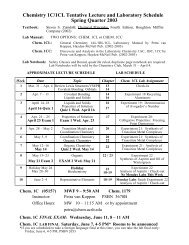
Chemistry 1C Review Problems, Chapters 13, 14 and 16 ...
Chemistry 1C Review Problems, Chapters 13, 14 and 16 ...
Chemistry 1C Review Problems, Chapters 13, 14 and 16 ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Problem: Predict the trend in boiling points for BF 3 , BCl 3 , BBr 3 , BI 3 In order to determine the intermolecular forces you must<br />
know the type of molecule. Is it covalent, polar-covalent or ionic For covalent molecules draw the Lewis structure <strong>and</strong><br />
determine if it is polar. The boron halides are all trigonal planar, non-polar molecules. So what is the intermolecular force<br />
LDF. How will LDF differ for BF 3 , BCl 3 , BBr 3 <strong>and</strong> BI 3 As the size of an atom or molecule increases, the polarizability<br />
increases <strong>and</strong> thus LDF increases. Now you can answer the question: because atom size increases down the group, F < Cl <<br />
Br < I, the LDF forces increase down the group, BF 3 < BCl 3 < BBr 3 < BI 3 <strong>and</strong> the boiling points will increase down the group,<br />
BF 3 < BCl 3 < BBr 3 < BI 3 . The boiling points are: BF 3 –101 o C, BCl 3 12 o C, BBr 3 91 o C, BI 3 210 o C. Quite a difference!<br />
<strong>Review</strong> <strong>Problems</strong><br />
1. Circle the formula that best fits each of the following descriptions:<br />
a) greatest electronegativity Al C Na N<br />
b) longest bond length HCl HF HI HBr<br />
c) largest ionic radius Mg 2+ F – Na + O 2–<br />
d) least polar bond C – O C – N O – H<br />
e) smallest atomic radius S Na Si Al<br />
2. Draw the Lewis structure for SeF 2 <strong>and</strong> PO 3– 3 , predict the molecular geometry, <strong>and</strong> if the molecule is polar indicate the<br />
direction of the net dipole.<br />
3.<br />
–<br />
a) Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following compounds. Nitrogen is the central atom in both NO 2 <strong>and</strong> NO – 3 .<br />
NO + –<br />
NO 2<br />
–<br />
NO 3<br />
b) Which one of the following has the longest NO bond length, NO + , NO – 2 , or NO – 3 <br />
c) Which one of the following has the shortest NO bond length, NO + , NO – 2 , or NO – 3 <br />
4. a) Using the molecular orbital model write the electronic configuration <strong>and</strong> bond order of N 2 <strong>and</strong> O 2 b) Are N 2 <strong>and</strong> O 2<br />
paramagnetic or diamagnetic What does it mean when a molecule is paramagnetic How can we observe the<br />
magnetism of a molecule experimentally c) Does N 2 or O 2 have a higher bond energy Why<br />
5. What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in CH 2 =CH <strong>and</strong> CH 2 2=C=CH 2 For each of these molecules are all the<br />
atoms in the same plane<br />
6. For each of the following molecules, indicate the number of σ-bonds, π-bonds, the steric number for each of the C <strong>and</strong> N<br />
atoms <strong>and</strong> hybridization on each of the C <strong>and</strong> N atoms. What are the angles a, b, <strong>and</strong> c in each of the molecules<br />
H<br />
• O• •<br />
H C C C H<br />
••<br />
H O N O<br />
•<br />
••<br />
••<br />
H<br />
7. Which of the following bonds is least polar C – O Br – Br O – H H – F<br />
8. Order Rb, F <strong>and</strong> O in increasing electronegativity. Order Na, Si, Ne <strong>and</strong> Cl in increasing atomic radius.<br />
9. Indicate the number of σ-bonds <strong>and</strong> π–bonds in each of the following molecules. a) N 2 b) CO c) O 2<br />
2- 2-<br />
10. Draw the Lewis structure for CO 3 including resonance structures. Determine the hybridization on the carbon in CO 3 <strong>and</strong><br />
give the molecular geometry<br />
11. What is the hybridization on each of the carbons in butane, CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 . Are all the carbon <strong>and</strong> hydrogen atoms in the<br />
same plane<br />
12. How many electrons are involved in the π-bonding in benzene, C 6 H 6 What is the hybridization on the carbon atoms Are<br />
all the carbon <strong>and</strong> hydrogen atoms in the same plane Why or why not<br />
<strong>13</strong>. Which one of the following molecules, C 2 H 2 , C 2 H 4 , <strong>and</strong> C 2 H 6 , has the shortest bond distance between the carbon bonds<br />
Why<br />
<strong>14</strong>. Write the electronic configuration using the molecular orbital model of the following species <strong>and</strong> determine which has the<br />
largest dissociation energy O 2 , O – 2 , O 2– 2+<br />
2 , O 2<br />
15. Write the electronic configuration <strong>and</strong> number of unpaired electrons for the following: O, Al 3+ , C, Se 2–<br />
<strong>16</strong>. a) Draw the Lewis structure for SF 6 . How many electrons does S share Is this consistent with the octet rule<br />
b) For SF 6 , valence shell expansion of S allows additional electrons to be accepted in which orbitals Is valence shell<br />
expansion observed for second row elements<br />
c) What is the hybridization of S in SF 6 <br />
17. Which elements most commonly form π-bonds<br />
18. Which has the highest boiling point, BF 3 , BCl 3 , BBr 3 , BI 3 Why<br />
19. What is the hybridization on carbon in O=C=O <br />
20. Why does hydrogen have such low boiling <strong>and</strong> melting points<br />
21. Highest boiling point. Explain. a) He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe b) NH 3 , PH 3 c) HF, HCl<br />
22. Predict the boiling point of H 2 O if H-bonding between water molecules did not occur (use Fig <strong>16</strong>.4 Pg. 732 text). Would<br />
water be a liquid at room temperature without H-bonding<br />
2– 2–<br />
23. Why can't carbon form a compound such as CCl 6 while tin can form SnCl 6 <br />
24. Why can carbon form π–bonds with carbon, nitrogen <strong>and</strong> oxygen while other group 4 elements, Si, Ge, Sn <strong>and</strong> Pb, cannot<br />
••<br />
2