Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Biology I (submitted
Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Biology I (submitted Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Biology I (submitted
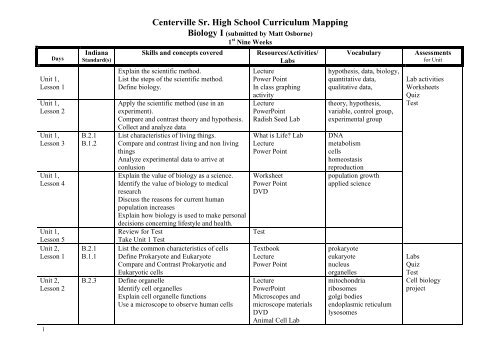
Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Biology I (submitted by Matt Osborne) 1 st Nine Weeks 1 Days Unit 1, Lesson 1 Unit 1, Lesson 2 Unit 1, Lesson 3 Unit 1, Lesson 4 Unit 1, Lesson 5 Unit 2, Lesson 1 Unit 2, Lesson 2 Indiana Standard(s) B.2.1 B.1.2 B.2.1 B.1.1 B.2.3 Skills and concepts covered Explain the scientific method. List the steps of the scientific method. Define biology. Apply the scientific method (use in an experiment). Compare and contrast theory and hypothesis. Collect and analyze data List characteristics of living things. Compare and contrast living and non living things Analyze experimental data to arrive at conlusion Explain the value of biology as a science. Identify the value of biology to medical research Discuss the reasons for current human population increases Explain how biology is used to make personal decisions concerning lifestyle and health. Review for Test Take Unit 1 Test List the common characteristics of cells Define Prokaryote and Eukaryote Compare and Contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Define organelle Identify cell organelles Explain cell organelle functions Use a microscope to observe human cells Resources/Activities/ Labs Lecture Power Point In class graphing activity Lecture PowerPoint Radish Seed Lab What is Life? Lab Lecture Power Point Worksheet Power Point DVD Test Textbook Lecture Power Point Lecture PowerPoint Microscopes and microscope materials DVD Animal Cell Lab Vocabulary hypothesis, data, biology, quantitative data, qualitative data, theory, hypothesis, variable, control group, experimental group DNA metabolism cells homeostasis reproduction population growth applied science prokaryote eukaryote nucleus organelles mitochondria ribosomes golgi bodies endoplasmic reticulum lysosomes Assessments for Unit Lab activities Worksheets Quiz Test Labs Quiz Test Cell biology project
- Page 2 and 3: Unit 2, Lesson 3 Unit 2, Lesson 4 U
- Page 4 and 5: Centerville Sr. High School Curricu
- Page 6 and 7: Unit 6, Lesson 2 Unit 6, Lesson 3 U
- Page 8 and 9: Unit 8, Lesson 3 Unit 8, Lesson 4 U
- Page 10 and 11: Biology I (submitted by Matt Osborn
- Page 12: Unit 12, Lesson 6 B.4.2 Describe th
<strong>Centerville</strong> <strong>Sr</strong>. <strong>High</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Mapping</strong><br />
<strong>Biology</strong> I (<strong>submitted</strong> by Matt Osborne)<br />
1 st Nine Weeks<br />
1<br />
Days<br />
Unit 1,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 1,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Unit 1,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 1,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 1,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 2,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 2,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Indiana<br />
Standard(s)<br />
B.2.1<br />
B.1.2<br />
B.2.1<br />
B.1.1<br />
B.2.3<br />
Skills and concepts covered<br />
Explain the scientific method.<br />
List the steps of the scientific method.<br />
Define biology.<br />
Apply the scientific method (use in an<br />
experiment).<br />
Compare and contrast theory and hypothesis.<br />
Collect and analyze data<br />
List characteristics of living things.<br />
Compare and contrast living and non living<br />
things<br />
Analyze experimental data to arrive at<br />
conlusion<br />
Explain the value of biology as a science.<br />
Identify the value of biology to medical<br />
research<br />
Discuss the reasons for current human<br />
population increases<br />
Explain how biology is used to make personal<br />
decisions concerning lifestyle and health.<br />
Review for Test<br />
Take Unit 1 Test<br />
List the common characteristics of cells<br />
Define Prokaryote and Eukaryote<br />
Compare and Contrast Prokaryotic and<br />
Eukaryotic cells<br />
Define organelle<br />
Identify cell organelles<br />
Explain cell organelle functions<br />
Use a microscope to observe human cells<br />
Resources/Activities/<br />
Labs<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
In class graphing<br />
activity<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Radish Seed Lab<br />
What is Life? Lab<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
Worksheet<br />
Power Point<br />
DVD<br />
Test<br />
Textbook<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Microscopes and<br />
microscope materials<br />
DVD<br />
Animal Cell Lab<br />
Vocabulary<br />
hypothesis, data, biology,<br />
quantitative data,<br />
qualitative data,<br />
theory, hypothesis,<br />
variable, control group,<br />
experimental group<br />
DNA<br />
metabolism<br />
cells<br />
homeostasis<br />
reproduction<br />
population growth<br />
applied science<br />
prokaryote<br />
eukaryote<br />
nucleus<br />
organelles<br />
mitochondria<br />
ribosomes<br />
golgi bodies<br />
endoplasmic reticulum<br />
lysosomes<br />
Assessments<br />
for Unit<br />
Lab activities<br />
Worksheets<br />
Quiz<br />
Test<br />
Labs<br />
Quiz<br />
Test<br />
Cell biology<br />
project
Unit 2,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 2,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 2,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 2,<br />
Lesson 6<br />
Unit 3,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 3,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Unit 3,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
B.2.2<br />
B.2.6<br />
B.6.2<br />
B.1.3<br />
B.3.3<br />
B.3.1<br />
B.3.4<br />
B.3.5<br />
Define cell wall, chloroplast, and vacuole<br />
Identify features common to plant cells<br />
Compare and contrast plant and animal cells<br />
Discuss the importance of cell membranes<br />
Identify chemical features of cell membranes<br />
Explain the fucntions of cell membrane<br />
proteins<br />
Explain what is meant by cell diversity.<br />
Compare and contrast stem cells and<br />
specialized cells<br />
List the levels of organization in animal<br />
biology<br />
Project Presentations<br />
Unit Test<br />
Define metabolism<br />
Explain the role of ATP in cellular respiration<br />
Describe how ATP is used within cells<br />
Compare ATP to a rechargeable battery<br />
Define photosysnthesis<br />
Put the steps of photosynthesis in order<br />
Identify trophic levels in a food chain<br />
Compare and contrast food chains and food<br />
webs<br />
Identify producers, consumers, and<br />
decomposers in a food web<br />
Explain the flow of energy in a food chain<br />
Identify the source of energy for food chains<br />
Argue the importance of the sun for all life on<br />
planet Earth<br />
Make a food chain consisting of 5 trophic<br />
levels<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Microscopes and<br />
microscope materials<br />
DVD<br />
Plant Cell Lab<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Microscopes and<br />
microscope materials<br />
DVD<br />
Pond Water Lab<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Microscopes and<br />
microscope materials<br />
DVD<br />
Virtual Cell Internet Lab<br />
Student projects<br />
Unit Test<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
Internet website<br />
animation<br />
Photosynthesis Lab<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
Food web activity<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
cell wall<br />
chloroplast<br />
vacuole<br />
cell membrane<br />
lipids<br />
channel proteins<br />
diffusion<br />
marker proteins<br />
stem cell<br />
cell specialization<br />
tissue<br />
organ<br />
organ systems<br />
metabolism<br />
ATP<br />
ADP<br />
photosynthesis<br />
autotroph<br />
heterotroph<br />
food chain<br />
food web<br />
food pyramid<br />
autotroph<br />
heterotroph<br />
food chain, web, and<br />
pyramid<br />
Labs<br />
Quiz<br />
Test:<br />
Cell biology<br />
project<br />
Internet Activity<br />
Labs<br />
Quiz<br />
Worksheet<br />
2
Unit 3,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 3,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 3,<br />
Lesson 6<br />
B.3.2<br />
Write the equation for anaerobic respiration.<br />
List the end products of anaerobic respiration.<br />
Define fermentation.<br />
Compare and contrast lactic acid and<br />
alcoholic fermentation.<br />
Identify common products produced thru<br />
fermentation<br />
Write the equation for aerobic cellular<br />
respiration.<br />
Explain the role of mitochondria in cellular<br />
respiration.<br />
Make a chart showing the differences<br />
between aerobic and anaerobic respiration<br />
Describe the physiological events that occur<br />
in oxygen debt<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Fermentation lab<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
Quiz<br />
Bromothymol blue<br />
demonstration<br />
DVD<br />
Burning peanut<br />
demonstration<br />
worksheet<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test<br />
anaerobic respiration<br />
fermentation<br />
lactic acid<br />
alcohol<br />
aerobic respiration<br />
mitochondria<br />
oxygen debt<br />
Kreb’s cycle<br />
Internet Activity<br />
Labs<br />
Quiz<br />
Worksheet<br />
Unit Test<br />
3
<strong>Centerville</strong> <strong>Sr</strong>. <strong>High</strong> <strong>School</strong> <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Mapping</strong><br />
<strong>Biology</strong> I (<strong>submitted</strong> by Matt Osborne)<br />
2 nd Nine Weeks<br />
Days<br />
Unit 4,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 4,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Indiana<br />
Standard(s)<br />
B.6.1<br />
B.6.1<br />
B.6.2<br />
Skills and concepts covered<br />
Explain why cell division is necessary for<br />
living things.<br />
Relate cell division to growth and repair in<br />
animal bodies.<br />
List the steps of the cell cycle.<br />
Explain how surface-to-volume ratio relates<br />
to the idea that cells must stay small.<br />
Define mitosis.<br />
List the steps of mitosis.<br />
Identify the steps of mitosis<br />
Explain the behavior of chromosomes during<br />
mitosis<br />
Resources/Activities/<br />
Labs<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Computer Lab Tutorial:<br />
Cell Size<br />
Lab: Mitosis in Action<br />
Classroom models of<br />
mitotic cells<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Vocabulary<br />
cell cycle<br />
asexual reproduction<br />
sexual reproduction<br />
surface to volume ration<br />
chromosome<br />
centrioles<br />
spindle fiber<br />
chromosome number<br />
Assessments<br />
for Unit<br />
Lab activities<br />
Worksheets<br />
Quiz<br />
Test: Cell<br />
Division<br />
DVD worksheets<br />
Unit 4,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 4,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 4,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.7.5<br />
B.6.4<br />
B.6.3<br />
Observe the relationship between<br />
chromosome number and species identity<br />
Define cancer<br />
List behavioral, environmental, and genetic<br />
causes of cancer<br />
Compare and contrast the causes of cancer<br />
Define meiosis.<br />
List the steps of meiosis.<br />
Identify the steps of meiosis.<br />
Explain why meiosis is essential for sexually<br />
reproducing species<br />
Explain the events that take place during<br />
fertilization.<br />
Compare and contrast the male gamete with<br />
the female gamete.<br />
Compare and contrast identical and fraternal<br />
twins<br />
Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis<br />
Take Unit 4 Test<br />
DVD, Chromosomes<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
DVD, Meiosis<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Lab: Meiosis in Action<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
cancer<br />
carcinogen<br />
benign<br />
malignant<br />
metastasis<br />
meiosis<br />
haploid<br />
diploid<br />
gamete<br />
fertilization<br />
zygote<br />
fraternal twins<br />
identical twins<br />
4
Unit 5,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 5,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Unit 5,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 5,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 5,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
B.5.1<br />
B.5.2<br />
B.7.1<br />
B.7.2<br />
B.7.3<br />
B.7.2<br />
B.7.3<br />
B.7.3<br />
B.7.3<br />
Define gene.<br />
Explain the relationship between genes and<br />
chromosomes.<br />
Give a brief biography of Gregor Mendel.<br />
Describe Mendel’s Law of Dominance.<br />
Define allele.<br />
Compare and contrast dominant and recessive<br />
alleles.<br />
Describe Mendel’s Law of Segregation<br />
Define homozygous, heterozygous, genotype<br />
and phenotype.<br />
Compare and contrast homozygous and<br />
heterozygous.<br />
Compare and contrast genotype and<br />
phenotype.<br />
Describe Mendel’s Law of Independent<br />
Assortment.<br />
Explain the concept of homologous<br />
chromosomes.<br />
Explain the following modes of inheritance:<br />
codominance, incomplete dominance,<br />
polygenic inheritance.<br />
Give examples of traits inherited through<br />
codominance, incomplete dominance, and<br />
polygenic inheritance.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Pea Plant Crosses--A<br />
Demonstration<br />
Human Genetics Traits<br />
Lab<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Pea Plant Crosses--A<br />
Demonstration<br />
Computer Software:<br />
Pea Plant Cross<br />
Simulation<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Pea Plant Crosses--A<br />
Demonstration<br />
Computer Software:<br />
Pea Plant Cross<br />
Simulation<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Lab: Other modes of<br />
inheritance.<br />
gene<br />
allele<br />
chromosome<br />
allele<br />
dominant<br />
recessive<br />
Law of Dominance<br />
homozygous<br />
heterozygous<br />
genotype<br />
phenotype<br />
Law of Independent<br />
Segregation<br />
homologous<br />
chromosomes<br />
codominance<br />
incomplete dominance<br />
polygenic inheritance<br />
Labs<br />
Computer Lab<br />
Reports<br />
Quiz<br />
Test:<br />
Mendelian<br />
genetics<br />
Unit 5,<br />
Lesson 6<br />
Unit 6,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
5<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.7.5<br />
Review<br />
Unit 5 Test<br />
Identify the number of chromosomes in<br />
human body cells and gametes.<br />
Compare and contrast autosomes and sex<br />
chromosomes.<br />
Explain how sex chromosomes are inherited,<br />
and how sex chromosomes determine sex.<br />
Review game<br />
Unit Test<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
chromosomes<br />
gametes<br />
autosomes<br />
sex chromosomes<br />
Computer Lab<br />
Reports<br />
Labs<br />
Quiz<br />
Worksheet<br />
Unit 6 Test
Unit 6,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Unit 6,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 6,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 6,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 6,<br />
Lesson 6<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.7.5<br />
B.7.3<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.7.5<br />
B.7.3<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.7.5<br />
B.7.3<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.7.5<br />
Use a karyotype to diagnose genetic diseases.<br />
Explain the appearance of a karyotype for the<br />
following disorders: Down Syndrome,<br />
Klinefelter’s Syndrome, Turner Syndrome.<br />
Identify the relationship between Down<br />
Syndrome and maternal age.<br />
Explain the inheritance pattern for autosomal<br />
recessive disorders.<br />
List the general characteristics of cystic<br />
fibrosis, albinism, and sickle cell anemia<br />
Explain the inheritance pattern for autosomal<br />
dominant disorders.<br />
List the general characteristics of Marfan<br />
Syndrome and Huntington’s disease<br />
Explain the inheritance pattern for sex-linked<br />
disorders.<br />
List the general characteristics of colorblindness,<br />
hemophilia, muscular dystrophy<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Lab: Prepare a<br />
Karyotype<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Punnett Square<br />
worksheet<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Punnett Square<br />
worksheet<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Punnett Square<br />
worksheet<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test<br />
karyotype<br />
amniocentesis<br />
Down Syndrome<br />
Klinefelter Syndrome<br />
Turner Syndrome<br />
nondisjunciton<br />
autosomal recessive<br />
cystic fibrosis<br />
albinism<br />
sickle cell anemia<br />
autosomal dominant<br />
Marfan Syndrome<br />
Huntington’s disease<br />
sex-linked inheritance<br />
hemophilia<br />
muscular dystrophy<br />
Computer Lab<br />
Reports<br />
Labs<br />
Quiz<br />
Worksheet<br />
Unit 6 Test:<br />
Human Genetics<br />
6
<strong>Biology</strong> I (<strong>submitted</strong> by Matt Osborne)<br />
3 rd Nine Weeks<br />
Days<br />
Unit 7,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 7,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Indiana<br />
Standard(s)<br />
B.5.3<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.2.4<br />
B.5.5<br />
Skills and concepts covered<br />
Explain the structure and function of DNA<br />
Describe the general shape of molecular DNA<br />
Compare DNA to a twisted ladder.<br />
Build a model of DNA.<br />
Label a diagram of DNA.<br />
Explain the main events of DNA replication<br />
Compare DNA to a recipe book for proteins.<br />
Describe the main events of gene expression,<br />
namely transcription and translation<br />
Resources/Activities/<br />
Labs<br />
DNA model lab<br />
DVD worksheet<br />
Classroom<br />
Demonstration<br />
Worksheet<br />
Vocabulary<br />
DNA<br />
nucleotide<br />
DNA replication<br />
gene expression<br />
protein<br />
transcription<br />
translation<br />
Assessments<br />
for Unit<br />
Lab activities<br />
Worksheets<br />
DVD worksheets<br />
Quiz<br />
Test: Gene<br />
Expression<br />
DNA model<br />
projects<br />
Unit 7,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 7,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 7,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 8,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 8,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
B.2.5<br />
B.5.4<br />
B.5.6<br />
B.7.4<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.7.5<br />
Use the genetic code to determine the<br />
sequence of amino acids, given a sequence of<br />
DNA.<br />
Given a sequence of DNA, carry out the<br />
process of transcription and translation.<br />
Define mutation.<br />
Compare and contrast point and frameshift<br />
mutations.<br />
Explain how mutations affect physical traits.<br />
Identify several mutagens that increase the<br />
rate of mutation.<br />
Review, Project presentations<br />
Test<br />
Give a brief history of genetic engineering.<br />
Describe how genetic engineering today is<br />
different from genetic engineering in the past.<br />
Explain how bacteria can be genetically<br />
engineering to produce proteins<br />
Identify the steps involved in creating GM<br />
bacteria<br />
List several medicines produced by GMO’s<br />
Worksheet<br />
Lab: Creature Feature<br />
Colored Pencils.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Classroom Demo<br />
Worksheet<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit 7 Test<br />
DVD & worksheet<br />
Lecture<br />
Power Point<br />
Lab: Genetic<br />
Engineering<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
mRNA<br />
tRNA<br />
rRNA<br />
amino acids<br />
mutagen<br />
mutation<br />
point mutation<br />
frameshift mutation<br />
genetic engineering<br />
selective breeding<br />
GMO<br />
plasmid<br />
restriction enzyme<br />
gene splicing<br />
Computer Lab<br />
Unit Test<br />
worksheet<br />
7
Unit 8,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 8,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 8,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
B.7.5<br />
B.8.3<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.1<br />
B.8.3<br />
B.8.4<br />
B.8.7<br />
Explain how plants can be genetically<br />
modified with genetic engineering<br />
Define “golden rice”<br />
List several agriculture products improved<br />
with genetic engineering.<br />
Define genetic profiling.<br />
Define gene therapy.<br />
Explain how a DNA fingerprint is produced.<br />
Describe how DNA fingerprinting can be<br />
used in practice.<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Give a brief biography of Charles Darwin.<br />
Describe how scientists determine the age of<br />
rocks, fossils, and the Earth.<br />
Identify the major events in the evolution of<br />
life on planet Earth.<br />
Define fossil.<br />
Explain the conditions necessary for<br />
fossilization.<br />
Describe the relationship between fossils and<br />
sedimentary rocks.<br />
Define homologous structures, artificial<br />
selection, and vestigial traits.<br />
Explain how each of the above are evidence<br />
for evolution.<br />
Describe how DNA provides a record for<br />
evolutionary change.<br />
Lab: GM Cut & Paste<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Computer Lab: Gel<br />
Electrophoresis<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
worksheet<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test<br />
DVD & worksheet<br />
Lab: Evolution<br />
Timeline<br />
Lab: Fossils<br />
DVD & worksheet<br />
Lecture, PowerPoint<br />
Lab: Evidence for<br />
evolution<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
golden rice<br />
vector<br />
Gel Electrophoresis<br />
genetic profiling<br />
DNA fingerprint<br />
gene thereapy<br />
Charles Darwin<br />
radiometric dating<br />
evolution<br />
fossil<br />
sedimentary rock<br />
homologous structures<br />
artificial selection<br />
vestigial traits<br />
Computer Lab<br />
Unit Test<br />
worksheet<br />
Internet Activity<br />
Labs<br />
Quizzes<br />
DVD Worksheets<br />
Unit Test:<br />
Evolution<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
B.6.5<br />
B.8.1<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
Identify sources of genetic variation.<br />
Explain how genetic variation is produced.<br />
Observe genetic variation in a population.<br />
Discuss the role of genetic variation in<br />
evolution.<br />
Lab: Observing genetic<br />
variation<br />
Quiz<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
genetic variation<br />
sexual reproduction<br />
mutation<br />
crossing over<br />
8
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
B.8.2<br />
B.8.5<br />
Define natural selection.<br />
List the basic principles of natural selection.<br />
Explain the process of adaptation.<br />
Compare and contrast natural selection and<br />
acquired characteristics.<br />
DVD & worksheet<br />
Lab: Opposable<br />
Thumbs<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
natural selection<br />
survival of the fittest<br />
adaptation<br />
acquired charactersitics<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 6<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 7<br />
Unit 9,<br />
Lesson 8<br />
B.8.1<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.1<br />
B.8.5<br />
Identify several examples of natural selection<br />
in nature.<br />
Define camouflage, mimicry, sexual selection<br />
Define speciation.<br />
Explain the conditions that promote<br />
speciation.<br />
Observe several examples of speciation.<br />
Explain the genetic changes that occur in<br />
gene pools during speciation.<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Peppered Moth lab<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Computer Lab:<br />
Speciation<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Lab: Spoons<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test<br />
camouflage<br />
mimicry<br />
sexual selection<br />
directional selection<br />
stabilizing selection<br />
disruptive selection<br />
gene pool<br />
speciation<br />
reproductive isolation<br />
Internet Activity<br />
Labs<br />
Quizzes<br />
DVD Worksheets<br />
Unit Test:<br />
Evolution<br />
9
<strong>Biology</strong> I (<strong>submitted</strong> by Matt Osborne)<br />
4 th Nine Weeks<br />
Days<br />
Unit 10,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 10,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Indiana<br />
Standard(s)<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
Skills and concepts covered<br />
Define prokaryote.<br />
Explain how bacteria are different from<br />
eukaryotic cells.<br />
Describe the conditions necessary for bacteria<br />
growth.<br />
Define pathogen.<br />
Identify modes of transmission for pathogenic<br />
bacteria.<br />
List the characteristics of several bacterial<br />
diseases.<br />
Resources/Activities/<br />
Labs<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
Lab: Bacteria<br />
everywhere<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
DVD & Worksheet<br />
prokaryote<br />
bacteria<br />
Vocabulary<br />
pathogen<br />
modes of transmission<br />
Assessments<br />
for Unit<br />
Lab activities<br />
Worksheets<br />
DVD worksheets<br />
Quiz<br />
Test: Bacteria and<br />
Viruses<br />
Unit 10,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
Explain how bacteria are essential for<br />
ecosystem balance on Earth<br />
Perform proper hand washing technique<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Classroom Demonstr.<br />
asexual reproduction<br />
nitrogen fixation<br />
decomposition<br />
Unit 10,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
Define virus.<br />
Identify modes of transmission for pathogenic<br />
viruses.<br />
List the characteristics of several viral<br />
diseases.<br />
Sequence the steps of viral infection.<br />
Compare and contrast antibiotics and<br />
vaccination<br />
Lab: Viral lifecycle<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
virus<br />
lytic cycle<br />
antibiotic<br />
vaccination<br />
Unit 10,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test<br />
10
Unit 11,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 11,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
Unit 11,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
Define invertebrate.<br />
Identify invertebrate groups based on<br />
distinguishing characteristics.<br />
Compare and contrast the 3 phyla of worms.<br />
Compare and contrast the 3 phyla of<br />
mollusks.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worm Lab<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Squid Lab<br />
invertebrate<br />
bilateral symmetry<br />
cephalization<br />
open circulatory system<br />
worksheets<br />
quiz<br />
Labs<br />
Dissection<br />
Unit Test:<br />
Invertebrates<br />
Unit 11,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
Unit 11,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 1<br />
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 2<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
B.4.3<br />
Describe the shared characteristics of<br />
arthropods.<br />
Compare and contrast insects, crustaceans,<br />
spiders, centipedes and millipedes.<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Define vertebrate.<br />
Identify vertebrate groups based on<br />
distinguishing characteristics.<br />
Compare and contrast the 4 classes of fish.<br />
Discuss the evolution of modern fishes.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Insect Lab<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test: Invertebrates<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Worksheet<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Fish Lab<br />
segmentation<br />
exoskeleton<br />
chitin<br />
vertebrate<br />
ectothermic<br />
spawning<br />
introduced species<br />
Labs<br />
Quizzes<br />
Worksheets<br />
Unit Test:<br />
Vertebrate<br />
Animals<br />
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 3<br />
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 4<br />
B.4.1<br />
B.4.4<br />
B.8.5<br />
B.8.6<br />
B.8.7<br />
Describe the shared characteristics of<br />
amphibians.<br />
Discuss the evolution of modern amphibians.<br />
Describe the shared characteristics of reptiles.<br />
Discuss the evolution of modern reptiles.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Amphibian Activity<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Reptile Dissection<br />
amphibian<br />
metamorphosis<br />
limiting factor<br />
indicator species<br />
reptile<br />
amniotic egg<br />
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 5<br />
B.4.2<br />
Describe the shared characteristics of birds.<br />
Discuss the evolution of modern birds.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Bird Worksheet<br />
endothermic<br />
DDT<br />
11
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 6<br />
B.4.2<br />
Describe the shared characteristics of<br />
mammals.<br />
Discuss the evolution of modern mammals.<br />
Lecture<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Mammal Dissection<br />
mammal<br />
gestation<br />
lactation<br />
Unit 12,<br />
Lesson 7<br />
Review<br />
Unit Test<br />
Review Game<br />
Unit Test: Invertebrates<br />
12