Research Profile - Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy ...
Research Profile - Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy ...
Research Profile - Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Ruth Cameron<br />
Reader in Polymers <strong>and</strong> Medical <strong>Materials</strong><br />
MA University <strong>of</strong> Cambridge<br />
PhD University <strong>of</strong> Cambridge<br />
+44 (0) 1223 334324<br />
rec11@cam.ac.uk<br />
www.msm.cam.ac.uk/ccmm/<br />
Polymers <strong>and</strong> Medical <strong>Materials</strong><br />
My work within the Cambridge Centre for Medical <strong>Materials</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> the Pfizer Institute for Pharmaceutical <strong>Materials</strong> <strong>Science</strong><br />
focuses on materials which interact therapeutically with the<br />
body. <strong>Research</strong> is undertaken in both materials <strong>and</strong> cell-culture<br />
laboratories.<br />
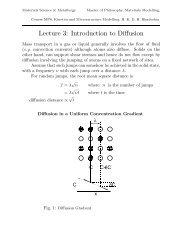
Biodegradable polymers <strong>and</strong> composites<br />
Resorbable polymers may be used in temporary load-bearing<br />
applications such as sutures <strong>and</strong> pins, in scaffolds for tissue<br />
engineering <strong>and</strong> in drug-delivery devices. We are exploring<br />
the complex temporal <strong>and</strong> spatial relationships between the<br />
processing <strong>and</strong> morphology <strong>of</strong> the polymer, the diffusion rates<br />
<strong>of</strong> water, drug <strong>and</strong> degradation products, the degradation rate <strong>of</strong><br />
the polymer <strong>and</strong> ultimate properties. An underst<strong>and</strong>ing <strong>of</strong> these<br />
factors allows informed device design. This work is extended into<br />
the study <strong>of</strong> composites with polymers <strong>and</strong> ceramics, ranging<br />
from the micro co-continuous to the nano-scale, for bone <strong>and</strong><br />
other tissue repair.<br />
Biostable implants<br />
We are researching materials <strong>and</strong> devices for applications<br />
in which the material must not change in the challenging<br />
environment <strong>of</strong> the body. Problems we are addressing include<br />
spinal-disc replacement <strong>and</strong> prostheses to engineer nerve repair.<br />
Drug delivery <strong>and</strong> pharmaceutics<br />
We are exploring issues relating to drug delivery to the body<br />
including drug polymorphism, tablet design <strong>and</strong> inhalation<br />
delivery systems.<br />
J Braunecker, M Baba, GE Milroy & RE Cameron, “The effects <strong>of</strong><br />
molecular weight <strong>and</strong> porosity on the degradation <strong>and</strong> drug release from<br />
polyglycolide” Int. J. Pharmaceutics 282, 19–34 (2004).<br />
JE Taylor, PR Laity, SS Wong, P Khunkamchoo, K Norris, J Hicks, AF<br />
Johnson & RE Cameron, “Iron pick-up efficiency in deferoxamine-coupled<br />
polyurethane dressings for treatment <strong>of</strong> chronic wounds” Biomater. 26,<br />
6024–6033 (2005).<br />
AC Renouf-Glauser, J Rose, DF Farrar & RE Cameron, “A comparison <strong>of</strong><br />
the degradation <strong>and</strong> deformation properties <strong>of</strong> a PLLA-lauric acid based<br />
family <strong>of</strong> biomaterials. Biomacromol. 7, 612–617 (2006).<br />
JS Capes & RE Cameron, “Effect <strong>of</strong> polymer addition on the contact line<br />
crystallisation <strong>of</strong> paracetamol” Cryst. Eng. Comm. 9, 84–90 (2007).<br />
Co-continuous resorbable polymer-ceramic<br />
composite for orthopaedic applications<br />
12 <strong>Research</strong> <strong>Pr<strong>of</strong>ile</strong>