P r o d u c t R a t i o n a l e S u r g i c a l T e c h n i q u e - Biomet
P r o d u c t R a t i o n a l e S u r g i c a l T e c h n i q u e - Biomet P r o d u c t R a t i o n a l e S u r g i c a l T e c h n i q u e - Biomet
Figure 12 Figure 13 Figure 14 Final Impaction and Cutting It is at this stage of surgery that the Nancy and ECMES Nails must be differentiated. The Nancy Nail is already the correct length and should now be impacted in its final position. The ECMES Nail must be cut to length prior to being impacted in its final position. ECMES Nail Once the ECMES Nail is located in the cancellous bone, impact it in its final position by lightly tapping the Cannulated T-Handle. Remove the Cannulated T-Handle and cut the nail using the cutter (M21840), ensuring that 1 to 2 cm of the nail remains outside the entry hole, as for the Nancy Nail, the tip of the nail can be moderately Nancy Nail curved using surgical forceps. The Impactor/Extractor (M21898) is used to impact the nail in its final position. By lightly tapping the hammer pad of the Impactor/Extractor with a mallet the tip of the nail inserted medially should finally rest against the cortex above Optional: In order to minimise the risks of soft tissue irritation caused by the cut tip of the nail, Polyethylene End Caps (M21941 to M21946) are provided to cover the tip. the medial femoral condyle (Figure 12). Post Operative Care Caution: Do not make unnecessary rotational movements whilst the Impactor/Extractor holds the nail as it may cause the rounded tip to snap off. No immobilisation is required. Once the patient can straighten the leg, partial weight bearing may commence. As soon as the patient feels ready, full weight bearing is allowed. Physiotherapy should reinforce the quadriceps muscle and the At this stage the atraumatic rounded tip of the nail can be moderately curved to facilitate its future retrieval (Figure 13). extension of the knee. Do not force the knee into flexion as the extremities of the nail may cause some discomfort. If distraction of the fracture is evident this may be overcome by exerting pressure on the knee. If the nail is too long, it may be shortened by using the Nail Cutter (M21840). Nail Retrieval The removal of the nails should be undertaken at around 4 - 6 months depending upon the appearance of the X-rays. For the Nancy Nail, use the Impactor/Extractor (M21898). For the ECMES Nails, use the Extraction Clamp (M21900). 9
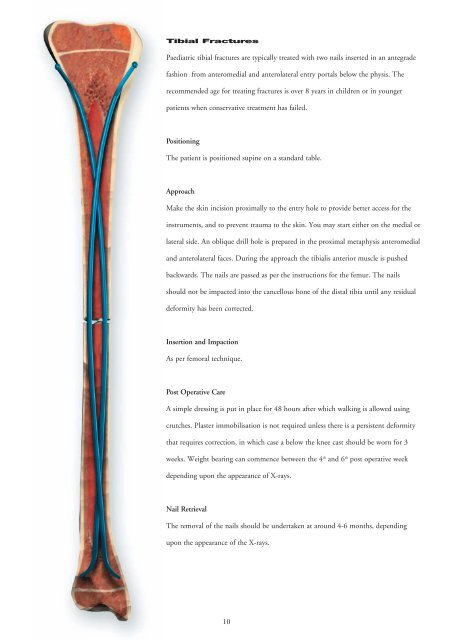
Tibial Fractures Paediatric tibial fractures are typically treated with two nails inserted in an antegrade fashion from anteromedial and anterolateral entry portals below the physis. The recommended age for treating fractures is over 8 years in children or in younger patients when conservative treatment has failed. Positioning The patient is positioned supine on a standard table. Approach Make the skin incision proximally to the entry hole to provide better access for the instruments, and to prevent trauma to the skin. You may start either on the medial or lateral side. An oblique drill hole is prepared in the proximal metaphysis anteromedial and anterolateral faces. During the approach the tibialis anterior muscle is pushed backwards. The nails are passed as per the instructions for the femur. The nails should not be impacted into the cancellous bone of the distal tibia until any residual deformity has been corrected. Insertion and Impaction As per femoral technique. Post Operative Care A simple dressing is put in place for 48 hours after which walking is allowed using crutches. Plaster immobilisation is not required unless there is a persistent deformity that requires correction, in which case a below the knee cast should be worn for 3 weeks. Weight bearing can commence between the 4 th and 6 th post operative week depending upon the appearance of X-rays. Nail Retrieval The removal of the nails should be undertaken at around 4-6 months, depending upon the appearance of the X-rays. 10
- Page 1: P r o d u c t S u r g i c a l R a t
- Page 4 and 5: Clinical Results Case 1 Case 2 Case
- Page 6 and 7: Nail Selection Nail diameter and le
- Page 8 and 9: Surgical Technique Femoral Fracture
- Page 12 and 13: Forearm Fractures Paediatric forear
- Page 14: Ordering Details Nancy Nail Instrum
Tibial Fractures<br />
Paediatric tibial fractures are typically treated with two nails inserted in an antegrade<br />
fashion from anteromedial and anterolateral entry portals below the physis. The<br />
recommended age for treating fractures is over 8 years in children or in younger<br />
patients when conservative treatment has failed.<br />
Positioning<br />
The patient is positioned supine on a standard table.<br />
Approach<br />
Make the skin incision proximally to the entry hole to provide better access for the<br />
instruments, and to prevent trauma to the skin. You may start either on the medial or<br />
lateral side. An oblique drill hole is prepared in the proximal metaphysis anteromedial<br />
and anterolateral faces. During the approach the tibialis anterior muscle is pushed<br />
backwards. The nails are passed as per the instructions for the femur. The nails<br />
should not be impacted into the cancellous bone of the distal tibia until any residual<br />
deformity has been corrected.<br />
Insertion and Impaction<br />
As per femoral technique.<br />
Post Operative Care<br />
A simple dressing is put in place for 48 hours after which walking is allowed using<br />
crutches. Plaster immobilisation is not required unless there is a persistent deformity<br />
that requires correction, in which case a below the knee cast should be worn for 3<br />
weeks. Weight bearing can commence between the 4 th and 6 th post operative week<br />
depending upon the appearance of X-rays.<br />
Nail Retrieval<br />
The removal of the nails should be undertaken at around 4-6 months, depending<br />
upon the appearance of the X-rays.<br />
10