Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives - CIMAP Staff - Central ...
Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives - CIMAP Staff - Central ...
Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives - CIMAP Staff - Central ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
RECENT ADVANCES IN PLANT HEPATOPROTECTIVES<br />
*<br />
755<br />
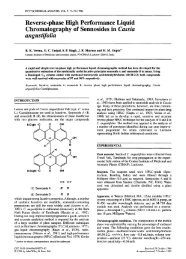
tetrahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong>, which are further converted to monoglucuronide conjugates 81 to tetrahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong><br />
and hexahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> human and rodents (Fig. 8). 82<br />
D. Mode of Action<br />
It is believed that the hepatoprotective activity of curcum<strong>in</strong> is due to its antioxidant activity which is<br />
comparable to vitam<strong>in</strong>s C and E. 83,84 Curcum<strong>in</strong> was demonstrated as a potent scavenger of a variety<br />
of reactive oxygen species <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g superoxide anion radicals, hydroxy radicals, 85 nitrogen dioxide<br />
radicals 86 , s<strong>in</strong>glet oxygen, etc. 87 Curcum<strong>in</strong> exhibited potent <strong>in</strong>hibitory activity aga<strong>in</strong>st P450 <strong>in</strong> rat<br />
liver. 88 One of its metabolites, tetrahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong> was found to have better protective effect when<br />
compared with silymar<strong>in</strong>. 89 The hydroxyl and the methoxyl groups of phenyl r<strong>in</strong>g and the 1,3-diketo<br />
systems are important structural features to contribute to these effects. Further, the antioxidant<br />
activity <strong>in</strong>creases when the phenolic hydroxyl is at ortho to the methoxyl group. Based on bond<br />
dissociation enthalpies us<strong>in</strong>g density function theory (DFT), it has been understood that the<br />
antioxidant mechanism of curcum<strong>in</strong> is due to hydrogen atom abstraction from the phenolic group and<br />
not from the central methylene group <strong>in</strong> the heptadienone l<strong>in</strong>k. 90<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O 3 SO<br />
OMe<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong> sulphate<br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
COO<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong> glucuronide<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
HO<br />
OMe<br />
Curcum<strong>in</strong><br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
HO<br />
OMe<br />
Tetrahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong><br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
HO<br />
OMe<br />
Hexahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong><br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
HO<br />
OH<br />
OMe<br />
OMe<br />
Hexahydrocurcum<strong>in</strong>ol<br />
Medic<strong>in</strong>al Research Reviews DOI 10.1002/med<br />
Figure 8. Major metabolites of curcum<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> rodents and humans.