Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Lecture handout including QS - Department of Materials Science ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
BH41 Course B: <strong>Materials</strong> for Devices BH41<br />
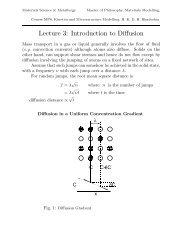
Cycling the field back and forth produces hysteresis:<br />
Residual magnetisation remaining at zero<br />
applied field (H = 0) is the remanent<br />
Reduce applied field ⇒ moment relaxes back to<br />
easy crystallographic axis, but then the domain<br />
remains stable as field is reduced further<br />
magnetisation, M r<br />
magnetisation<br />
M sat<br />
Continued field reversal ⇒ domains<br />
grow in the opposite direction<br />
M = 0 (multi-domain umagnetised<br />
state) at the coercive field, H C .<br />
applied field<br />
Further field reversal ⇒<br />
saturation in the opposite<br />
direction<br />
M sat<br />
• area within the loop ∝ energy dissipated during one<br />
cycle, i.e. 2 × energy needed to switch M<br />
• imperfections (grain boundaries, impurities, vacancies, etc.) pin domain walls, ⇒ increase H C