Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
BH55 Course B: <strong>Materials</strong> for Devices BH55<br />
Cross-linking: a process in which bonds are formed joining adjacent molecules. At low density<br />
these bonds add to the elasticity <strong>of</strong> a polymer, at higher densities they produce rigidity.<br />
Crossed polars: two sheets <strong>of</strong> polarizing material (polarizer and analyzer), oriented at 90° to each<br />
other, between which a sample is placed for optical examination.<br />
Curie temperature: the temperature above which ferroelectric / ferromagnetic behaviour is lost<br />
(°C or K).<br />
Current density, j: the current flowing through unit cross-sectional area (A m -2 ).<br />
Diamagnetism: the effect caused by the magnetic moment due to orbiting electrons which produces<br />
a slight opposition to imposed magnetic field.<br />
Dielectric: an electrical insulator which is polarisable.<br />
Dielectric breakdown: the passage <strong>of</strong> current through a dielectric material upon application <strong>of</strong> a<br />
large electric field. The maximum field that a dielectric can sustain without breakdown is the<br />
dielectric strength.<br />
Dielectric constant, κ : a measure <strong>of</strong> the rate <strong>of</strong> change <strong>of</strong> polarisation with electric field; the ratio<br />
<strong>of</strong> the permittivity <strong>of</strong> a material to the permittivity <strong>of</strong> free space.<br />
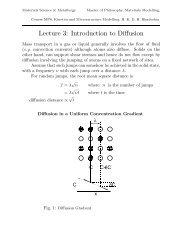
Diffusion: transport <strong>of</strong> atoms in which the diffusing atom moves relative to its neighbours.<br />
Diffusion coefficient (or diffusivity), D: a temperature dependent coefficient related to the rate at<br />
which atoms diffuse, which also depends on the activation energy (m 2 s -1 )<br />
Dipole: two equal charges <strong>of</strong> opposite sign, separated by a small distance.<br />
Dipole moment, µ: the electric field generated by a spatial separation <strong>of</strong> positive and negative<br />
charges (C m) or the magnetic moment generated by electron orbitals and spin.<br />
Director, D: the direction <strong>of</strong> preferred orientation <strong>of</strong> molecules in liquid crystals.<br />
Disclination: point at which the Director in a liquid crystal undergoes an abrupt change in<br />
orientation.<br />
Displacement field, D: resultant total polarisation field created in a material by application <strong>of</strong> an<br />
electric field (C m -2 )<br />
Domains: regions within a material in which all the electric / magnetic dipoles are aligned.<br />
Domain wall: the boundary between ferroelectric / magnetic domains.<br />
Drift velocity: the average rate at which charge carriers move through a material under the<br />
application <strong>of</strong> an electric field (m s -1 )<br />
Exchange interaction / exchange energy: a quantum mechanical electron – electron interaction<br />
which favours parallel alignment <strong>of</strong> magnetic moments. A negative exchange interaction favours antiparallel<br />
alignment <strong>of</strong> moments.<br />
Extinction positions: orientations in which an anisotropic material appears black between crossed<br />
polars. (They occur every 90°, when the permitted vibration directions <strong>of</strong> the sample are parallel<br />
to the polarizer / analyzer.)<br />
Fatigue: accumulation <strong>of</strong> defects in a ferroelectric material which gradually degrades the amount <strong>of</strong><br />
switched charge.