Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Reference Manual<br />
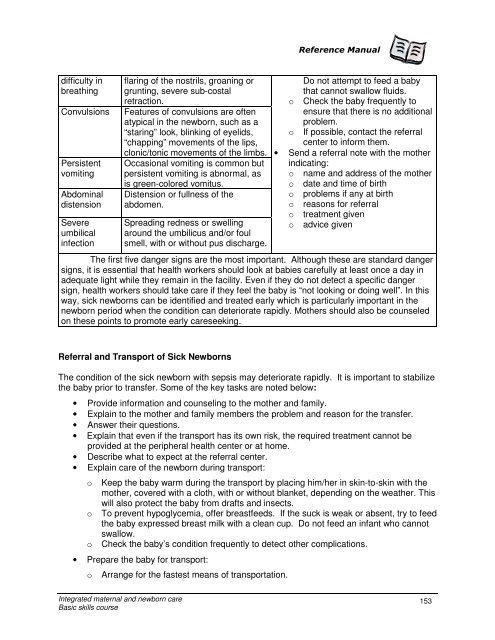
difficulty in<br />
breathing<br />
Convulsions<br />
Persistent<br />
vomiting<br />
Abdominal<br />
distension<br />
Severe<br />
umbilical<br />
infection<br />
flaring of the nostrils, groaning or<br />
grunting, severe sub-costal<br />
retraction.<br />
Features of convulsions are often<br />
atypical in the newborn, such as a<br />
“staring” look, blinking of eyelids,<br />
“chapping” movements of the lips,<br />
clonic/tonic movements of the limbs.<br />
Occasional vomiting is common but<br />
persistent vomiting is abnormal, as<br />
is green-colored vomitus.<br />
Distension or fullness of the<br />
abdomen.<br />
Spreading redness or swelling<br />
around the umbilicus <strong>and</strong>/or foul<br />
smell, with or without pus discharge.<br />
Do not attempt to feed a baby<br />
that cannot swallow fluids.<br />
o Check the baby frequently to<br />
ensure that there is no additional<br />
problem.<br />
o If possible, contact the referral<br />
center to inform them.<br />
• Send a referral note with the mother<br />
indicating:<br />
o name <strong>and</strong> address of the mother<br />
o date <strong>and</strong> time of birth<br />
o problems if any at birth<br />
o reasons for referral<br />
o treatment given<br />
o advice given<br />
The first five danger signs are the most important. Although these are st<strong>and</strong>ard danger<br />
signs, it is essential that health workers should look at babies carefully at least once a day in<br />
adequate light while they remain in the facility. Even if they do not detect a specific danger<br />
sign, health workers should take care if they feel the baby is “not looking or doing well”. In this<br />
way, sick newborns can be identified <strong>and</strong> treated early which is particularly important in the<br />
newborn period when the condition can deteriorate rapidly. Mothers should also be counseled<br />
on these points to promote early careseeking.<br />
Referral <strong>and</strong> Transport of Sick <strong>Newborn</strong>s<br />
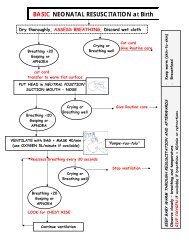
The condition of the sick newborn with sepsis may deteriorate rapidly. It is important to stabilize<br />
the baby prior to transfer. Some of the key tasks are noted below:<br />
• Provide information <strong>and</strong> counseling to the mother <strong>and</strong> family.<br />
• Explain to the mother <strong>and</strong> family members the problem <strong>and</strong> reason for the transfer.<br />
• Answer their questions.<br />
• Explain that even if the transport has its own risk, the required treatment cannot be<br />
provided at the peripheral health center or at home.<br />
• Describe what to expect at the referral center.<br />
• Explain care of the newborn during transport:<br />
o Keep the baby warm during the transport by placing him/her in skin-to-skin with the<br />
mother, covered with a cloth, with or without blanket, depending on the weather. This<br />
will also protect the baby from drafts <strong>and</strong> insects.<br />
o To prevent hypoglycemia, offer breastfeeds. If the suck is weak or absent, try to feed<br />
the baby expressed breast milk with a clean cup. Do not feed an infant who cannot<br />
swallow.<br />
o Check the baby’s condition frequently to detect other complications.<br />
• Prepare the baby for transport:<br />
o Arrange for the fastest means of transportation.<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> maternal <strong>and</strong> newborn care<br />
<strong>Basic</strong> skills course<br />
153