EE462L, Power Electronics, DC-DC Boost Converter Version ... - ECS
EE462L, Power Electronics, DC-DC Boost Converter Version ... - ECS
EE462L, Power Electronics, DC-DC Boost Converter Version ... - ECS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
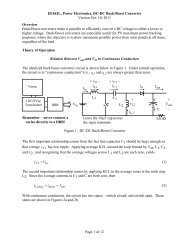
<strong>EE462L</strong>, <strong>Power</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong>, <strong>DC</strong>-<strong>DC</strong> <strong>Boost</strong> <strong>Converter</strong><br />
<strong>Version</strong> Oct. 3, 2011<br />
Save screen<br />
snapshot #1<br />
VDS for 90kHz, 120V<br />
11. With your circuit turned off, quickly and carefully use your hand to check MOSFET<br />
heat sink temperature and any other hot components. You can also use an infrared<br />
thermometer for this step.<br />
12. Compare your measured Vout/Vin to theory. Multiply voltages and currents to compute<br />
input and output powers, and then compute the efficiency of your circuit for each Vout<br />
measured. Plot your results in your written report.<br />
13. Take can also take your solar lab data while you are doing the boost converter. Use a<br />
150W light bulb as a load. Connect a DBR between a solar panel pair and your boost<br />
converter to steady the panel current. Sweep D to find the maximum power point.<br />
Compute the maximum power point value of Rload = Vout/Iout and the corresponding<br />
equivalent max power resistance seen by the solar panels. Does the ratio of Rload<br />
resistance to equivalent resistance seem by the solar panels check with D<br />
Page 10 of 11