(best examples and good practices) on household organic waste ...
(best examples and good practices) on household organic waste ... (best examples and good practices) on household organic waste ...
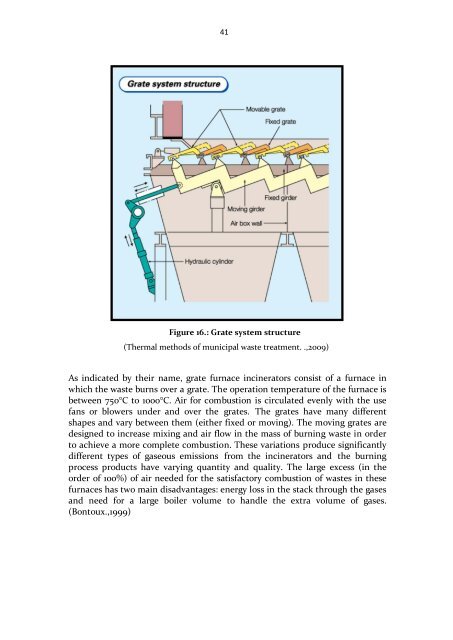
41 Figure 16.: Grate system structure (Thermal methods of municipal waste treatment. .,2009) As indicated by their name, grate furnace incinerators consist of a furnace in which the waste burns over a grate. The operation temperature of the furnace is between 750°C to 1000°C. Air for combustion is circulated evenly with the use fans or blowers under
42 Rotary kiln furnaces Rotary kiln waste incinerators (Figure 17.) are not so popular for the mass incineration of waste in Europe but are commonly used for the incineration of hazardous wastes. A rotary kiln rotates the waste in a cylindrical furnace in order to optimize mixing
- Page 1 and 2: National Technical University of At
- Page 3 and 4: 3.3.4. Landfill sy
- Page 5 and 6: 10.4.2.Susteren sewage treatment <s
- Page 7 and 8: Figure 44.: Västerås concept ....
- Page 9 and 10: Picture 30.: The heat exchanger sys
- Page 11 and 12: (Table 8.): The Ljungsjöverket pla
- Page 13 and 14: 2 1. Bio-WASTE MANAGEMENT LEGISLATI
- Page 15 and 16: 4 The Directive envisages the possi
- Page 17 and 18: 6 In the Commission's estimation, a
- Page 19 and 20: 8 of yard waste and</strong
- Page 21 and 22: 10 conditions (i.e., as brief as a
- Page 23 and 24: 12 Picture2.: View of machine used
- Page 25 and 26: 14 In-Vessel Composting Systems In
- Page 27 and 28: 16 The duration of the composting p
- Page 29 and 30: 18 Figure 7.: Principal emissions f
- Page 31 and 32: 20 2.2 Anaerobic Digestion (AD) 2.2
- Page 33 and 34: 22 4. Finally, methanogenic organis
- Page 35 and 36: 24 If the proper conditions cannot
- Page 37 and 38: 26 Considerations such as the desig
- Page 39 and 40: 28 to the viscosity of the feed, th
- Page 41 and 42: 30 The Netherlands
- Page 43 and 44: 32 Heavy metals in digestate usuall
- Page 45 and 46: 34 3. Large scale biodegradable was
- Page 47 and 48: 36 power and 1,200
- Page 49 and 50: 38 filtration or electrostatic prec
- Page 51: 40 acceptable range, but reduce the
- Page 55 and 56: 44 It has been processed an
- Page 57 and 58: 46 Heavy metals can be grouped into
- Page 59 and 60: 48 choices for a commercial plant w
- Page 61 and 62: 50 Gasification (Figure.19) using o
- Page 63 and 64: 52 AC plasma CO2 plasma arc Microwa
- Page 65 and 66: 54 pulled through an induced draft
- Page 67 and 68: 56 the non-biodegradables a
- Page 69 and 70: 58 3.3.8. Bioreactor land</
- Page 71 and 72: 60 4. Materials Sorting Processes 4
- Page 73 and 74: 62 Plastics Plastics (Fiqure.32) po
- Page 75 and 76: 64 separate containers. There are a
- Page 77 and 78: 66 The sorting of recyclables may b
- Page 79 and 80: 68 4.5. Mechanical and</str
- Page 81 and 82: 70 glass breakage on the tipping fl
- Page 83 and 84: 72 within solution under the influe
- Page 85 and 86: 74 material, and t
- Page 87 and 88: 76 changing pole configuration or w
- Page 89 and 90: 78 4.7. Mechanical Biological Treat
- Page 91 and 92: 80 Biological processing compartmen
- Page 93 and 94: 82 equivalence considerations <stro
- Page 95 and 96: 84 5.2. Waste streams considered in
- Page 97 and 98: 86 Figure 27.: Percentage of munici
- Page 99 and 100: 88 6.Italy The Italian strategy Ita
- Page 101 and 102: 90 Italy also set targets for colle
41<br />
Figure 16.: Grate system structure<br />
(Thermal methods of municipal <strong>waste</strong> treatment. .,2009)<br />
As indicated by their name, grate furnace incinerators c<strong>on</strong>sist of a furnace in<br />
which the <strong>waste</strong> burns over a grate. The operati<strong>on</strong> temperature of the furnace is<br />
between 750°C to 1000°C. Air for combusti<strong>on</strong> is circulated evenly with the use<br />
fans or blowers under <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> over the grates. The grates have many different<br />
shapes <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> vary between them (either fixed or moving). The moving grates are<br />
designed to increase mixing <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> air flow in the mass of burning <strong>waste</strong> in order<br />
to achieve a more complete combusti<strong>on</strong>. These variati<strong>on</strong>s produce significantly<br />
different types of gaseous emissi<strong>on</strong>s from the incinerators <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> the burning<br />
process products have varying quantity <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> quality. The large excess (in the<br />
order of 100%) of air needed for the satisfactory combusti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>waste</strong>s in these<br />
furnaces has two main disadvantages: energy loss in the stack through the gases<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> need for a large boiler volume to h<str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g>le the extra volume of gases.<br />
(B<strong>on</strong>toux.,1999)