A manual of rice seed health testing - IRRI books - International Rice ...
A manual of rice seed health testing - IRRI books - International Rice ...
A manual of rice seed health testing - IRRI books - International Rice ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Table 6.3 percent incidence <strong>of</strong> different <strong>seed</strong>borne pathogens on treated incoming <strong>seed</strong> lots<br />
received for postentry clearance by the IRRl Seed Health Unit, 1987-1990. a<br />
Pathogen<br />
Affected<br />
<strong>seed</strong> lots<br />
1987 1988<br />
Detection<br />
levels<br />
Mean<br />
value<br />
Affected<br />
<strong>seed</strong> lots<br />
Detection<br />
levels<br />
Mean<br />
value<br />
Alternaria padwickii<br />
Curvularia spp.<br />
Sarocladium oryzae<br />
Microdochium oryzae<br />
Fusarium moniliforme<br />
Drechslera oryzae<br />
Pyricularia oryzae<br />
Tilletia barclayana<br />
Aphelenchoides besseyi b<br />
33.3<br />
44.4<br />
10.2<br />
9.3<br />
1.8<br />
36.0<br />
0.0<br />
46.2<br />
44.0<br />
1 - 44<br />
1-15<br />
1-27<br />
1-14<br />
1<br />
1-62<br />
0<br />
1-52<br />
1-797<br />
10.5<br />
3.1<br />
6.3<br />
5.0<br />
1.0<br />
8.4<br />
10.6<br />
67.0<br />
17.5<br />
24.9<br />
4.6<br />
0.9<br />
1.4<br />
18.9<br />
0.0<br />
37.3<br />
25.8<br />
1- 40<br />
1- 41<br />
1-11<br />
1-3<br />
1<br />
1-44<br />
0<br />
1-75<br />
1-344<br />
8.0<br />
5.4<br />
2.1<br />
2.0<br />
1.0<br />
6.2<br />
11.4<br />
26.5<br />
Pathogen<br />
Affected<br />
<strong>seed</strong> lots<br />
1989<br />
Detection<br />
levels<br />
Mean<br />
value<br />
Affected<br />
<strong>seed</strong> lots<br />
1990<br />
Detection<br />
levels<br />
Mean<br />
value<br />
Alternaria padwickii<br />
4.1<br />
Curvularia spp.<br />
30.3<br />
Sarocladium oryzae<br />
7.4<br />
Microdochium oryzae<br />
1.6<br />
Fusarium moniliforme 0.0<br />
Drechslera oryzae<br />
14.8<br />
Pyricularia oryzae<br />
12.3<br />
Tilletia barclayana<br />
98.4<br />
Aphelenchoides besseyi b 27.0<br />
1-49<br />
1-10<br />
1-4<br />
1-3<br />
0<br />
1-12<br />
1-17<br />
1-89<br />
1-84<br />
11.4<br />
1.6<br />
1.6<br />
2.0<br />
1.9<br />
5.5<br />
24.4<br />
15.8<br />
24.2<br />
44.7<br />
0.8<br />
2.3<br />
1.5<br />
35.6<br />
0.0<br />
41.7<br />
31.1<br />
1-21<br />
1-66<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1-31<br />
0<br />
1-83<br />
1-54<br />
3.1<br />
10.8<br />
1.0<br />
1.0<br />
1.0<br />
2.5<br />
18.0<br />
10.9<br />
a Based on 200 <strong>seed</strong>s per <strong>seed</strong> lot. No. <strong>of</strong> <strong>seed</strong> lots examined: 225 (1987), 217 (1988), 122 (1989), 132 (1990).<br />
b Actual nematode count.<br />
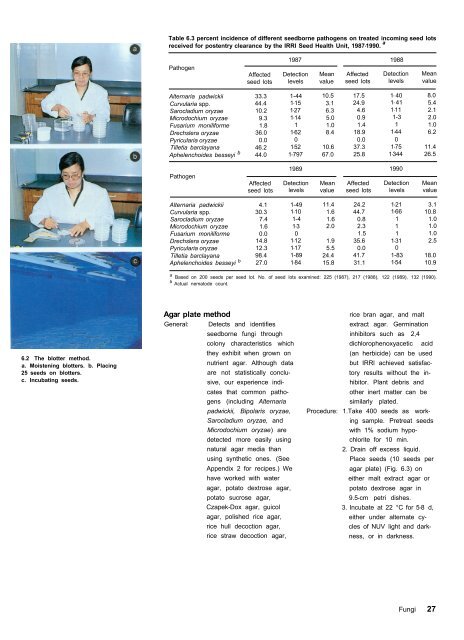
6.2 The blotter method.<br />
a. Moistening blotters. b. Placing<br />
25 <strong>seed</strong>s on blotters.<br />
c. Incubating <strong>seed</strong>s.<br />
Agar plate method<br />
General: Detects and identifies<br />
<strong>seed</strong>borne fungi through<br />
colony characteristics which<br />
they exhibit when grown on<br />
nutrient agar. Although data<br />
are not statistically conclusive,<br />
our experience indicates<br />
that common pathogens<br />
(including Alternaria<br />
padwickii, Bipolaris oryzae,<br />
Sarocladium oryzae, and<br />
Microdochium oryzae ) are<br />
detected more easily using<br />
natural agar media than<br />
using synthetic ones. (See<br />
Appendix 2 for recipes.) We<br />
have worked with water<br />
agar, potato dextrose agar,<br />
potato sucrose agar,<br />
Czapek-Dox agar, guicol<br />
agar, polished <strong>rice</strong> agar,<br />
<strong>rice</strong> hull decoction agar,<br />
<strong>rice</strong> straw decoction agar,<br />
<strong>rice</strong> bran agar, and malt<br />
extract agar. Germination<br />
inhibitors such as 2,4<br />
dichlorophenoxyacetic acid<br />
(an herbicide) can be used<br />
but IRRl achieved satisfactory<br />
results without the inhibitor.<br />
Plant debris and<br />
other inert matter can be<br />
similarly plated.<br />
Procedure: 1.Take 400 <strong>seed</strong>s as working<br />
sample. Pretreat <strong>seed</strong>s<br />
with 1% sodium hypochlorite<br />
for 10 min.<br />
2. Drain <strong>of</strong>f excess liquid.<br />
Place <strong>seed</strong>s (10 <strong>seed</strong>s per<br />
agar plate) (Fig. 6.3) on<br />
either malt extract agar or<br />
potato dextrose agar in<br />
9.5-cm petri dishes.<br />
3. Incubate at 22 °C for 5-8 d,<br />
either under alternate cycles<br />
<strong>of</strong> NUV light and darkness,<br />
or in darkness.<br />
Fungi 27