PDF, 1536K - Measure DHS
PDF, 1536K - Measure DHS
PDF, 1536K - Measure DHS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ural women, women residing in the<br />
Benishangul-Gumuz and Gambela regions,<br />
and those with little or no education<br />
are more likely than others to believe<br />
that this information should be<br />
kept a secret. Similar patterns are observed<br />
for men by age and marital status,<br />
but in contrast to women, urban<br />
men and men with at least secondary<br />
education are more likely than their<br />
counterparts to oppose making this<br />
information public.<br />
About one in two women and<br />
men who have heard of AIDS<br />
(45 percent and 50 percent, respectively)<br />
are willing to care for relatives<br />
who are infected with the AIDS virus in<br />
their house (Table 12.7). Young respondents<br />
age 15-19, never-married<br />
respondents, urban residents, those<br />
living in Addis Ababa, and respondents<br />
with at least secondary education are<br />
more willing than others to care for<br />
relatives with HIV/AIDS in their house.<br />
Two additional questions on<br />
AIDS were asked of men who have<br />
heard of AIDS but not women. Men<br />
were asked whether they have ever<br />
been tested for AIDS, and if not,<br />
whether they would like to be tested.<br />
Overall, a very small percentage of men<br />
(2 percent) said that they have been<br />
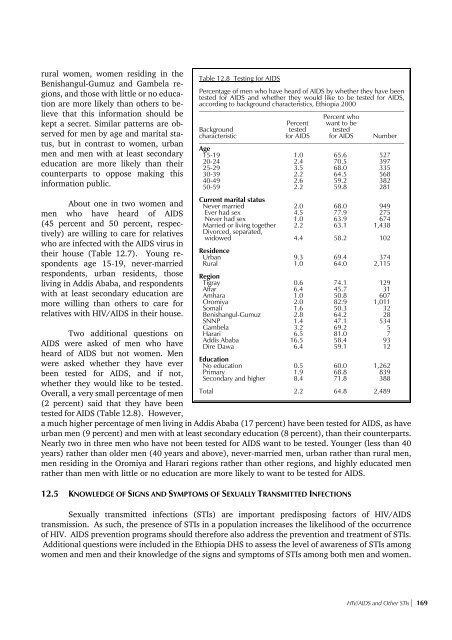
tested for AIDS (Table 12.8). However,<br />
Table 12.8 Testing for AIDS<br />
Percentage of men who have heard of AIDS by whether they have been<br />
tested for AIDS and whether they would like to be tested for AIDS,<br />
according to background characteristics, Ethiopia 2000<br />
____________________________________________________________<br />
Percent who<br />
Percent want to be<br />
Background tested tested<br />
characteristic for AIDS for AIDS Number<br />
____________________________________________________________<br />
Age<br />
15-19<br />
20-24<br />
25-29<br />
30-39<br />
40-49<br />
50-59<br />
Current marital status<br />
Never married<br />
Ever had sex<br />
Never had sex<br />
Married or living together<br />
Divorced, separated,<br />
widowed<br />
Residence<br />
Urban<br />
Rural<br />
Region<br />
Tigray<br />
Affar<br />
Amhara<br />
Oromiya<br />
Somali<br />
Benishangul-Gumuz<br />
SNNP<br />
Gambela<br />
Harari<br />
Addis Ababa<br />
Dire Dawa<br />
Education<br />
No education<br />
Primary<br />
Secondary and higher<br />
Total<br />
1.0 65.6 527<br />
2.4 70.5 397<br />
3.5 68.0 335<br />
2.2 64.5 568<br />
2.6 59.2 382<br />
2.2 59.8 281<br />
2.0 68.0 949<br />
4.5 77.9 275<br />
1.0 63.9 674<br />
2.2 63.1 1,438<br />
4.4 58.2 102<br />
9.3 69.4 374<br />
1.0 64.0 2,115<br />
0.6 74.1 129<br />
6.4 45.7 31<br />
1.0 50.8 607<br />
2.0 82.9 1,011<br />
1.6 50.3 32<br />
2.8 64.2 28<br />
1.4 47.1 534<br />
3.2 69.2 5<br />
6.5 81.0 7<br />
16.5 58.4 93<br />
6.4 59.1 12<br />
0.5 60.0 1,262<br />
1.9 68.8 839<br />
8.4 71.8 388<br />
2.2 64.8 2,489<br />
a much higher percentage of men living in Addis Ababa (17 percent) have been tested for AIDS, as have<br />
urban men (9 percent) and men with at least secondary education (8 percent), than their counterparts.<br />
Nearly two in three men who have not been tested for AIDS want to be tested. Younger (less than 40<br />
years) rather than older men (40 years and above), never-married men, urban rather than rural men,<br />
men residing in the Oromiya and Harari regions rather than other regions, and highly educated men<br />
rather than men with little or no education are more likely to want to be tested for AIDS.<br />
12.5 KNOWLEDGE OF SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS<br />
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are important predisposing factors of HIV/AIDS<br />
transmission. As such, the presence of STIs in a population increases the likelihood of the occurrence<br />
of HIV. AIDS prevention programs should therefore also address the prevention and treatment of STIs.<br />
Additional questions were included in the Ethiopia <strong>DHS</strong> to assess the level of awareness of STIs among<br />
women and men and their knowledge of the signs and symptoms of STIs among both men and women.<br />
HIV/AIDS and Other STIs* 169







![Obtaining Informed Consent for HIV Testing [QRS4] - Measure DHS](https://img.yumpu.com/49850117/1/190x245/obtaining-informed-consent-for-hiv-testing-qrs4-measure-dhs.jpg?quality=85)








