- Page 1:
UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INS
- Page 4 and 5:
Fernandes, F., Loura, L. M. S., Fed
- Page 6 and 7:
Ao Pedro e Hugo, amigos de longa da
- Page 8 and 9:
2.2. - Peptides as models 2.3. - Am
- Page 11 and 12:
ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOL LIST ABBRE
- Page 13:
RESUMO RESUMO As biomembranas são
- Page 17 and 18:
SINOPSE SINOPSE Nas últimas duas d
- Page 19 and 20:
SINOPSE podem fornecer informação
- Page 21 and 22:
SINOPSE aceitantes. Dadores mais pr
- Page 23 and 24:
OUTLINE OUTLINE The last two decade
- Page 25 and 26:
OUTLINE membranes with a distributi
- Page 27:
OUTLINE BAR domains (tubulation of
- Page 30 and 31:
ion diffusion, as the energy requir
- Page 32 and 33:
acid. If no more groups are linked
- Page 34 and 35:
sphingomyelin, the most abundant sp
- Page 36 and 37:
signal for neighbouring cells to ph
- Page 38 and 39:
functional role in process such as
- Page 40 and 41:
in the L α phase, while lateral di
- Page 42 and 43:
1.7. Lateral heterogeneity in lipid
- Page 44 and 45:
the vesicle through bilayer deforma
- Page 46 and 47:
Figure I.9 - Depiction of the sever
- Page 48 and 49:
Figure I.11 - Experimentally obtain
- Page 50 and 51:
drying into a film and ressuspensio
- Page 52 and 53:
deactivating agents. Zwitterionic d
- Page 54 and 55:
amphipatic helices (see Section 2.3
- Page 56 and 57:
size corresponding to the hydrophob
- Page 58 and 59:
changes abruptly in the interfacial
- Page 60 and 61:
thickness of the bilayer (Section 1
- Page 62 and 63:
some α-helical membrane proteins a
- Page 64 and 65:
The formation of a lipid population
- Page 66 and 67:
homogeneous distribution of lipids
- Page 68 and 69:
Figure I.20 - Relative binding cons
- Page 70 and 71:
2.9. Lipid phase preferential parti
- Page 72 and 73:
In Figure I.21, theoretical simulat
- Page 75 and 76:
PROTEIN-PROTEIN AND PROTEIN-LIPID I
- Page 77 and 78: PROTEIN-PROTEIN AND PROTEIN-LIPID I
- Page 79: PROTEIN-PROTEIN AND PROTEIN-LIPID I
- Page 83 and 84: 2430 Biophysical Journal Volume 85
- Page 85 and 86: 2432 Fernandes et al. Coat protein
- Page 87 and 88: 2434 Fernandes et al. leads to an a
- Page 89 and 90: 2436 Fernandes et al. FIGURE 4 (A)
- Page 91 and 92: 2438 Fernandes et al. section of th
- Page 93 and 94: 2440 Fernandes et al. tein oligomer
- Page 95: QUANTIFICATION OF PROTEIN-LIPID SEL
- Page 98 and 99: FRET Study of Protein-Lipid Selecti
- Page 100 and 101: FRET Study of Protein-Lipid Selecti
- Page 102 and 103: FRET Study of Protein-Lipid Selecti
- Page 104 and 105: FRET Study of Protein-Lipid Selecti
- Page 107 and 108: BINDING OF INHIBITORS TO A PUTATIVE
- Page 109 and 110: BINDING OF INHIBITORS TO A PUTATIVE
- Page 111: INTERACTION OF THE INDOLE CLASS OF
- Page 114 and 115: 5272 Biochemistry, Vol. 45, No. 16,
- Page 116 and 117: 5274 Biochemistry, Vol. 45, No. 16,
- Page 118 and 119: 5276 Biochemistry, Vol. 45, No. 16,
- Page 120 and 121: 5278 Biochemistry, Vol. 45, No. 16,
- Page 123: BINDING ASSAYS OF INHIBITORS TOWARD
- Page 126 and 127: 1778 F. Fernandes et al. / Biochimi
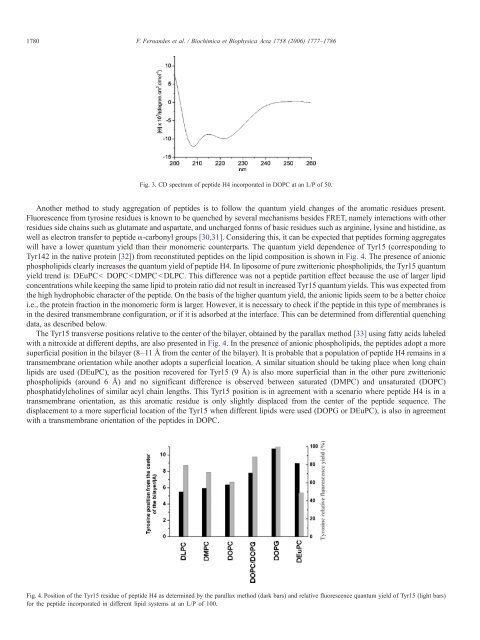
- Page 130 and 131: 1782 F. Fernandes et al. / Biochimi
- Page 132 and 133: 1784 F. Fernandes et al. / Biochimi
- Page 134 and 135: 1786 F. Fernandes et al. / Biochimi
- Page 136 and 137: apparently the most significant as
- Page 138 and 139: 110
- Page 140 and 141: Introduction Quinolones are broad-s
- Page 142 and 143: [9-12]. Having this into considerat
- Page 144 and 145: any case, very similar, probably wi
- Page 146 and 147: placement of the protein around the
- Page 148 and 149: ⎛ II t ⎛ R ⎞ 0 ρ () t = exp
- Page 150 and 151: APPENDIX - Derivation of the FRET r
- Page 152 and 153: 2 2w J ( t) = '2 R − R + w / 1
- Page 154 and 155: [14] L. Plançon, M. Chami, L. Lete
- Page 156 and 157: acceptors) (Eqs. 4-6) (⋅-⋅-⋅)
- Page 158 and 159: FIGURE 1A FIGURE 1B 130
- Page 160 and 161: FIGURE 4A FIGURE 4B 132
- Page 162 and 163: FIGURE 6A FIGURE 6B 134
- Page 164 and 165: 136
- Page 166 and 167: dynamin. Soon after, the same group
- Page 168 and 169: 140
- Page 170 and 171: 142
- Page 172 and 173: Introduction Control of membrane re
- Page 174 and 175: Steady-state fluorescence measureme
- Page 176 and 177: Rho-DOPE (acceptor). The increase o
- Page 178 and 179:
where η is the viscosity of the me
- Page 180 and 181:
ound conformation of the BAR domain
- Page 182 and 183:
19. Fernandes, F., L. M. S. Loura,
- Page 184 and 185:
Figure Legends Fig.1: N-terminal am
- Page 186 and 187:
FIG. 1A FIG.1B 17
- Page 188 and 189:
FIG. 3A FIG. 3B 19
- Page 190 and 191:
FIG.5A 21
- Page 192 and 193:
FIG 6. 23
- Page 194 and 195:
FIG. 8 A B 25
- Page 196 and 197:
The signalling functions of PI(4,5)
- Page 198 and 199:
172
- Page 200 and 201:
174
- Page 202 and 203:
zoxadiazol (NBD)-PC were obtained f
- Page 204 and 205:
Fig. 3. Fluorescence decays of diph
- Page 206 and 207:
CONCLUSIONS VII CONCLUSIONS Chapter
- Page 208 and 209:
CONCLUSIONS constants recovered by
- Page 210 and 211:
CONCLUSIONS Chapter IV ‐ Binding
- Page 212 and 213:
CONCLUSIONS Chapter VI - Clustering
- Page 214 and 215:
FINAL CONSIDERATIONS AND PROSPECTS
- Page 216 and 217:
BIBLIOGRAPHY IX BIBLIOGRAPHY Albert
- Page 218 and 219:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Phosphatidylinositol 4
- Page 220 and 221:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Glaubitz, C., Grobner,
- Page 222 and 223:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Koehorst, R. B. M., Sp
- Page 224 and 225:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Mishra, V. K., Palguna
- Page 226 and 227:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Pluschke, G., Hirota,
- Page 228 and 229:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Sperotto, M. M., and M
- Page 230:
BIBLIOGRAPHY Williamson, I. M., Alv