Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives - CIMAP Staff - Central ...
Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives - CIMAP Staff - Central ...
Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives - CIMAP Staff - Central ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
754<br />
*<br />
NEGI ET AL.<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
HO<br />
OH<br />
HO<br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
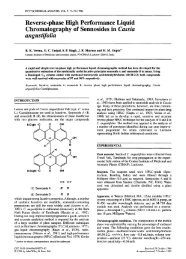
9: Demethoxy curcum<strong>in</strong> 10: Bisdemethoxy curcum<strong>in</strong><br />
Figure 7. Structures of other two curcum<strong>in</strong>oids found <strong>in</strong> C. longa.<br />
(ii) The hepatotoxic effects of ethanol are attributed to generation of hydroxyethyl radicals, which<br />
<strong>in</strong>duce lipid peroxidation. 74 The polyunsaturated fatty acids of cellular membranes are<br />
particularly susceptible to this oxidative attack lead<strong>in</strong>g to membrane lesions and loss of<br />
cellular homeostasis. Lipid peroxidation <strong>in</strong> liver slices was found to be doubled <strong>in</strong> presence of<br />
ethanol and curcum<strong>in</strong> reduced the condition significantly. Naik et al. 75 clearly po<strong>in</strong>ted out that<br />
curcum<strong>in</strong> mitigates the ethanol <strong>in</strong>duced liver cell damage by decreas<strong>in</strong>g lipid peroxidation.<br />
Presumably, curcum<strong>in</strong> functions as an antioxidant to scavenge free radicals. S<strong>in</strong>ce curcum<strong>in</strong><br />
also reduces H 2 O 2 <strong>in</strong>duced renal cell <strong>in</strong>jury 76 it seems to serve as an antioxidant <strong>in</strong> cells <strong>in</strong><br />
general.<br />
Also, the hepatoprotective activity aga<strong>in</strong>st alcohol <strong>in</strong>duced toxicity was assessed by monitor<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the changes <strong>in</strong> the serum enzyme levels of aspartate transm<strong>in</strong>ase (AST) and alkal<strong>in</strong>e phosphatase.<br />
77,78 The levels of serum lipids and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) <strong>in</strong><br />
alcoholic rats were also assessed (Table I). It was found that adm<strong>in</strong>istration of curcum<strong>in</strong> reduced the<br />
levels of serum lipids and TBARS due to either scaveng<strong>in</strong>g of peroxides and other activated oxygen<br />
species or neutralization of the free radicals. 79 Curcum<strong>in</strong> also showed antihepatotoxic activity aga<strong>in</strong>st<br />
paracetamol <strong>in</strong>duced liver toxicity <strong>in</strong> rats.<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong> is poorly absorbed from <strong>in</strong>test<strong>in</strong>e after oral adm<strong>in</strong>istration. It was shown that oral<br />
consumption of curcum<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> rats resulted <strong>in</strong> approximately 75% be<strong>in</strong>g excreted <strong>in</strong> the feces and<br />
only traces appeared <strong>in</strong> the ur<strong>in</strong>e. 80 Curcum<strong>in</strong> is biotransformed <strong>in</strong>to dihydrocurcum<strong>in</strong> and<br />
Table I. Activities of Serum AST, ALP and Levels of Serum Cholesterol, Phospholipids, Free Fatty<br />
Acids, and TBARS <strong>in</strong> Control, Alcohol and Alcohol þ Curcum<strong>in</strong> Treated Rats<br />
Parameter<br />
Group I<br />
Control<br />
(Sal<strong>in</strong>e 9.875g/kg)<br />
GroupIIa<br />
25% Aqueous alcohol<br />
(9.875g/kg)<br />
AST (U/L) 8.2±1.6 57.8±4.11 35.4±1.85<br />
ALP (U/L) 123.6±5.31 185±5.21 141.4±2.8<br />
Cholesterol (mg/100<br />
mL of serum)<br />
Phospholipids<br />
(mg/100 mL of<br />
serum)<br />
Free fatty acids<br />
(mg/100 mL of<br />
serum)<br />
Group IIb<br />
25% Aqueous alcohol<br />
+curcum<strong>in</strong> (80mg/kg)<br />
101±10.04 183.33±8.29 145.33±7.45<br />
98.12±10.87 163.52±8.656 134.15±7.45<br />
82.38±5.4 169.44±8.48 123.23±7.61<br />
TBARS<br />
1.336±0.206 3.428±0.371 2.06±0.06<br />
(nmol/ mL of serum)<br />
Groups IIa and IIb compared with group I p