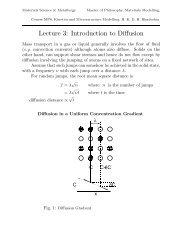
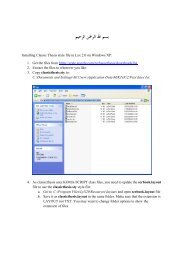
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
BH4 Course B: <strong>Materials</strong> for Devices BH4<br />
Liquid Crystals<br />
• Crystalline materials have long-range order. This means that they are anisotropic: their properties<br />
(e.g. refractive index, thermal expansion coefficient, electrical conductivity) may differ, depending<br />
upon the direction <strong>of</strong> measurement.<br />
• In contrast, liquids, which have no long-range order, are isotropic: they are invariant with respect<br />
to direction. The absence <strong>of</strong> long-range order means that all directions are equivalent.<br />
• Somewhere in between there are Liquid Crystals, which are anisotropic liquids. Their anisotropy,<br />
or directionality, comes from molecular shape.<br />
Liquid crystals <strong>of</strong>ten consist <strong>of</strong> rod-shaped molecules, with a rigid long axis:<br />
e.g. Methoxybenzylidene Butylaniline, or MBBA<br />
The central region <strong>of</strong> the<br />
molecule (between the<br />
rings) is rigid, whilst the<br />
ends are flexible.<br />
These rod-shaped<br />
molecules are free to<br />
move relative to each<br />
other and flow past<br />
each other, so that<br />
there is no long-range<br />
positional order.<br />
However, because <strong>of</strong> their shape, they tend to line up, with their long axes lying roughly parallel, i.e.<br />
they have some orientational order. This alignment stems from packing considerations, and also<br />
electrostatic interactions.<br />
Nematic Liquid Crystal (LC) structure<br />
No positional order.<br />
Long range orientational order, defined by a<br />
Director, D.<br />
D<br />
This leads to useful anisotropic optical<br />
properties, which are the basis for electronic<br />
displays.