Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Reference Manual<br />
If the mother’s HIV status is positive:<br />
• Take particular care not to suction the mouth <strong>and</strong> the nose unless it is absolutely<br />
necessary.<br />
• Consider swabbing the whole body of the baby with chlorhexidine (0.25%) swabs/wipes as<br />
recommended by the Ministry of Health.<br />
• Administer ARV prophylaxis (niverapine <strong>and</strong> AZT or others as recommended by the<br />
Ministry of Health).<br />
• Infant feeding options for mothers whose HIV status is positive include the following:<br />
o exclusive breastfeeding, taking care to avoid problems such as engorged breasts<br />
<strong>and</strong> sore nipples, until six months, followed by rapid switch to formula feeds <strong>and</strong><br />
complementary feeding with semi-solids.<br />
o use of expressed breast milk (EBM) rendered safe by flash heating of the milk (see<br />
below), continued with complementary feeds with semisolids from the age of six<br />
months (see chapter 11 on breastfeeding).<br />
o use of formula feeds with complementary feeds from birth with semi-solids from the<br />
age of six months. Formula feeds are applicable when replacement feeding is<br />
acceptable, feasible, affordable, sustainable, <strong>and</strong> safe (AFASS); avoidance of all<br />
breastfeeding by HIV-infected women is recommended. (WHO, 2009)<br />
• The actual type of feeding will depend on the mother’s choice. You as the health care<br />
provider should ensure that she is given the counseling <strong>and</strong> support she needs.<br />
• It is important to stress the dangers of “mixed” feeding (breast milk <strong>and</strong> formula).<br />
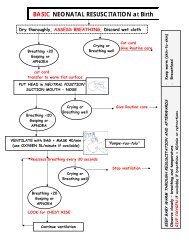
Table 5. Key Steps for Immediate <strong>Care</strong> of the <strong>Newborn</strong><br />
(The order may be changed according to the local needs, except for steps 1-3.)<br />
Step 1 Dry the baby <strong>and</strong> keep him/her warm by placing the baby on the mother’s<br />
abdomen.<br />
Step 2 Assess breathing. Make sure the baby is breathing well.<br />
Step 3 If the baby does not breathe, clamp/tie <strong>and</strong> cut the cord immediately <strong>and</strong> start<br />
resuscitation.<br />
If the baby does cry/breathes well, clamp/tie <strong>and</strong> cut the cord after pulsations<br />
stop or after 2-3 minutes.<br />
Step 4 Place the infant in skin-to-skin contact on the mother’s chest <strong>and</strong> cover both with<br />
clean linen <strong>and</strong> blanket as required. Carry out all the steps noted below up to #9,<br />
preferably with the baby on the mother’s chest.<br />
Step 5 Administer eye drops/eye ointment.<br />
Step 6 Administer vitamin K1.<br />
Step 7<br />
Step 8<br />
Step 9<br />
Step 10<br />
Note<br />
Place the baby identification b<strong>and</strong>s on the wrist <strong>and</strong> ankle.<br />
Initiate breastfeeding within the first hour.<br />
Select the appropriate method of feeding for the HIV-infected mother, based on<br />
informed choice.<br />
Weigh the infant when he/she is stable.<br />
Record observations <strong>and</strong> treatment provided in the registers/appropriate<br />
chart/cards.<br />
Defer the bath for at least six hours.<br />
Clean the newborn of an HIV-infected mother as recommended by the Ministry of<br />
Health.<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> maternal <strong>and</strong> newborn care<br />
<strong>Basic</strong> skills course<br />
61