You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
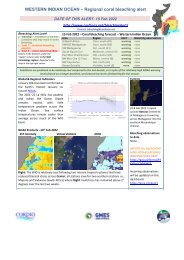
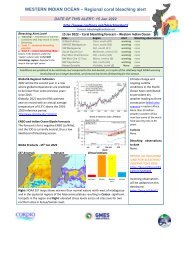
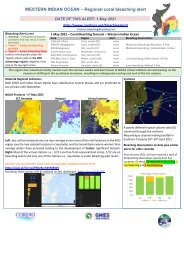
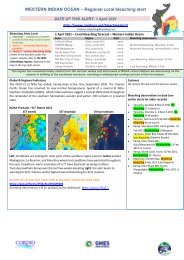
WASTEWATER<br />
Wastewater problems are becoming acute in many parts<br />
of the world and, for the future of cities, wastewater<br />
treatment is one of the most critical areas of development.<br />
The discharge of sewage into coastal waters can have<br />
a destructive impact on coral reefs and coastal ecosystems.<br />
The population in coastal areas grows rapidly, and<br />
the use of freshwater and discharge of sewage will increase.<br />
As this has destructive effects on coastal environments,<br />
in particular coral reefs, it is essential that especially<br />
cities and tourist resorts aim to reduce the amount<br />
of freshwater used and discharged as sewage. This can<br />
be achieved by implementing alternative ways of use,<br />
and treatment of the sewage.<br />
Biological treatment of organic wastes has been used<br />
for centuries. Composting, for example, is a natural way<br />
to enhance nutrient cycling. Nature sees sewage as a resource,<br />
while modern society sees sewage as a problem,<br />
and often thinks the solution is to transport it to rivers<br />
or directly to the sea.<br />
We need to seriously change our way of thinking.<br />
Instead of discharging treated or untreated sewage into<br />
the sea, it should be kept inland for some productive<br />
uses. Several demonstration projects shows that complete<br />
use of wastewater for aquaculture and agriculture<br />
is possible.<br />
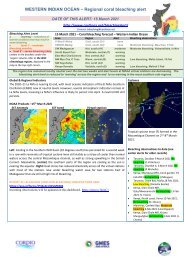
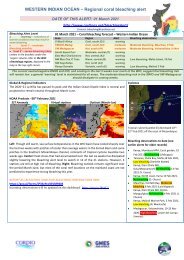
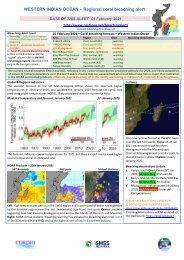
The Chinese developed aquaculture systems several<br />
thousand years ago. These systems use the sewage/nutrients<br />
and produce fish. Today China is the world’s leading<br />
producer of farmed fish (Figure 1).<br />
Another way of doing it is to separate the sewage at<br />
source. Today, most sanitation systems mix faeces and<br />
urine. In the human body, urine is separated from faeces.<br />
If we keep it that way, we will get two valuable resources.<br />
The faeces can be composted to produce biogas,<br />
which in turn can be used for cooking or to generate<br />
electricity. The urine can be used as fertiliser on farmland<br />
or in greenhouses.<br />
Table 1. Toilet water content<br />
Urine<br />
Faeces<br />
Nitrogen (N) 5,6 kg 0,09 kg<br />
Phosphorus (P) 0,4 kg 0,19 kg<br />
Potassium (K) 1,0 kg 0,17 kg<br />
Million tons<br />
16<br />
12<br />
8<br />
4<br />
China<br />
Developing countries<br />
(without China)<br />
Industrial countries<br />
0<br />
1984 1988 1996 2000<br />
Figure 1. Aquaculture production by region 1984–1995.<br />
Source: FAO<br />
By implementing modern technology, a community<br />
can be self-sufficient on energy and by using<br />
existing resources, pollution of coastal waters can<br />
be avoided and instead sewage can be used to<br />
supply the community with food products. This<br />
will strengthen the economy of the community,<br />
as well as increase the quality of life. A better<br />
environment will also strengthen the tourism. By<br />
re-using the nutrients for food production and<br />
fertilising plants, communities can support the<br />
tourist resorts and thereby create a source of<br />
income.<br />
– 88 –