Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Reference Manual<br />
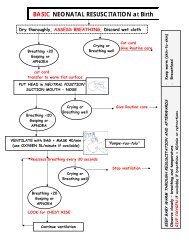
The following three adaptations may be necessary during an examination of a newborn:<br />
• Count the respiratory rate whenever the baby is quiet.<br />
• If the baby cries, take advantage to examine the mouth to look for cleft palate or thrush.<br />
• If feeding is necessary to calm the baby, take advantage to observe attachment at the<br />
breast <strong>and</strong> quality <strong>and</strong> adequacy of the sucking.<br />
Check for danger signs<br />
Check for the following newborn danger signs:<br />
• Difficulty in sucking. The danger signs related to sucking/feeding can be assessed by<br />
asking the mother <strong>and</strong> verified by direct observation.<br />
• Lethargy, diminished activity, moving only when stimulated. Except in deep sleep,<br />
babies move frequently, both spontaneously <strong>and</strong> on stimulation. The arms <strong>and</strong> legs are<br />
flexed. If a limb is consistently kept straight, evaluate for paralysis. Note also if the limbs<br />
seem very limp or flaccid.<br />
• Fever or hypothermia. Assess the body temperature by at least touching the baby’s<br />
abdomen, h<strong>and</strong>s, <strong>and</strong> feet <strong>and</strong> ensuring that all are warm. Where possible, note the<br />
axillary temperature with a thermometer leaving it in place for four minutes or as<br />
recommended by the manufacturer for axillary temperature recording. The normal<br />
temperature is 36.5-37.5 °C. The thermometer should be clean, preferably washed with<br />
soap <strong>and</strong> clean water, <strong>and</strong> wiped with an alcohol swab to prevent cross infection. Storing<br />
in liquid antiseptics should be done only if they are changed frequently. Otherwise there<br />
is risk of infections with Pseudomonas sps which may be highly resistant organisms. It is<br />
not recommended to take a rectal temperature as it is associated with a higher risk of<br />
infection <strong>and</strong> trauma. In the newborn infant, both fever <strong>and</strong> low body temperature<br />
outside the normal range of 36.5-37.5 °C are danger signs, especially if they are not<br />
reversed rapidly with simple steps, such as warming through skin-to-skin contact, or<br />
through removal of excess clothes, or covering in the hot weather.<br />
• Rapid breathing/difficulty in breathing. Assess respiration: the normal respiratory rate<br />
is 30-60 breaths/minute. There should be no flaring of the nostrils, grunting, or subcostal<br />
retractions. Although breathing can be somewhat irregular with short pauses, there<br />
should be no apnea, which is defined as cessation of breathing lasting for more than 20<br />
seconds or of a shorter duration associated with cyanosis, pallor, or bradycardia with a<br />
heart rate less than 110/minute. The normal heart rate ranges between 110-160<br />
beats/minute, with the lower rates when the baby is asleep <strong>and</strong> the higher rates when<br />
the baby is active or crying.<br />
• Convulsions. Features of convulsions are often atypical in the newborn, such as a<br />
“staring” look, blinking of eyelids, “chapping” movements of the lips, <strong>and</strong> clonic/tonic<br />
movements of the limbs.<br />
• Persistent vomiting <strong>and</strong>/or abdominal fullness . Vomiting is determined from the<br />
history taken from the mother. Occasional vomiting is normal, but persistent vomiting or<br />
green-colored vomitus are abnormal.<br />
• Severe umbilical infection. Lift the cord to see the base; check for pus discharge,<br />
redness, swelling, <strong>and</strong> foul smell. In the first day or two also check the cord for bleeding<br />
or oozing of blood.<br />
The danger signs are summarized in Table 10 below.<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> maternal <strong>and</strong> newborn care<br />
<strong>Basic</strong> skills course<br />
111