<br />
causing specific<br />
conditions<br />
related to<br />
organ, e.g.,<br />
hepatitis, cysts,<br />
abscess, etc.<br />
The most<br />
common<br />
symptoms of<br />
amoebiasis are<br />
diarrhea (which<br />
may contain<br />
blood), stomach<br />
cramps and<br />
fever.<br />
♦ Maintain oral<br />
restrictions, bed rest<br />
and avoidance of<br />
exertion.<br />
♦ Observe for overt<br />
bleeding and test<br />
stool daily for occult<br />
blood.<br />
♦ Note generalized<br />
muscle weakness or<br />
cardiac<br />
dysrhythmias.<br />
COLLABORATIVE:<br />
♦ Administer<br />
parenteral fluids as<br />
indicated.<br />
♦ Administer<br />
medications as<br />
indicated:<br />
Antidiarrheal and<br />
antibiotics.<br />
♦ Colon is placed<br />
at rest for<br />
healing and to<br />
decrease<br />
intestinal fluid<br />
losses.<br />
♦ Inadequate diet<br />
and decreased<br />
absorption may<br />
lead to vitamin K<br />
deficiency and<br />
defects in<br />
coagulation,<br />
potentiating risk<br />
for hemorrhage.<br />
♦ Excessive<br />
intestinal loss<br />
may lead to<br />
electrolyte<br />
imbalance.<br />
♦ Maintenance of<br />
bowel rest<br />
requires<br />
alternative fluid<br />
replacement to<br />
correct losses.<br />
♦ To reduces fluid<br />
losses in the<br />
intestine and to<br />
prevent further<br />
spread of the<br />
bacteria.