Chapter 15 Urinary System
Chapter 15 Urinary System
Chapter 15 Urinary System
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Chapter</strong> <strong>15</strong><br />
<strong>Urinary</strong> <strong>System</strong><br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> Objectives<br />
Upon completion of the chapter the participant will be able to:<br />
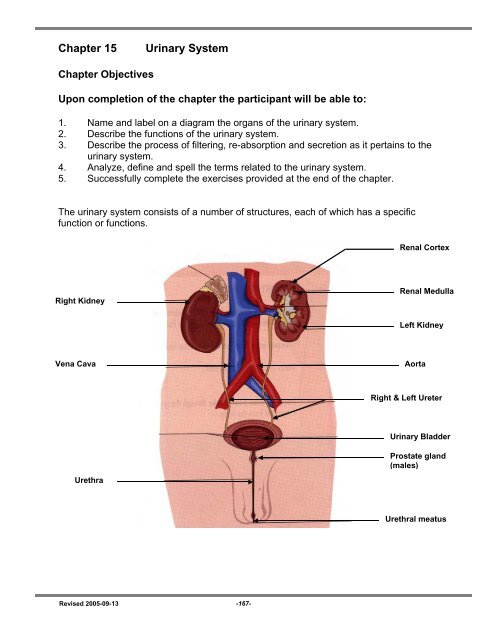
1. Name and label on a diagram the organs of the urinary system.<br />
2. Describe the functions of the urinary system.<br />
3. Describe the process of filtering, re-absorption and secretion as it pertains to the<br />
urinary system.<br />
4. Analyze, define and spell the terms related to the urinary system.<br />
5. Successfully complete the exercises provided at the end of the chapter.<br />
The urinary system consists of a number of structures, each of which has a specific<br />
function or functions.<br />
Renal Cortex<br />
Right Kidney<br />
Renal Medulla<br />
Left Kidney<br />
Vena Cava<br />
Aorta<br />
Right & Left Ureter<br />
<strong>Urinary</strong> Bladder<br />
Prostate gland<br />
(males)<br />
Urethra<br />
Urethral meatus<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -167-
The components are:<br />
‣ Kidneys<br />
‣ Ureters<br />
‣ <strong>Urinary</strong> bladder<br />
‣ Urethra<br />
Kidneys (ren/o, nephr/o)<br />
‣ Bean shaped, fist sized organs that lie on either side of the lumbar spine.<br />
‣ Their position is retroperitoneal which means they lie behind the peritoneal<br />
membrane.<br />
‣ Each kidney is covered with tissue that is referred to as the renal capsule.<br />
‣ Under the capsule layer is the renal cortex (cortic/o) and below that is the renal<br />
medulla (medull/o)<br />
‣ Blood flows into each kidney through the renal artery and out of the kidney<br />
through renal vein.<br />
Cortex<br />
Pyramids of<br />
Medulla<br />
Renal Pelvis<br />
Ureter<br />
Capsule<br />
‣ While the blood is going through the kidney fluid and elements can be<br />
reabsorbed and the remaining product forms urine to be eliminated from the<br />
body.<br />
‣ The functioning unit of the kidney is the nephron and that is the area where all<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -168-
the filtering occurs. An important part of the nephron is the glomerulus<br />
(glomerul/o). It is here that you find all the small capillaries that allows<br />
substances to move back and forth through the thin membrane.<br />
‣ Urine that is to be secreted by the kidneys is stored in the renal pelvis (pyel/o).<br />
Ureters (ureter/o)<br />
‣ Narrow tubes that connect the kidney with the bladder. Urine is moved along<br />
each tube by peristalsis. This is the same muscle activity that moves food<br />
through the digestive system.<br />
<strong>Urinary</strong> Bladder (cyst/o, vesic/o)<br />
‣ A hollow muscular organ that acts as a reservoir for urine until it is to be<br />
eliminated from the body.<br />
‣ When the bladder has a sufficient amount of urine present in it, the muscle fibers<br />
in the walls will contract giving you the urge to go to the bathroom. This process<br />
of passing urine is referred to as micturition.<br />
‣ The end of the bladder has a sphincter that holds the urine in the bladder until<br />
there is an adequate amount present for elimination.<br />
Urethra (urethr/o)<br />
‣ A tube which extends from the lower end of the bladder to the outside of the<br />
body.<br />
‣ The external end of the urethra is referred to as the urethral meatus (meat/o)<br />
‣ The male urethra is approximately 8 inches long while the female is 1.5 inches.<br />
‣ In males the neck of the urethra is surrounded by one of the reproductive glands,<br />
the prostate gland. This was discussed in the previous chapter.<br />
Urine Production in the Kidney<br />
In each kidney are about one million nephrons. These structures are responsible for<br />
producing urine. In general terms they do this by filtering out excess electrolytes and<br />
waste products from the blood. This is done by the network of capillaries contained in<br />
the glomerulus. The capillary walls allow water, electrolytes and waste products to<br />
leave the blood and enter Bowman’s Capsule which surrounds the glomerulus.<br />
The filtrate then moves through the long system of twisted tubes called the renal<br />
tubules. As the filtrate moves through the tubes there is a constant exchange of<br />
substances occurring. When the end of the tubules is reached the remaining solution is<br />
urine (ur/o).<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -169-
Word Parts for the <strong>Urinary</strong> <strong>System</strong><br />
Roots<br />
‣ calic/o, calyc/o<br />
‣ catheter/o<br />
‣ corpor/o<br />
‣ cortic/o<br />
‣ cyst/o, vesic/o<br />
‣ glomerul/o<br />
‣ lith/o<br />
‣ meat/o<br />
‣ medull/o<br />
‣ nephr/o, ren/o<br />
‣ olig/o<br />
‣ py/o<br />
‣ pyel/o<br />
‣ spad/o<br />
‣ ureter/o<br />
‣ urethr/o<br />
‣ urin/o, ur/o<br />
calyx, calyx<br />
something inserted<br />
body<br />
cortex, outer layer<br />
bladder<br />
glomerulus<br />
stone<br />
opening, passageway<br />
middle or inner portion<br />
kidney<br />
scanty, few<br />
pus<br />
renal pelvis<br />
draw off<br />
ureter<br />
urethra<br />
urine, urinary organs<br />
Suffixes<br />
‣ -cele<br />
‣ -chrome<br />
‣ -ectasis<br />
‣ -emia<br />
‣ -lithasis<br />
‣ -osis, -pathy<br />
‣ -pexy<br />
‣ -ptosis<br />
‣ -lysis<br />
‣ -tripsy<br />
‣ -uria<br />
hernia<br />
color<br />
enlargement, stretching<br />
blood<br />
presence of stones<br />
abnormal condition, disease<br />
surgical fixation<br />
drooping, dropping down<br />
breakdown, destruction<br />
crush<br />
urine, urination<br />
Prefixes<br />
‣ an-<br />
‣ epi-<br />
‣ in-<br />
‣ para-<br />
‣ poly-<br />
‣ retro-<br />
without<br />
upper, above<br />
no, not<br />
beside<br />
many<br />
backward<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -170-
Term Analysis and Definition<br />
Word Part Term Term Analysis Definition<br />
calic/o,<br />
calyc/o<br />
caliceal<br />
calic = calyx<br />
-eal = pertaining to<br />
Pertaining to the calices of the<br />
kidney<br />
catheter/o catheterization catheter =<br />
something inserted<br />
-ion = process<br />
corpor/o extracorporeal corpor = body<br />
extra = outside<br />
-eal = pertaining to<br />
Cortic/o cortical cortic = cortex, outer<br />
layer<br />
-al = pertaining to<br />
Process of inserting a tube into<br />
a body cavity, like the bladder,<br />
to remove fluid<br />
Pertaining to outside the body<br />
Pertaining to the outer layer of<br />
the kidney.<br />
cyst/o<br />
vesic/o<br />
cystitis<br />
cyst = bladder<br />
-itis = inflammation<br />
Inflammation of the bladder<br />
cystoscope<br />
-scope = instrument<br />
used to visually<br />
examine<br />
Instrument used to visually<br />
examine the bladder<br />
vesicoureteral<br />
vesic = bladder<br />
ureter = ureter<br />
-al = pertaining to<br />
Pertaining to the bladder and<br />
ureters.<br />
glomerul/o<br />
Glomerulonephritis<br />
glomerul =<br />
glomerulus<br />
nephr = kidney<br />
-itis = inflammation<br />
Inflammation of the glomerulus<br />
of the kidney<br />
glomerulosclerosis<br />
-sclerosis =<br />
hardening<br />
Hardening of the glomerulus<br />
lith/o lithotripsy lith = stone<br />
-tripsy = crushing<br />
meat/o meatotomy meat = meatus<br />
-tomy = process of<br />
cutting<br />
medull/o medullary medull = medulla<br />
-ary = pertaining to<br />
Crushing of kidney stones<br />
using sound waves<br />
Process of cutting into the<br />
urinary meatus<br />
Pertaining to the medulla<br />
nephr/o,<br />
ren/o<br />
nephrolithiasis<br />
nephr = kidney<br />
-iasis = condition<br />
lith = stones<br />
Kidney stones<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -171-
Word Part Term Term Analysis Definition<br />
nephrolithotomy<br />
-tomy = Surgical<br />
incision<br />
Process of removing stones<br />
through a surgical incision into<br />
the kidney<br />
nephropathy<br />
-pathy = disease<br />
Disease of the kidney<br />
nephropexy<br />
-pexy = surgical<br />
fixation<br />
Surgical fixation of the kidney<br />
nephroptosis<br />
-ptosis = drooping<br />
Drooping of the kidney<br />
hydronephrosis<br />
hydro = water<br />
-osis = condition<br />
Conition where there is<br />
accumulation of fluid in the<br />
kidney<br />
nephroblastoma<br />
-blast = immature<br />
-oma = tumor<br />
Tumor of the kidney made up<br />
of underdeveloped material<br />
renal<br />
ren = kidney<br />
-al = pertaining to<br />
Pertaining to the kidneys<br />
pyel/o<br />
pyelogram<br />
pyel = renal pelvis<br />
-gram = record<br />
Record of the ureter and<br />
kidney, particularly the renal<br />
pelvis<br />
pyelonephritis<br />
nephr = kidney<br />
-itis = inflammation<br />
Inflammation of the kidney and<br />
the renal pelvis<br />
ureter/o<br />
ureteral<br />
ureter = ureter<br />
-al = pertaining to<br />
Pertaining to the ureter<br />
ureterectasis<br />
-ectasis = stretching<br />
Stretching of the ureter<br />
ureterostenosis<br />
-stenosis =<br />
narrowing<br />
Narrowing of the ureter<br />
ureterostomy<br />
-stomy = permanent<br />
new opening<br />
Creation of a permanent new<br />
opening into the ureter<br />
urethr/o<br />
Cystourethrography<br />
cysto = bladder<br />
urethr = urethra<br />
-graphy = process<br />
of recording<br />
Process of recording an image<br />
of the bladder and urethra<br />
using X-Ray<br />
transurethral<br />
trans = across<br />
-al = pertaining to<br />
Performed across or through<br />
the urethra<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -172-
Word Part Term Term Analysis Definition<br />
utethroplasty -plasty = surgical Surgical repair of the urethra<br />
repair<br />
urin/o urinary urin = urine<br />
-ary = pertaining to<br />
Pertaining to urine<br />
ur/o<br />
uremia<br />
ur = urinary tract,<br />
urine, urination<br />
-emia = blood<br />
Accumulation of urine in the<br />
blood because of kidney<br />
dysfunction<br />
urogram<br />
-gram = record<br />
Record of the urinary tract<br />
urologist<br />
-logist = one who<br />
specializes<br />
One who specializes in the<br />
urinary system<br />
-lysis<br />
dialysis<br />
dia = through<br />
-lysis = separate,<br />
breakdown<br />
Mechanical replacement of<br />
kidney function with a machine.<br />
Blood passes through the<br />
machine and the waste<br />
products are separated out and<br />
the blood returns to the patient.<br />
urinalysis<br />
urin = urine<br />
-lysis = apart<br />
Laboratory test analysis of<br />
urine<br />
-uria<br />
anuria<br />
an = no, lack of<br />
-uria = urine,<br />
urination<br />
No urine formation<br />
bacteriuria<br />
bacteri = bacteria<br />
Bacteria in the urine<br />
dysuria<br />
dys = painful,<br />
difficult<br />
Painful urination<br />
hematuria<br />
hemat = blood<br />
Blood in the urine<br />
nocturia<br />
noct = night<br />
Frequent urination at night<br />
oliguria<br />
pyuria<br />
oligo = deficient,<br />
scanty<br />
py = pus<br />
Decreased urination<br />
Pus in the urine<br />
in-<br />
incontinence<br />
in = no, not<br />
-continence = to<br />
stop<br />
No control of excretion<br />
functions such as urination<br />
poly- polyuria poly = many<br />
-uria = urine<br />
Excretion of large amounts of<br />
urine<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -173-
Word Part Term Term Analysis Definition<br />
Abbreviations:<br />
polycystic<br />
kidneys<br />
cyst = sac<br />
-ic = pertaining to<br />
Pertaining to kidneys with<br />
many cysts.<br />
ADH:<br />
BUN:<br />
CRF:<br />
C and S:<br />
ECSL:<br />
ESWL:<br />
GU:<br />
H 2 O:<br />
I and O:<br />
IVP:<br />
KUB:<br />
UTI:<br />
antidiuretic hormone<br />
blood urea nitrogen<br />
chronic renal failure<br />
culture and sensitivity<br />
extracorporeal shockwave lithotriptor<br />
extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy<br />
genitourinary<br />
water<br />
intake and output<br />
intravenous pyelogram<br />
kidney, ureter, bladder<br />
urinary tract infection<br />
Revised 2005-09-13 -174-