Lab C: Osmosis in a Plant Cell -- Plant Cell ... - Explore Biology
Lab C: Osmosis in a Plant Cell -- Plant Cell ... - Explore Biology
Lab C: Osmosis in a Plant Cell -- Plant Cell ... - Explore Biology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name _____________________________<br />
AP <strong>Biology</strong><br />
Period _________<br />
Date ______________________<br />
LAB _____. OSMOSIS IN A PLANT CELL<br />
PLANT CELL PLASMOLYSIS<br />
INTRODUCTION<br />
<strong>Cell</strong>s lose or ga<strong>in</strong> water due to the difference <strong>in</strong> solute concentrations between the cytoplasm<br />
(the <strong>in</strong>tracellular fluid) and the solution surround<strong>in</strong>g the cell (the extracellular fluid). The<br />
movement of water <strong>in</strong> and out of a cell is governed by the laws of diffusion: water flows from a<br />
region of higher water concentration to a region of lower concentration.<br />
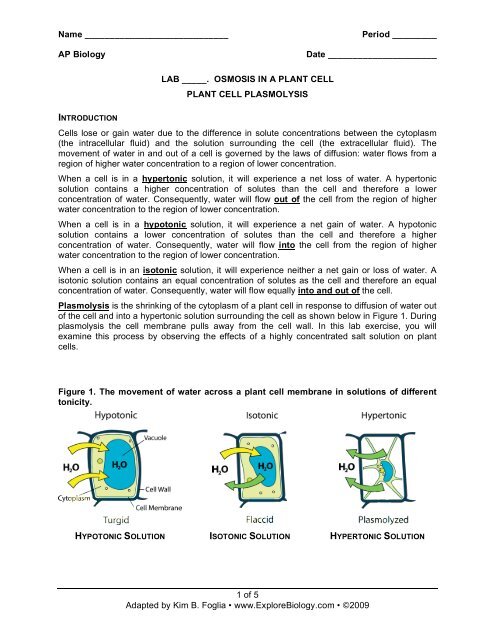
When a cell is <strong>in</strong> a hypertonic solution, it will experience a net loss of water. A hypertonic<br />
solution conta<strong>in</strong>s a higher concentration of solutes than the cell and therefore a lower<br />
concentration of water. Consequently, water will flow out of the cell from the region of higher<br />
water concentration to the region of lower concentration.<br />
When a cell is <strong>in</strong> a hypotonic solution, it will experience a net ga<strong>in</strong> of water. A hypotonic<br />
solution conta<strong>in</strong>s a lower concentration of solutes than the cell and therefore a higher<br />
concentration of water. Consequently, water will flow <strong>in</strong>to the cell from the region of higher<br />
water concentration to the region of lower concentration.<br />
When a cell is <strong>in</strong> an isotonic solution, it will experience neither a net ga<strong>in</strong> or loss of water. A<br />
isotonic solution conta<strong>in</strong>s an equal concentration of solutes as the cell and therefore an equal<br />
concentration of water. Consequently, water will flow equally <strong>in</strong>to and out of the cell.<br />
Plasmolysis is the shr<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g of the cytoplasm of a plant cell <strong>in</strong> response to diffusion of water out<br />
of the cell and <strong>in</strong>to a hypertonic solution surround<strong>in</strong>g the cell as shown below <strong>in</strong> Figure 1. Dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
plasmolysis the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall. In this lab exercise, you will<br />
exam<strong>in</strong>e this process by observ<strong>in</strong>g the effects of a highly concentrated salt solution on plant<br />
cells.<br />
Figure 1. The movement of water across a plant cell membrane <strong>in</strong> solutions of different<br />
tonicity.<br />
HYPOTONIC SOLUTION ISOTONIC SOLUTION HYPERTONIC SOLUTION<br />
1 of 5<br />
Adapted by Kim B. Foglia • www.<strong>Explore</strong><strong>Biology</strong>.com • ©2009
Name _____________________________<br />
AP <strong>Biology</strong><br />
PROCEDURE<br />
1. Prepare a wet mount of red onion epidermis. Locate a good section of leaf under low power<br />
and then observe under high power. Sketch a s<strong>in</strong>gle red onion cell <strong>in</strong> the space below and<br />
describe the appearance of the plant cell.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
2. Add 2 or 3 drops of 15% NaCl to one edge of the cover slip. Draw the salt solution across<br />
the slide by touch<strong>in</strong>g a piece of paper towel to the fluid under the opposite edge of the cover<br />
slip. Observe the plant cells <strong>in</strong> the microscope while you draw the salt water across the<br />
slide. Sketch a s<strong>in</strong>gle red onion cell <strong>in</strong> the space below and describe what has happened to<br />
the plant cell.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
3. Remove the cover slip and flood the red onion tissue with fresh water. Observe under high<br />
power. Describe and expla<strong>in</strong> what has happened.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
4. Complete the Summary Questions.<br />
2 of 5<br />
Adapted by Kim B. Foglia • www.<strong>Explore</strong><strong>Biology</strong>.com • ©2009
Name _____________________________<br />
AP <strong>Biology</strong><br />
SUMMARY QUESTIONS<br />
1. What is plasmolysis<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
2. Expla<strong>in</strong> the changes observed <strong>in</strong> the red onion cells us<strong>in</strong>g the terms hypertonic and<br />
hypotonic.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
3. In the w<strong>in</strong>ter, icy roads are often salted to remove the ice and make them less slippery.<br />
Grasses and other herbaceous plants often die near the side of these roads. What causes<br />
this to happen<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
4. When a person is given fluid <strong>in</strong>travenously (an I.V.) <strong>in</strong> the hospital, the fluid is typically a<br />
sal<strong>in</strong>e solution isotonic to human body tissues. Expla<strong>in</strong> why this is necessary.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
3 of 5<br />
Adapted by Kim B. Foglia • www.<strong>Explore</strong><strong>Biology</strong>.com • ©2009
Name _____________________________<br />
AP <strong>Biology</strong><br />
5. What if the unth<strong>in</strong>kable happened at the hospital! A patient was given an I.V. bag with<br />
distilled water <strong>in</strong> it rather than sal<strong>in</strong>e solution. Describe what would happen to their red blood<br />
cells and expla<strong>in</strong> why this would occur.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
6. Many freshwater one-celled organisms, like Paramecium, have contractile vacuoles. These<br />
structures collect and pump out excess water that accumulates <strong>in</strong> the cell. Expla<strong>in</strong> why<br />
these organisms needs such a structure.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
7. Expla<strong>in</strong> why contractile vacuoles would be of little value to one-celled organisms liv<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> salt<br />
water.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
8. Popcorn sold at movie theaters is very salty, caus<strong>in</strong>g people to become thirsty and to buy<br />
soft dr<strong>in</strong>ks. Expla<strong>in</strong> why salty popcorn causes this thirst.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
4 of 5<br />
Adapted by Kim B. Foglia • www.<strong>Explore</strong><strong>Biology</strong>.com • ©2009
Name _____________________________<br />
AP <strong>Biology</strong><br />
9. Expla<strong>in</strong> why soft-bodied <strong>in</strong>vertebrates, like slugs, die when you pour salt on them.<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
___________________________________________________________________________<br />
10. In each case, label the diagrams as to whether the red blood cells are <strong>in</strong> a hypertonic,<br />
isotonic, or hypotonic solution<br />
11. In the space below, draw a molecular diagram of the cell membrane. Illustrate the follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
processes and the cellular structures and materials that are <strong>in</strong>volved:<br />
a. diffusion of water molecules across the cell membrane<br />
b. active transport of a sodium ion across the cell membrane<br />
c. diffusion of non-polar molecules (i.e., a lipid) across the cell membrane<br />
5 of 5<br />
Adapted by Kim B. Foglia • www.<strong>Explore</strong><strong>Biology</strong>.com • ©2009