Programmable Logic Design Quick Start Handbook
Programmable Logic Design Quick Start Handbook
Programmable Logic Design Quick Start Handbook
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
XILINX SOLUTIONS<br />
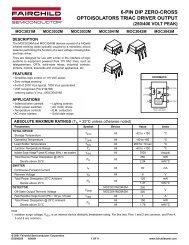
At the high level, the p-terms reside in a PLA. This structure is extremely<br />
flexible and very robust when compared to fixed or cascaded p-term function<br />
blocks.<br />
Classic CPLDs typically have a few p-terms available for a high-speed path<br />
to a given macrocell. They rely on capturing unused p-terms from neighboring<br />
macrocells to expand their product term tally when needed.<br />
The result of this architecture is a variable timing model and the possibility<br />
of stranding unusable logic within the function block.<br />
The PLA is different – and better. First, any p-term can be attached to any<br />
OR gate inside the function block macrocell(s).<br />
Second, any logic function can have as many p-terms as needed attached to<br />
it within the function block, to an upper limit of 56.<br />
Third, you can reuse product terms at multiple macrocell OR functions so<br />
that within a function block, you need only create a particular logical product<br />
once, but you can reuse it as many as 16 times within the function block. Naturally,<br />
this works well with the fitting software, which identifies product terms<br />
that can be shared.<br />
FIGURE 2-29:<br />
LOGIC ALLOCATION – TYPICAL PAL VS. PLA<br />
Xilinx • 59