- Page 1 and 2:
Introduction to Enzyme and Coenzyme
- Page 4 and 5:
Introduction to Enzyme and Coenzyme
- Page 6 and 7:
Contents Preface Representation of
- Page 8:
Contents vii 8 Enzymatic Addition/E
- Page 11 and 12:
Representation of Protein Three-Dim
- Page 13 and 14:
2 Chapter 1 H 2 N O NH 2 + H 2 O Ja
- Page 15 and 16:
4 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 The vitamins.
- Page 17 and 18:
6 Chapter 1 has very diVerent biolo
- Page 19 and 20:
2 All Enzymes are Proteins 2.1 Intr
- Page 21 and 22:
10 Chapter 2 (Gln). There are three
- Page 23 and 24:
12 Chapter 2 AAA Lys ACA Thr AGA Ar
- Page 25 and 26:
14 Chapter 2 H N O H N O Figure 2.8
- Page 27 and 28:
16 Chapter 2 (a) (b) Figure 2.12 St
- Page 29 and 30:
18 Chapter 2 Figure 2.14 Structure
- Page 31 and 32:
20 Chapter 2 (a) X Y Enzyme + Subst
- Page 33 and 34:
22 Chapter 2 maintaining protein te
- Page 35 and 36:
24 Chapter 2 surface glycoprotein g
- Page 37 and 38:
26 Chapter 2 O-linked glycosylation
- Page 39 and 40:
28 Chapter 2 Metalloproteins I. Ber
- Page 41 and 42:
30 Chapter 3 O N H R CO 2 H acylase
- Page 43 and 44:
32 Chapter 3 (a) Free energy uncata
- Page 45 and 46:
34 Chapter 3 Ester k rel Effective
- Page 47 and 48:
36 Chapter 3 3.4 The importance of
- Page 49 and 50:
38 Chapter 3 pKa Tyrosine CH 2 O H
- Page 51 and 52:
40 Chapter 3 glycoside hydrolysis (
- Page 53 and 54:
42 Chapter 3 O O Glu 143 O − R H
- Page 55 and 56:
44 Chapter 3 the hydroxyl groups of
- Page 57 and 58:
46 Chapter 3 E + S E + S ES' ES ‘
- Page 59 and 60:
48 Chapter 3 Examination of protein
- Page 61 and 62:
50 Chapter 3 (Note: Similar results
- Page 63 and 64:
52 Chapter 4 (1) Direct UV (2) Radi
- Page 65 and 66:
54 Chapter 4 Figure 4.3 PuriWcation
- Page 67 and 68: 56 Chapter 4 The two kinetic consta
- Page 69 and 70: 58 Chapter 4 Lineweaver−Burk Plot
- Page 71 and 72: 60 Chapter 4 E + S K i EI+ I ES E +
- Page 73 and 74: 62 Chapter 4 (2) by treatment with
- Page 75 and 76: 64 Chapter 4 In general the stereoc
- Page 77 and 78: H D T CO 2 H CO − 2 T HO D H −
- Page 79 and 80: 68 Chapter 4 4.5 The existence of i
- Page 81 and 82: 70 Chapter 4 18O 18O 18 O O P O −
- Page 83 and 84: 72 Chapter 4 If a reaction involves
- Page 85 and 86: 74 Chapter 4 O D H ketosteroid isom
- Page 87 and 88: 76 Chapter 4 Table 4.3 Group speciW
- Page 89 and 90: 78 Chapter 4 [S] (mM) Rate of produ
- Page 91 and 92: 80 Chapter 4 Enzyme kinetics I.H. S
- Page 93 and 94: 82 Chapter 5 O = C NHR peptidase H
- Page 95 and 96: 84 Chapter 5 non-speciWc protease c
- Page 97 and 98: 86 Chapter 5 His 57 His 57 Asp 102
- Page 99 and 100: 88 Chapter 5 Other serine proteases
- Page 101 and 102: 90 Chapter 5 Figure 5.8 Structure o
- Page 103 and 104: 92 Chapter 5 now predominate Perhap
- Page 105 and 106: OH R O Zn 2+ O O O Ph Glu 270 H 2 N
- Page 107 and 108: 96 Chapter 5 CASE STUDY: HIV-1 prot
- Page 109 and 110: 98 Chapter 5 HO Transition state pe
- Page 111 and 112: 100 Chapter 5 The aminoacyl group o
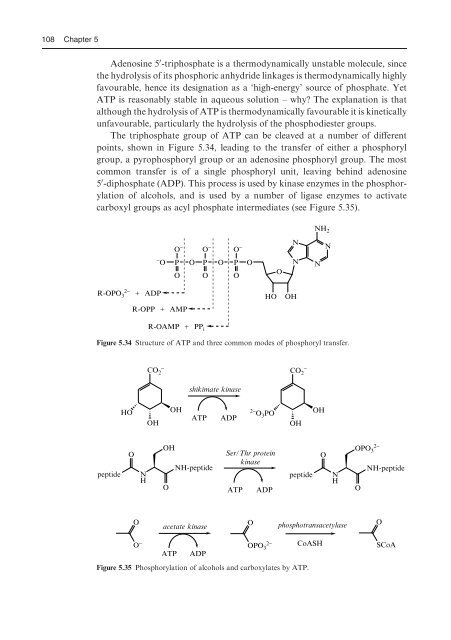
- Page 113 and 114: 102 Chapter 5 5.5 Enzymatic phospho
- Page 115 and 116: 104 Chapter 5 Figure 5.29 Structure
- Page 117: 106 Chapter 5 Figure 5.32 Structure
- Page 121 and 122: 110 Chapter 5 functional group. Gly
- Page 123 and 124: 112 Chapter 5 CH 2 OH O RO HO OH O
- Page 125 and 126: 114 Chapter 5 to these atoms that t
- Page 127 and 128: 116 Chapter 5 Problems (1) Using pa
- Page 129 and 130: 118 Chapter 5 (6) Retaining glycosi
- Page 131 and 132: 120 Chapter 5 J.R. Knowles (1980) E
- Page 133 and 134: 122 Chapter 6 +1.0 Redox potential
- Page 135 and 136: Table 6.1 Classes of redox enzymes.
- Page 137 and 138: 126 Chapter 6 An important point is
- Page 139 and 140: 128 Chapter 6 O H − OH − O OH H
- Page 141 and 142: 130 Chapter 6 one-electron transfer
- Page 143 and 144: 132 Chapter 6 (a) R N H + N O R N H
- Page 145 and 146: 134 Chapter 6 Inactivation by trany
- Page 147 and 148: 136 Chapter 6 Figure 6.20 Structure
- Page 149 and 150: 138 Chapter 6 (a) (b) Figure 6.23 S
- Page 151 and 152: 140 Chapter 6 glutathione called tr
- Page 153 and 154: 142 Chapter 6 neither has a stable
- Page 155 and 156: 144 Chapter 6 of the haem cofactor
- Page 157 and 158: 146 Chapter 6 Figure 6.33 Active si
- Page 159 and 160: 148 Chapter 6 HO H N N O O H N prol
- Page 161 and 162: 150 Chapter 6 R R R O 2 , Fe 2+ O O
- Page 163 and 164: 152 Chapter 6 CoA. Explain these re
- Page 165 and 166: 154 Chapter 6 NADH models O. Almars
- Page 167 and 168: 7 Enzymatic Carbon-Carbon Bond Form
- Page 169 and 170:
158 Chapter 7 O H − OH O − O H
- Page 171 and 172:
160 Chapter 7 Figure 7.4 Structure
- Page 173 and 174:
162 Chapter 7 Figure 7.6 Active sit
- Page 175 and 176:
164 Chapter 7 7.3 Claisen enzymes I
- Page 177 and 178:
166 Chapter 7 CoAS O EnzB − H D T
- Page 179 and 180:
168 Chapter 7 onto the acetyl-thioe
- Page 181 and 182:
170 Chapter 7 In the case of erythr
- Page 183 and 184:
172 Chapter 7 O HO O − O ATP ADP
- Page 185 and 186:
174 Chapter 7 CO 2 − vitamin K-de
- Page 187 and 188:
176 Chapter 7 7.8 Thiamine pyrophos
- Page 189 and 190:
178 Chapter 7 HN N + N H NH S O OPP
- Page 191 and 192:
180 Chapter 7 O OH OH camphor geran
- Page 193 and 194:
182 Chapter 7 CH 3 * OPP (−)pinen
- Page 195 and 196:
184 Chapter 7 Figure 7.36 Structure
- Page 197 and 198:
186 Chapter 7 C C C C C O OCH 3 C H
- Page 199 and 200:
188 Chapter 7 AcO HO HO NHAc O OH +
- Page 201 and 202:
190 Chapter 7 (9) Usnic acid is a n
- Page 203 and 204:
192 Chapter 7 Radical couplings W.M
- Page 205 and 206:
194 Chapter 8 C-O cleavage H E1 H C
- Page 207 and 208:
196 Chapter 8 leads to the formatio
- Page 209 and 210:
198 Chapter 8 aconitase citrate cis
- Page 211 and 212:
200 Chapter 8 *H R H H CO 2 − NH
- Page 213 and 214:
202 Chapter 8 EnzB − 2 H − O 2
- Page 215 and 216:
204 Chapter 8 involves no change in
- Page 217 and 218:
206 Chapter 8 Glyphosate H H N CO
- Page 219 and 220:
208 Chapter 8 (5) Chorismic acid (s
- Page 221 and 222:
9 Enzymatic Transformations of Amin
- Page 223 and 224:
CO − − 2 CO 2 H H CO 2 − N +
- Page 225 and 226:
214 Chapter 9 - BEnz CO − 2 Cl H
- Page 227 and 228:
216 Chapter 9 Arg 292 Arg 292 Lys 2
- Page 229 and 230:
218 Chapter 9 Arg 292 Asp 292 HN H
- Page 231 and 232:
220 Chapter 9 S − B 1 Enz H − C
- Page 233 and 234:
222 Chapter 9 9.6 N-Pyruvoyl-depend
- Page 235 and 236:
224 Chapter 9 The biosyntheses of n
- Page 237 and 238:
226 Chapter 9 Further reading Gener
- Page 239 and 240:
228 Chapter 10 B 1 - H + NH 3 CO
- Page 241 and 242:
230 Chapter 10 ‘low-barrier’ +
- Page 243 and 244:
232 Chapter 10 H S C 6 H 13 HN His
- Page 245 and 246:
234 Chapter 10 O H NH 3 CO 2 − CO
- Page 247 and 248:
236 Chapter 10 sub-units. Each sub-
- Page 249 and 250:
238 Chapter 10 Further reading Gene
- Page 251 and 252:
11 Radicals in Enzyme Catalysis 11.
- Page 253 and 254:
242 Chapter 11 CH 2 Co III Ad H OH
- Page 255 and 256:
244 Chapter 11 − O 2 C − O CO
- Page 257 and 258:
246 Chapter 11 H N H O 734 H N H PF
- Page 259 and 260:
248 Chapter 11 H H* + H + H 3 N CO
- Page 261 and 262:
250 Chapter 11 O HN NH + H 3 N H 3
- Page 263 and 264:
252 Chapter 11 cofactor is involved
- Page 265 and 266:
254 Chapter 11 Protein Radicals J.
- Page 267 and 268:
256 Chapter 12 self-splicing reacti
- Page 269 and 270:
258 Chapter 12 Figure 12.2 Structur
- Page 271 and 272:
260 Chapter 12 antigen combining si
- Page 273 and 274:
262 Chapter 12 R O OR' OH − R O
- Page 275 and 276:
264 Chapter 12 CO 2 − − O 2 C O
- Page 277 and 278:
266 Chapter 12 (1) Selective substr
- Page 279 and 280:
268 Chapter 12 HO O HO OH HO OH O O
- Page 281 and 282:
270 Chapter 12 Problems (1) How rev
- Page 283 and 284:
Appendix 1: Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rule
- Page 285 and 286:
Appendix 2: Amino Acid Abbreviation
- Page 287 and 288:
276 Appendix 3 Preparation of orang
- Page 289 and 290:
278 Appendix 4 (2) Intramolecular a
- Page 291 and 292:
280 Appendix 4 from water at a-posi
- Page 293 and 294:
282 Appendix 4 Chapter 8 (1) Treat
- Page 295 and 296:
284 Appendix 4 (b) Formation of rad
- Page 297 and 298:
286 Index b-hydroxydecanoyl thioest
- Page 299 and 300:
288 Index glycosylation 26-7 glysop
- Page 301 and 302:
290 Index phenylalanine ammonia lya
- Page 303:
292 Index transition states 31-2 an