CST Guide:
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Section I: Research Areas<br />
chapter 02: Signaling<br />
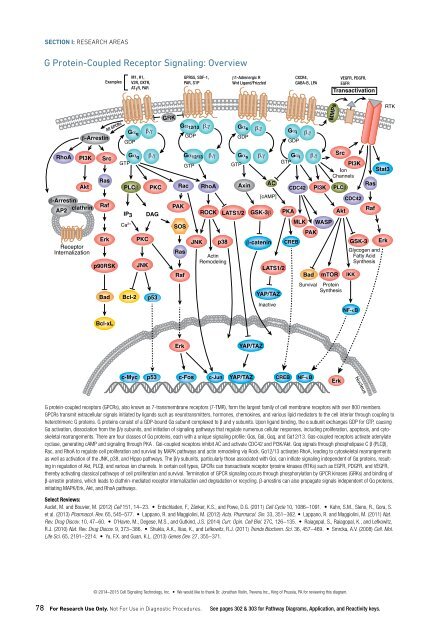
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling: Overview<br />
RhoA<br />
β-Arrestin<br />
AP2<br />
clathrin<br />
Receptor<br />
Internalization<br />
β-Arrestin<br />
PI3K<br />
Akt<br />
Examples<br />
Src<br />
Ras<br />
Raf<br />
Erk<br />
All GPCRs<br />
p90RSK<br />
Bad<br />
M1, H1,<br />
V2R, OXTR,<br />
AT 1 R, PAR<br />
Gα q<br />
GDP<br />
Gα q<br />
GTP<br />
β,γ<br />
β,γ<br />
GRK<br />
GPR55, SDF-1,<br />
PAR, S1P<br />
Gα 12/13 β,γ<br />
GDP<br />
Gα 12/13<br />
GTP<br />
β,γ<br />
β1-Adrenergic R<br />
Wnt Ligand/Frizzled<br />
Gα s<br />
GDP<br />
Gα s<br />
GTP<br />
β,γ<br />
β,γ<br />
CXCR4,<br />
GABA-B, LPA<br />
Gα i β,γ<br />
GDP<br />
Gα i β,γ<br />
GTP<br />
MMPs<br />
VEGFR, PDGFR,<br />
EGFR<br />
Transactivation<br />
Src<br />
PI3K<br />
Ion<br />
Channels<br />
Stat3<br />
PLCβ PKC Rac RhoA Axin AC<br />
CDC42 PI3K PLCβ<br />
Ras<br />
[cAMP]<br />
CDC42<br />
IP3<br />
PAK<br />
Akt<br />
Raf<br />
PKA<br />
DAG<br />
ROCK LATS1/2 GSK-3β<br />
Ca 2+<br />
SOS<br />
MLK WASP<br />
PAK<br />
PKC<br />
JNK p38 β-catenin CREB<br />
GSK-3 Erk<br />
Ras<br />
Glycogen and<br />
Actin<br />
Fatty Acid<br />
JNK<br />
Remodeling<br />
Synthesis<br />
LATS1/2<br />
Raf<br />
Bad mTOR IKK<br />
Survival Protein<br />
Bcl-2<br />
Synthesis<br />
YAP/TAZ<br />
p53<br />
Inactive<br />
NF-κB<br />
RTK<br />
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling to MAP Kinase/Erk<br />
Gi-Coupled<br />
Receptor<br />
Dynamin<br />
G i<br />
βγ<br />
PLCβ<br />
β-Arrestin GRK2<br />
Src<br />
PI3Kγ<br />
Receptor<br />
Internalization<br />
endosome<br />
H+<br />
JNK3<br />
Focal Adhesions<br />
Catecholamines<br />
MP<br />
Src-like<br />
Src c-Raf<br />
β-Arrestin1 MEK<br />
Erk<br />
C-TAK1<br />
TH<br />
PKC<br />
RTKs<br />
IMP<br />
Src<br />
GRB2<br />
RasGEF<br />
SOS<br />
Ras<br />
GAP<br />
MEK1/2<br />
KSR<br />
Src<br />
FAK<br />
Gα<br />
PLCβ q<br />
PYK2<br />
GTP<br />
RACK1<br />
IP 3<br />
[Ca 2+ ]<br />
PKC<br />
Ras<br />
c-Raf<br />
Erk1/2<br />
Integrins<br />
Ras<br />
GRP<br />
CaMKII,-IV<br />
Ras<br />
GRF<br />
c-Raf B-Raf<br />
Heterodimer<br />
Gq-Coupled<br />
Receptor<br />
Syn<br />
GAP<br />
RGS<br />
EPAC<br />
Rap1<br />
B-Raf<br />
DUSP6<br />
cPLA 2<br />
Synapsins<br />
AC<br />
Gα s<br />
GTP<br />
[cAMP]<br />
PKA<br />
Gs-Coupled<br />
Receptor<br />
RGS<br />
Bcl-xL<br />
Erk<br />
YAP/TAZ<br />
Cytoplasm<br />
Erk1/2 p90RSK<br />
PEA-15<br />
p90RSK<br />
cdc25<br />
c-Myc<br />
p53<br />
c-Fos<br />
c-Jun<br />
YAP/TAZ<br />
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as 7-transmembrane receptors (7-TMR), form the largest family of cell membrane receptors with over 800 members.<br />
GPCRs transmit extracellular signals initiated by ligands such as neurotransmitters, hormones, chemokines, and various lipid mediators to the cell interior through coupling to<br />
heterotrimeric G proteins. G proteins consist of a GDP-bound Gα subunit complexed to β and γ subunits. Upon ligand binding, the α subunit exchanges GDP for GTP, causing<br />
Gα activation, dissociation from the β/γ subunits, and initiation of signaling pathways that regulate numerous cellular responses, including proliferation, apoptosis, and cytoskeletal<br />
rearrangements. There are four classes of Gα proteins, each with a unique signaling profile: Gαs, Gαi, Gαq, and Gα12/13. Gαs-coupled receptors activate adenylate<br />
cyclase, generating cAMP and signaling through PKA . Gαi-coupled receptors inhibit AC and activate CDC42 and PI3K/Akt. Gαq signals through phospholipase C β (PLCβ),<br />
Rac, and RhoA to regulate cell proliferation and survival by MAPK pathways and actin remodeling via Rock. Gα12/13 activates RhoA, leading to cytoskeletal rearrangements<br />
as well as activation of the JNK, p38, and Hippo pathways. The β/γ subunits, particularly those associated with Gαi, can initiate signaling independent of Gα proteins, resulting<br />
in regulation of Akt, PLCβ, and various ion channels. In certain cell types, GPCRs can transactivate receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) such as EGFR, PDGFR, and VEGFR,<br />
thereby activating classical pathways of cell proliferation and survival. Termination of GPCR signaling occurs through phosphorylation by GPCR kinases (GRKs) and binding of<br />
β-arrestin proteins, which leads to clathrin-mediated receptor internalization and degradation or recycling. β-arrestins can also propagate signals independent of Gα proteins,<br />
initiating MAPK/Erk, Akt, and RhoA pathways.<br />
Select Reviews:<br />
Audet, M. and Bouvier, M. (2012) Cell 151, 14−23. • Entschladen, F., Zänker, K.S., and Powe, D.G. (2011) Cell Cycle 10, 1086−1091. • Kahn, S.M., Sleno, R., Gora, S.<br />
et al. (2013) Pharmacol. Rev. 65, 545–577. • Lappano, R. and Maggiolini, M. (2012) Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 33, 351−362. • Lappano, R. and Maggiolini, M. (2011) Nat.<br />
Rev. Drug Discov. 10, 47−60. • O’Havre, M., Degese, M.S., and Gutkind, J.S. (2014) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 27C, 126−135. • Raiagopal, S., Raiagopal, K., and Lefkowitz,<br />
R.J. (2010) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 373−386. • Shukla, A.K., Xiao, K., and Lefkowitz, R.J. (2011) Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 457−469. • Smrcka, A.V. (2008) Cell. Mol.<br />
Life Sci. 65, 2191−2214. • Yu, F.X. and Guan, K.L. (2013) Genes Dev. 27, 355−371.<br />
CREB<br />
NF-κB<br />
Erk<br />
Nucleus<br />
Nucleus<br />
p90RSK<br />
Transcription<br />
Erk1/2<br />
FoxO3<br />
Tumorigenesis<br />
MSK1/2<br />
MAPKAPK2<br />
Progression<br />
of Cell Cycle<br />
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are activated by a wide variety of external stimuli. Upon receptor activation, the G protein exchanges GDP for GTP, causing the dissociation<br />
of the GTP-bound α and β/γ subunits and triggering diverse signaling cascades. Receptors coupled to different heterotrimeric G protein subtypes can utilize different scaffolds<br />
to activate the small G protein/ MAPK cascade, employing at least three different classes of Tyr kinases. Src family kinases are recruited following activation of PI3Kγ by β/γ<br />
subunits. They are also recruited by receptor internalization, crossactivation of receptor Tyr kinases, or by signaling through an integrin scaffold involving Pyk2 and/or FAK.<br />
GPCRs can also employ PLCβ to mediate activation of PKC and CaMKII, which can have either stimulatory or inhibitory consequences for the downstream MAPK pathway.<br />
Select Reviews:<br />
Aoki, Y., Niihori, T., Narumi, Y., Kure, S., and Matsubara, Y. (2008) Hum. Mutat. 29, 992–1006. • Caunt, C.J., Finch, A.R., Sedgley, K.R., and McArdle, C.A. (2006) Trends<br />
Endocrinol. Metab. 17, 276–283. • Goldsmith, Z.G. and Dhanasekaran, D.N. (2007) Oncogene 26, 3122–3142. • Kim, E.K. and Choi, E.J. (2010) Biochim. Biophys. Acta.<br />
1802, 396–405. • McKay, M.M. and Morrison, D.K. (2007) Oncogene 26, 3113–3121.<br />
© 2014–2015 Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. • We would like to thank Dr. Jonathan Violin, Trevena Inc., King of Prussia, PA for reviewing this diagram.<br />
78 For Research Use Only. Not For Use in Diagnostic Procedures. See pages 302 & 303 for Pathway Diagrams, Application, and Reactivity keys.<br />
© 2002–2015 Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. • We would like to thank Prof. John Blenis, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, for reviewing this diagram.<br />
www.cellsignal.com/cstpathways 79