High performance capillary electrophoresis - T.E.A.M.
High performance capillary electrophoresis - T.E.A.M.
High performance capillary electrophoresis - T.E.A.M.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
a)<br />
0.005 AU<br />
19 23<br />
p(dA) 20<br />
0.001 AU<br />
p(dA) 47<br />
b)<br />
Instrumentation/Operation<br />
19<br />
p(dA) 47<br />
23<br />
c)<br />
0.001 AU<br />
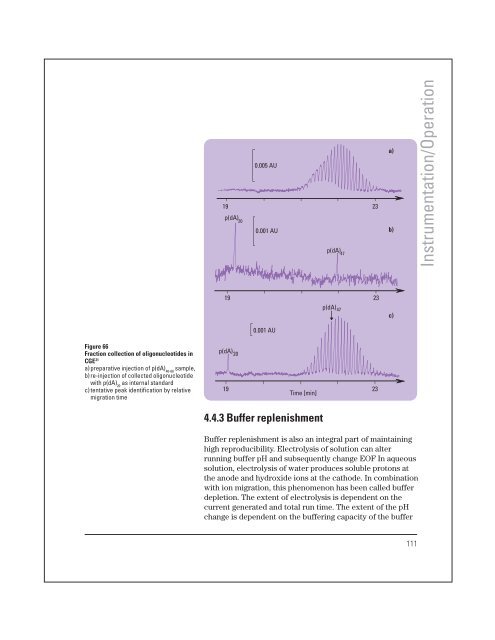
Figure 66<br />
Fraction collection of oligonucleotides in<br />
CGE 21<br />
a) preparative injection of p(dA) 40-60<br />
sample,<br />
b) re-injection of collected oligonucleotide<br />
with p(dA) 20<br />
as internal standard<br />
c) tentative peak identification by relative<br />
migration time<br />
p(dA) 20<br />
19 23<br />
Time [min]<br />
4.4.3 Buffer replenishment<br />
Buffer replenishment is also an integral part of maintaining<br />
high reproducibility. Electrolysis of solution can alter<br />
running buffer pH and subsequently change EOF In aqueous<br />
solution, electrolysis of water produces soluble protons at<br />
the anode and hydroxide ions at the cathode. In combination<br />
with ion migration, this phenomenon has been called buffer<br />
depletion. The extent of electrolysis is dependent on the<br />
current generated and total run time. The extent of the pH<br />
change is dependent on the buffering capacity of the buffer<br />
111