Lecture notes for Introduction to Representation Theory
Lecture notes for Introduction to Representation Theory
Lecture notes for Introduction to Representation Theory
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
⇒<br />
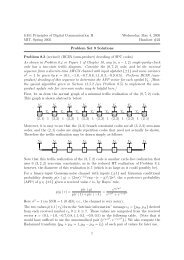
4.24.3 Principal series representations<br />
Let<br />
(the set of upper triangular matrices); then<br />
∼<br />
B → G, B = {<br />
0<br />
∼ }<br />
∼<br />
and<br />
|B| = (q − 1) 2 q,<br />
1 ∼<br />
[B, B] = U = { },<br />
0 1<br />
B/[B, B] ∪ = F ×<br />
q × F× q<br />
(the isomorphism maps an element of B <strong>to</strong> its two diagonal entries).<br />
Let<br />
∂ : B ⊃ C ×<br />
be a homomorphism defined by<br />
a b<br />
∂ = ∂ 1 (a)∂ 2 (c),<strong>for</strong> some pair of homomorphisms ∂ 1 , ∂ 2 : F × q ⊃ C × .<br />
0 c<br />
Define<br />
V 1 , 2<br />
= Ind G<br />
B C ,<br />
where C is the 1-dimensional representation of B in which B acts by ∂. We have<br />
dim(V 1 , 2<br />
) = |G| = q + 1.<br />
|B|<br />
Theorem 4.71.<br />
1. ∂ 1 = ⇒ ∂ 2 ≥ V 1 , 2<br />
is irreducible.<br />
2. ∂ 1 = ∂ 2 = µ ≥ V 1 , 2<br />
= C µ W µ , where W µ is a q-dimensional irreducible representation of<br />
G.<br />
3. W ∪<br />
∪<br />
1 , ⊗ {∂ ⊗ ⊗<br />
µ = W ξ if and only if µ = λ; V 1 , 2<br />
= V ⊗ if and only if {∂<br />
2<br />
1 , ∂ 2 } = 1 , ∂ 2 } (in the<br />
⊗ ⊗<br />
second case, ∂ 1 = ∂ 2 , ∂ = ∂ 2 ).<br />
Proof. From the Mackey <strong>for</strong>mula, we have<br />
1 ⇒<br />
1 <br />
tr V1 , 2<br />
(g) =<br />
∂(aga −1 ).<br />
|B|<br />
aG, aga −1 B<br />
If<br />
the expression on the right evaluates <strong>to</strong><br />
x 0<br />
<br />
g = ,<br />
0 x<br />
∂(g) |G| = ∂ 1 (x)∂ 2 (x) ⎩ q + 1 .<br />
|B|<br />
If<br />
x 1<br />
<br />
g = ,<br />
0 x<br />
71