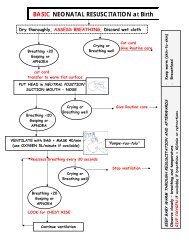
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
APPENDIX C: Glossary<br />
Active management of the third stage of labor (AMTSL): A combination of actions<br />
performed during the third stage of labor to prevent PPH. AMTSL speeds delivery of the<br />
placenta by increasing uterine contractions <strong>and</strong> prevents PPH by minimizing uterine<br />
atony. The components of AMTSL are:<br />
• Administration of a uterotonic drug within one minute after the baby is born (oxytocin is<br />
the uterotonic of choice) after verifying that there is no second baby.<br />
• Controlled cord traction (CCT).<br />
• Uterine massage immediately after delivery of the placenta.<br />
Controlled cord traction (CCT): Traction on the cord during a contraction combined<br />
with countertraction upward on the uterus with the provider’s h<strong>and</strong> placed immediately<br />
above the symphysis pubis. CCT facilitates expulsion of the placenta once it has<br />
separated from the uterine wall.<br />
Delayed cord clamping: Clamping the umbilical cord after cord pulsations have<br />
ceased. Studies show that delaying clamping <strong>and</strong> cutting of the umbilical cord is helpful<br />
to both full-term <strong>and</strong> preterm babies. In situations where cord clamping <strong>and</strong> cutting was<br />
delayed for preterm babies, these infants had higher hematocrit <strong>and</strong> hemoglobin levels<br />
<strong>and</strong> a lesser need for transfusions in the first 4 to 6 weeks of life than preterm babies<br />
whose cords were clamped <strong>and</strong> cut immediately after birth.<br />
Delayed PPH: Excessive vaginal bleeding (vaginal bleeding increases rather than<br />
decreases after delivery), occurring more than 24 hours after childbirth.<br />
Immediate PPH: Vaginal bleeding in excess of 500 mL, occurring less than 24 hours<br />
after childbirth.<br />
Immediate postpartum period: See fourth stage of labor.<br />
Infant mortality rate: Number of deaths during the first year of life, expressed per 1000<br />
live births.<br />
Live birth: A baby who is born alive as indicated by the baby moving, crying, breathing, having<br />
heart beats, or showing cord pulsations.<br />
Low birth weight infant: A newborn weighing less than 2500 grams at birth. A low birth weight<br />
infant (LBW) may be preterm, with or without intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), or full term,<br />
or post term with IUGR.<br />
Neonatal mortality rate: Number of newborn deaths during the first 28 days of life, expressed<br />
per 1000 live births.<br />
Neonatal period: This period commences at birth <strong>and</strong> ends at 28 completed days of life. The<br />
neonatal period is divided into two parts: the early neonatal period extends from day 1 to 7<br />
completed days; the late neonatal period extends from day 8 to 28 completed days.<br />
Perinatal mortality rate: The number of stillbirths <strong>and</strong> deaths in the first week of life, expressed<br />
per 1000 live plus stillbirths.<br />
Perinatal period: This period extends from the 22d week of gestation to the end of the first<br />
week of life (7 completed days). In some developing countries, authorities feel that since<br />
168<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> maternal <strong>and</strong> newborn care<br />
<strong>Basic</strong> skills course