Evaluating Student Learning PPT
Evaluating Student Learning PPT
Evaluating Student Learning PPT
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Evaluating</strong><br />
<strong>Student</strong> <strong>Learning</strong><br />
Chapter 10<br />
What is Developmentally<br />
Appropriate Evaluation<br />
• Appropriate evaluation is ongoing.<br />
• Multiple measures should be<br />
taken.<br />
• A single assessment should not be<br />
used as the sole basis for<br />
evaluation.<br />
• PE students should be assessed on<br />
fitness and motor skills as well as<br />
their cognitive understanding of<br />
those skills.<br />
What is Developmentally<br />
Appropriate Evaluation<br />
• Formative evaluation<br />
–Provides students and teachers<br />
with an idea of progress.<br />
–Affords teachers an opportunity<br />
to optimize the learning<br />
environment at any given time.<br />
–Provides ample time for student<br />
improvement.<br />
What is Developmentally<br />
Appropriate Evaluation<br />
• Summative Evaluation<br />
–Generally performed at the end<br />
of the instructional unit.<br />
–Indicates student performance<br />
and progress<br />
–Identifies program and teacher<br />
effectiveness<br />
Why is Assessment Important<br />
(pages 196-197)<br />
• Individualize instruction<br />
– Identify student progress and<br />
achievement<br />
• Curriculum planning<br />
– Develop weekly and yearly plans<br />
• Identify children with special needs<br />
• Communicate with parents<br />
– <strong>Student</strong> progress and achievement<br />
• Evaluate programs<br />
– Evaluate teacher effectiveness<br />
• <strong>Student</strong> Motivation<br />
How Do You Get <strong>Student</strong>s<br />
Involved (pages 197-198)<br />
• Children should be active<br />
participants in the evaluation<br />
process.<br />
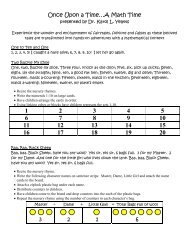
• 7 hints and ideas about using<br />
children to evaluate. (page 197)<br />
• What Should be Assessed<br />
• Selecting and Designing<br />
Assessment Tools<br />
1
Selecting and Designing<br />
Assessment Tools (page 198)<br />
• Select test items that are simple and easy to understand.<br />
• Test items should be directly related to what has been taught.<br />
– Aligned with the lesson objective<br />
• Consider how much time will be spent on the evaluation.<br />
• Do not spend more time on evaluating than you do on<br />
teaching.<br />
• Administration of the assessment should be relatively simple.<br />
• Consider what the test will be used for:<br />
– Psychomotor development<br />
– Cognitive development<br />
– Affective aspects of motor development<br />
• Match the testing instrument to the developmental level of<br />
the children.<br />
Psychomotor Assessments<br />
(pages 198-204)<br />
• What is it<br />
• Evaluation Fitness<br />
• Fitness Assessment Instruments<br />
• Fitness Test Sheets<br />
• <strong>Evaluating</strong> Motor Skills<br />
• Profile Checklists<br />
• Developmental Checklists<br />
• Critical Element Process Checklist<br />
• <strong>Evaluating</strong> Dance and Gymnastics<br />
• Dance and Gymnastics Assessment<br />
Instruments<br />
Sample Assessments<br />
Kaya describes how to throw a football<br />
Cognitive Assessments<br />
(pages 204-206)<br />
• What is it<br />
• Check for understanding<br />
• Poker Chip Survey<br />
• Shadowing<br />
• Choral Responding<br />
• Reiteration<br />
• Group Alerting<br />
• Task Cards<br />
• Videotape Analysis<br />
• Journals or <strong>Student</strong> Logs<br />
Affective Assessments<br />
(pages 206-208)<br />
• What is it<br />
• Paper-and-Pencil Tests<br />
• <strong>Student</strong> Logs<br />
• Smiled-Face Exit Poll<br />
• Portfolios<br />
2
How Can Assessment Be<br />
Integrated with Other Subjects<br />
(pages 208-210)<br />
• Mathematics<br />
–Fitness Index Cards<br />
–Graphs<br />
–Frequency Distributions<br />
• Science<br />
Article<br />
• Skill assessment in elementary physical<br />
education: an appropriate progression<br />
– by Gosset, Michael<br />
– JOPERD--The Journal of Physical Education,<br />
Recreation & Dance, January, 2007<br />
– Assessment, assessment, assessment. It<br />
seems as if we are hearing more about<br />
assessment with the No Child Left Behind<br />
education reform act unfolding. With<br />
respect to physical education, which<br />
domain should be assessed: the physical,<br />
cognitive, affective, or all three In a high<br />
quality, progressive K-12 program, all three<br />
domains should be taken into account.<br />
Assessment Tips<br />
• Be very clear about WHAT is being assessed<br />
– Is it worth learning and demonstrating<br />
• Know WHY you are assessing<br />
– What will you do with the information<br />
– Is it feedback for students, parents, your instruction,<br />
program<br />
• Assessment is more than grading!<br />
– Assessments should demonstrate what students know or<br />
are able to do.<br />
– Assessments can "show off" learning in your program.<br />
• SHARE the information with students, administrators, other<br />
teachers, and parents as appropriate.<br />
– This will lend credibility to your program.<br />
• Be CLEAR about the criteria for making judgments.<br />
– Rubric Standard<br />
• Allow students in on the process.<br />
– Using your criteria they can evaluate self, partner or<br />
others<br />
– allow students some choices in the manner in which they<br />
want to be assessed<br />
– include the criteria for each assessment.<br />
Rubric Standards<br />
Criterion A: Knowledge and Understanding<br />
<strong>Student</strong>s are expected to have a knowledge and understanding of the<br />
physical activities or themes studied. This criterion includes<br />
understanding the principles related to a variety of physical<br />
activities, the importance of physical activity to a healthy lifestyle<br />
and the various components that contribute to health-related fitness.<br />
Level of Achievement<br />
0<br />
1--2<br />
3--4<br />
5--6<br />
Descriptor<br />
The student does not reach a standard described by any of the<br />
descriptors given below.<br />
The student shows some knowledge of the principles under<br />
consideration. The understanding of these principles is basic at<br />
best.<br />
The student shows a good knowledge and general understanding<br />
of the principles under consideration.<br />
The student shows a thorough knowledge and understanding of<br />
the principles under consideration.<br />
3