Pneumoperitoneum Caused by Ruptured Gas-Containing Pyogenic ...
Pneumoperitoneum Caused by Ruptured Gas-Containing Pyogenic ...
Pneumoperitoneum Caused by Ruptured Gas-Containing Pyogenic ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
16<br />
J Emerg Crit Care Med. Vol. 23, No. 1, 2012<br />
Table 3 Poor prognostic factors of pyogenic liver abscess<br />
APACHE II score at admission ≥15 Compromised immune status<br />
Malignancy<br />
Diabetes mellitus<br />
Uremia<br />
Senility<br />
Hyperbilirubinemia 1 High level of blood creatinine 2<br />
High level of blood urea nitrogen 3<br />
Hyperglycemia<br />
MDR isolates<br />
Bacteremia<br />
Polymicrobial infection 4 Anaerobic infection 4<br />
Non-K. pneumoniae infection 4<br />
Antibiotics alone<br />
Diagnostic delay<br />
Multiple abscesses<br />
Bi-lobe involvement<br />
<strong>Gas</strong>-forming liver abscess<br />
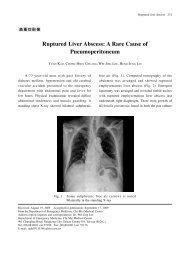
Alveolar gas pattern and pneumoperitoneum as viewed on radiographs<br />
Globular configuration, shaggy margin, alveolar internal structure, and total gas content on CT scans.<br />
APACHE = Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation, MDR = multi-drug resistant, K. pneumoniae<br />
= Klebsiella pneumoniae, 1 = blood total bilirubin > 20.52 μmol/L, 2 = blood creatinine > 115 μmol/L, 3 =<br />
blood urea nitrogen>7.86 mmol/L, 4 = isolated pathogen growing in blood or abscess cultures<br />
Klebsiella pneumonia and Escherichia coli (18) . The<br />
impairment of local perfusion may also inhibit the<br />
removal of gas from the infected tissue and cause<br />
the GPLA (5) . However, if rupture of PLA occurs<br />
and signs of acute peritonitis present, surgery<br />
is the only treatment for this condition (5) . Poor<br />
prognostic factors of PLA are listed at Table 3 (19,20) .<br />
Multivariate analysis revealed that gas-forming<br />
abscess, multi-drug resistant isolates, anaerobic<br />
infection, blood urea nitrogen level >7.86 mmol/l,<br />
and APACHE II score ≥15 were associated with<br />
high mortality (20) .<br />
I n s u m m a r y, i n s o m e o f t h e c a s e s o f<br />
pneumoperitoneum, the physicians didn’t make<br />
a proper diagnosis until surgical intervention.<br />
<strong>Pneumoperitoneum</strong> with acute abdominal pain is<br />
mostly secondary to hollow organ perforation, but<br />
there are still some other causes which present the<br />
similar clinical condition. Rupture of GPLA is a<br />
rare one of them and can mimic intra-abdominal<br />
visceral perforation. When physicians meet patients<br />
who have pneumoperitoneum with acute abdominal<br />
pain and the clinical clues of PLA exist. It must<br />
be borne in mind that rupture of GPLA is one<br />
of the differential diagnoses. Further abdominal<br />
sonography, even abdominal CT scan is needed to<br />
establish the proper diagnosis for immediate and<br />
definite managements.<br />
References<br />
1. Mularski RA, Sippel JM, Osbrone ML.<br />
<strong>Pneumoperitoneum</strong>: a review of nonsurgical<br />
causes. Crit Care Med 2000;28:2638-44.<br />
2. Mularski RA, Ciccolo ML, Rappaport WD.<br />
Nonsurgical causes of pneumoperitoneum.<br />
West J Med 1999;170:41-6.<br />
3. Lee CH, Leu HS, Wu TS, Su LH, Liu JW. Risk<br />
factors of spontaneous rupture of liver abscess<br />
caused <strong>by</strong> Klebsiella pneumoniae. Diagn<br />
Microbiol Infect Dis 2005;52:79-84.<br />
4. Chou FF, Sheen-Chen SM, Lee TY. Rupture<br />
of pyogenic liver abscess. Am J <strong>Gas</strong>troenterol<br />
1995;90:767-70.<br />
5. Ukikusa M, Inomoto T, Kitai T, et al.<br />
<strong>Pneumoperitoneum</strong> following the spontaneous