High performance capillary electrophoresis - T.E.A.M.
High performance capillary electrophoresis - T.E.A.M.
High performance capillary electrophoresis - T.E.A.M.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Modes<br />
Absorbance<br />
0 10 20 30 40<br />
Retention time [min]<br />
Retention time [min]<br />
40<br />
30<br />
R<br />
R<br />
20<br />
1.2<br />
0.8<br />
0.4<br />
1.2<br />
0.8<br />
0.4<br />
0 0.01 0.02 0.03<br />
Concentration [M]<br />
Phosphate conc. [M]<br />
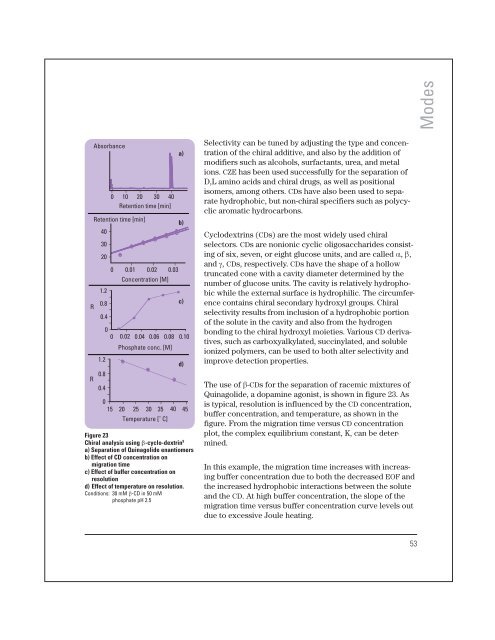
Figure 23<br />
Chiral analysis using b-cyclo-dextrin 9<br />
a) Separation of Quinagolide enantiomers<br />
b) Effect of CD concentration on<br />
migration time<br />
c) Effect of buffer concentration on<br />
resolution<br />
d) Effect of temperature on resolution.<br />
Conditions: 30 mM b-CD in 50 mM<br />
phosphate pH 2.5<br />
a)<br />
b)<br />
c)<br />
0<br />
0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10<br />
d)<br />
0<br />
15 20 25 30 35 40 45<br />
Temperature [˚ C]<br />
Selectivity can be tuned by adjusting the type and concentration<br />
of the chiral additive, and also by the addition of<br />
modifiers such as alcohols, surfactants, urea, and metal<br />
ions. CZE has been used successfully for the separation of<br />
D,L amino acids and chiral drugs, as well as positional<br />
isomers, among others. CDs have also been used to separate<br />
hydrophobic, but non-chiral specifiers such as polycyclic<br />
aromatic hydrocarbons.<br />
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are the most widely used chiral<br />
selectors. CDs are nonionic cyclic oligosaccharides consisting<br />
of six, seven, or eight glucose units, and are called a, b,<br />
and g, CDs, respectively. CDs have the shape of a hollow<br />
truncated cone with a cavity diameter determined by the<br />
number of glucose units. The cavity is relatively hydrophobic<br />
while the external surface is hydrophilic. The circumference<br />
contains chiral secondary hydroxyl groups. Chiral<br />
selectivity results from inclusion of a hydrophobic portion<br />
of the solute in the cavity and also from the hydrogen<br />
bonding to the chiral hydroxyl moieties. Various CD derivatives,<br />
such as carboxyalkylated, succinylated, and soluble<br />
ionized polymers, can be used to both alter selectivity and<br />
improve detection properties.<br />
The use of b-CDs for the separation of racemic mixtures of<br />
Quinagolide, a dopamine agonist, is shown in figure 23. As<br />
is typical, resolution is influenced by the CD concentration,<br />
buffer concentration, and temperature, as shown in the<br />
figure. From the migration time versus CD concentration<br />
plot, the complex equilibrium constant, K, can be determined.<br />
In this example, the migration time increases with increasing<br />
buffer concentration due to both the decreased EOF and<br />
the increased hydrophobic interactions between the solute<br />
and the CD. At high buffer concentration, the slope of the<br />
migration time versus buffer concentration curve levels out<br />
due to excessive Joule heating.<br />
53