Graz University of Technology Austria Institute of Biochemistry ...
Graz University of Technology Austria Institute of Biochemistry ...
Graz University of Technology Austria Institute of Biochemistry ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Biophysical chemistry group<br />
Group leader: Albin Hermetter<br />
Postdoctoral Fellow: Heidemarie Ehammer<br />
PhD students: Ute Stemmer, Daniel Koller, Claudia Ramprecht, Lingaraju Marlingapla<br />
Halasiddappa, Bojana Stojcic<br />
Master students: Andreas Gasser, Gabriel Pürstinger, Hannah Jaritz<br />
Technicians: Elfriede Zenzmaier<br />
General description<br />
Our research deals with the role <strong>of</strong> glycero(phospho)lipids and lipid modifying enzymes as<br />
components <strong>of</strong> membranes and lipoproteins, their function as mediators in cellular<br />
(patho)biochemistry, and their application as analytical tools in enzyme technology.<br />
Fluorescence spectroscopy is used as a main technique to investigate the behaviour <strong>of</strong> these<br />
biomolecules in the respective supramolecular systems.<br />
Section 1 <strong>of</strong> the following report summarizes our studies on lipid oxidation, the effects <strong>of</strong><br />
oxidized lipids on intracellular signalling, and the inhibition <strong>of</strong> these processes by synthetic<br />
and natural antioxidants.<br />
Section 2 describes the development <strong>of</strong> fluorescence for functional proteomic analysis <strong>of</strong><br />
lipolytic enzymes in microbial, animal and human cells.<br />
1. Lipid oxidation and atherosclerosis – Lipotoxicity<br />
1.1. Interaction <strong>of</strong> oxidized phospholipids with vascular cells<br />
Sphingomyelin<br />
acid<br />
Sphingomyelinase<br />
Oxidized -<br />
Phospholipids<br />
O<br />
H<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O P O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O P O<br />
OH<br />
+<br />
N<br />
N +<br />
Ceramide<br />
OXPHOS-EuroMEMBRANE<br />
JNK<br />
p38 MAPK<br />
Caspase 3<br />
ERK<br />
AKT/PKB<br />
NFkB<br />
PROLIFERATION<br />
SURVIVAL<br />
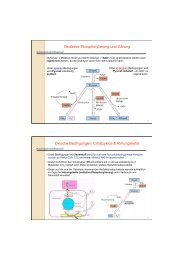
Interactions <strong>of</strong> oxidized lipoproteins with<br />
the cells <strong>of</strong> the arterial wall induce and<br />
influence the progress <strong>of</strong> atherosclerosis.<br />
Accumulation <strong>of</strong> foam cells originating<br />
from macrophages and excessive intimal<br />
growth <strong>of</strong> vascular smooth muscle cells<br />
(SMC) alternating with focal massive cell<br />
death are characteristics typical <strong>of</strong> the atherosclerotic lesion. These phenomena are largely<br />
mediated by the oxidized phospholipid components <strong>of</strong> the modified particles that are<br />
generated under the conditions <strong>of</strong> oxidative stress. In the framework <strong>of</strong> the research consortia<br />
LIPOTOX (SFB) and OXPHOS (EuroMEMBRANE), we investigate the “Toxicity <strong>of</strong><br />
oxidized phospholipids in macrophages” and “The protein targets and apoptotic signaling <strong>of</strong><br />
oxidized phospholipids”. These studies aim at identifying the molecular and cellular effects <strong>of</strong><br />
an important subfamily <strong>of</strong> the oxidized phospholipids containing long hydrocarbon chains in<br />
27