CST Guide:
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
c-IAP<br />
TRADD<br />
FADD<br />
Section I: Research Areas<br />
chapter 03: Cell Growth and Death<br />
Regulation of Apoptosis Overview<br />
Inhibition of Apoptosis<br />
TNF, FasL, TRAIL<br />
TNF, FasL, TRAIL<br />
Trophic Factors<br />
TNF-α<br />
TNF-R1<br />
Survival Factors:<br />
Growth Factors,<br />
Cytokines, etc.<br />
Cytoplasm<br />
IKKα<br />
IκBα<br />
TAK1<br />
IKKγ<br />
IκBα<br />
NF-κB<br />
NF-κB<br />
Cytoplasm<br />
Nucleus<br />
IKKβ<br />
Calpain<br />
[Ca 2+ ]<br />
FLIP<br />
XIAP<br />
c-IAP<br />
TRAF2<br />
NIK Casp-8,-10<br />
RIP<br />
TRAF2<br />
Casp-12<br />
Casp-9<br />
ER Stress<br />
RIP1<br />
TRADD<br />
NF-κB<br />
FADD<br />
CYLD<br />
PARP<br />
Itch<br />
FLIP<br />
TRADD<br />
FADD<br />
BID<br />
ROCK<br />
• Cell shrinking<br />
• Membrane<br />
blebbing<br />
DFF40<br />
XIAP<br />
AIF<br />
RIP RAIDD<br />
PIDD<br />
Casp-2<br />
p53<br />
SirT2<br />
HtrA2<br />
Arts<br />
Casp-3,-6,-7<br />
Lamin<br />
A/C<br />
APP<br />
DNA<br />
Fragmentation<br />
RIP<br />
Smac/<br />
Diablo<br />
Endo G<br />
TRAF2<br />
tBID<br />
DFF40<br />
JNK<br />
Cyto c<br />
DFF45<br />
ASK1<br />
Bax<br />
DNA Damage<br />
Bak<br />
Mcl-1<br />
Casp-9<br />
Apaf-1<br />
AIF<br />
PKC<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Bim<br />
ATM/ATR<br />
p53<br />
Puma<br />
Noxa<br />
p90RSK<br />
Puma<br />
Bcl-xL<br />
Noxa<br />
HECTH9<br />
Endo G<br />
Chk1/2<br />
FoxO1<br />
p53<br />
Bad<br />
p53<br />
PI3K<br />
Cell Cycle<br />
Erk1/2<br />
cdc2<br />
14-3-3<br />
Akt<br />
Cellular Stress<br />
FoxO1<br />
JNK<br />
JNK<br />
Bim<br />
c-Jun<br />
NIK<br />
IKKγ CDC37<br />
IKKβ HSP90<br />
IκB<br />
IκB<br />
NF-κB<br />
NF-κB<br />
Cytoplasm<br />
Nucleus<br />
NF-κB<br />
cIAP<br />
TAK1<br />
TAB<br />
IKKα IKKβ<br />
IKKγ<br />
TRAF2<br />
TRADD<br />
HSP90<br />
Casp-8<br />
XIAP<br />
CYLD<br />
HSP70<br />
FADD<br />
HSP90<br />
JNK<br />
HSP27<br />
A20<br />
GSK-3<br />
FoxO1<br />
PTEN<br />
PI3K<br />
PIP 3<br />
Akt<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Casp-3,-6,-7<br />
Bax<br />
HSP27<br />
Apoptosis<br />
Casp-9<br />
Apaf-1 Cyto c HECTH9 HSP70<br />
Akt<br />
FLIP<br />
XIAP<br />
A20<br />
FLIP<br />
BID<br />
Smac/<br />
Diablo<br />
RIP1<br />
HSP70<br />
tBID<br />
HSP27<br />
HSP90<br />
Bax<br />
Bax<br />
Mcl-1<br />
Bak<br />
Bcl-xL<br />
Bim<br />
Bim<br />
PDK1<br />
p70S6K<br />
FAS<br />
Bim<br />
Bad<br />
Bim<br />
PKA<br />
[cAMP]<br />
FoxO1<br />
Ras<br />
Raf<br />
Erk1/2<br />
FoxO1<br />
PKC<br />
p90RSK<br />
Jak<br />
Src<br />
CREB Stat1 Stat3<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Bcl-xL<br />
Cytoplasm<br />
CREB<br />
Stat1<br />
Stat3<br />
HSP90<br />
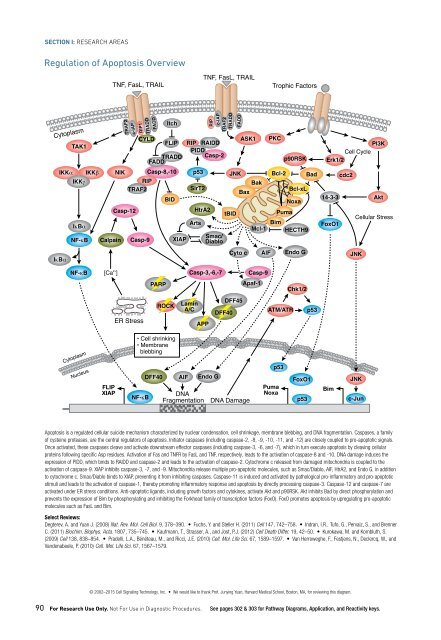
Apoptosis is a regulated cellular suicide mechanism characterized by nuclear condensation, cell shrinkage, membrane blebbing, and DNA fragmentation. Caspases, a family<br />
of cysteine proteases, are the central regulators of apoptosis. Initiator caspases (including caspase-2, -8, -9, -10, -11, and -12) are closely coupled to pro-apoptotic signals.<br />
Once activated, these caspases cleave and activate downstream effector caspases (including caspase-3, -6, and -7), which in turn execute apoptosis by cleaving cellular<br />
proteins following specific Asp residues. Activation of Fas and TNFR by FasL and TNF, respectively, leads to the activation of caspase-8 and -10. DNA damage induces the<br />
expression of PIDD, which binds to RAIDD and caspase-2 and leads to the activation of caspase-2. Cytochrome c released from damaged mitochondria is coupled to the<br />
activation of caspase-9. XIAP inhibits caspase-3, -7, and -9. Mitochondria release multiple pro-apoptotic molecules, such as Smac/Diablo, AIF, HtrA2, and Endo G, in addition<br />
to cytochrome c. Smac/Diablo binds to XIAP, preventing it from inhibiting caspases. Caspase-11 is induced and activated by pathological pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic<br />
stimuli and leads to the activation of caspase-1, thereby promoting inflammatory response and apoptosis by directly processing caspase-3. Caspase-12 and caspase-7 are<br />
activated under ER stress conditions. Anti-apoptotic ligands, including growth factors and cytokines, activate Akt and p90RSK. Akt inhibits Bad by direct phosphorylation and<br />
prevents the expression of Bim by phosphorylating and inhibiting the Forkhead family of transcription factors (FoxO). FoxO promotes apoptosis by upregulating pro-apoptotic<br />
molecules such as FasL and Bim.<br />
Select Reviews:<br />
Degterev, A. and Yuan J. (2008) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 378–390. • Fuchs, Y. and Steller H. (2011) Cell 147, 742–758. • Indran, I.R., Tufo, G., Pervaiz, S., and Brenner<br />
C. (2011) Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1807, 735–745. • Kaufmann, T., Strasser, A., and Jost, P.J. (2012) Cell Death Differ. 19, 42–50. • Kurokawa, M. and Kornbluth, S.<br />
(2009) Cell 138, 838–854. • Pradelli, L.A., Bénéteau, M., and Ricci, J.E. (2010) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 1589–1597. • Van Herreweghe, F., Festjens, N., Declercq, W., and<br />
Vandenabeele, P. (2010) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 1567–1579.<br />
Cell survival requires the active inhibition of apoptosis, which is accomplished by inhibiting the expression of pro-apoptotic factors as well as promoting the expression of<br />
anti-apoptotic factors. The PI3K pathway, activated by many survival factors, leads to the activation of Akt, an important player in survival signaling. PTEN negatively regulates<br />
the PI3K/Akt pathway. Activated Akt phosphorylates and inhibits the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bad, Bax, caspase-9, GSK-3, and FoxO1. Many growth factors and<br />
cytokines induce anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members. The Jaks and Src phosphorylate and activate Stat3, which in turn induces the expression of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2. Erk1/2<br />
and PKC activate p90RSK, which activates CREB and induces the expression of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2. These Bcl-2 family members protect the integrity of mitochondria, preventing<br />
cytochrome c release and the subsequent activation of caspase-9. TNF-α may activate both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic pathways; TNF-α can induce apoptosis by<br />
activating caspase-8 and -10, but can also inhibit apoptosis via NF-κB, which induces the expression of anti-apoptotic genes such as Bcl-2. cIAP1/2 inhibit TNF-α signaling<br />
by binding to TRAF2. FLIP inhibits the activation of caspase-8.<br />
Select Reviews:<br />
Brumatti, G., Salmanidis, M., and Ekert, P.G. (2010) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 1619–1630. • Fuchs, Y. and Steller, H. (2011) Cell 147, 742–758. • Fulda, S. and Vucic, D.<br />
(2012) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 109–124. • Kaufmann, T., Strasser, A., and Jost, P.J. (2012) Cell Death Differ. 19, 42–50. • Lopez, J. and Meier, P. (2010) Curr. Opin.<br />
Cell Biol. 22, 872–881. • Rong, Y. and Distelhorst, C.W. (2008) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 70, 73–91. • Srinivasula, S.M. and Ashwell, J.D. (2008) Mol. Cell 30, 123–135. •<br />
Zhang, X., Tang, N., Hadden, T.J., and Rishi, A.K. (2011) Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1813, 1978–1986.<br />
© 2002–2015 Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. • We would like to thank Prof. Junying Yuan, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, for reviewing this diagram.<br />
90 For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic Procedures. See pages 302 & 303 for Pathway Diagrams, Application, and Reactivity keys.<br />
© 2002–2015 Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. • We would like to thank Prof. Junying Yuan, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, for reviewing this diagram.<br />
www.cellsignal.com/cstpathways 91