Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Integrated Maternal and Newborn Care Basic Skills Course ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Reference Manual<br />
Identifying a Baby with Birth Asphyxia<br />
The baby may have the following features:<br />
• does not cry at birth<br />
• is either not breathing or has very slow breathing (less than 20/minute) or is gasping<br />
• is blue or pale<br />
• is limp <strong>and</strong> not moving or not responding properly to stimulation<br />
The Apgar score is used at hospitals to assess the status of the baby in relation to breathing,<br />
heart rate, color, muscle tone, <strong>and</strong> reflex response to stimulation at 1, 5, <strong>and</strong> 10 minutes after<br />
birth. Low scores at 5 <strong>and</strong> 10 minutes have also had some correlation with a poorer long-term<br />
outcome, but this correlation is not always consistent. However, in most peripheral centers the<br />
scoring is frequently carried out in a wrong/inappropriate manner. The score, in any case, is not<br />
required <strong>and</strong> must not be used to make decisions to carry out resuscitation. Hence, the Apgar<br />
score will not be covered in this training session.<br />
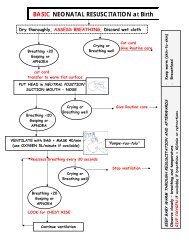
STEPS IN NEWBORN RESUSCITATION<br />
The initial actions for resuscitation are similar for all babies, irrespective of the status of the baby<br />
<strong>and</strong> presence or absence of asphyxia. After each step, an evaluation of the condition must be<br />
made to judge progress so that the appropriate next step can be implemented. Evaluation <strong>and</strong><br />
action constitute a cycle that has to be repeated in a timely manner until the baby recovers or a<br />
decision is made to discontinue an unsuccessful resuscitation. Universal precautions for the<br />
safety of the baby <strong>and</strong> the staff <strong>and</strong> steps for prevention of infection are also m<strong>and</strong>atory.<br />
Preparation<br />
Switch on the heating source before the delivery to warm the table top/mattress for the baby.<br />
Place the linen for the baby on the table under the warmer so that it gets warmed up before the<br />
delivery. Wash your h<strong>and</strong>s <strong>and</strong> wear sterile gloves.<br />
Immediate <strong>Care</strong> in the Case of Meconium in the Amniotic Fluid<br />
If the amniotic fluid is stained by meconium, <strong>and</strong> especially in case of thick meconium:<br />
• Suction the mouth <strong>and</strong> nose as soon as the head is delivered on the perineum <strong>and</strong> before<br />
the delivery of the shoulders. Tell the mother not to push for a little while, giving time to<br />
suction the mouth <strong>and</strong> nose of the baby. Based on research results, this preliminary<br />
suction before full delivery is not carried out in centers in advanced countries; instead,<br />
early suction, including endotracheal suction, is carried out immediately after delivery if the<br />
baby is not crying. However, in low-resource settings, such as peripheral centers in<br />
developing countries where intubation is not feasible, suctioning of the mouth <strong>and</strong> nose<br />
before delivery of the shoulders is likely to decrease the risk of meconium inhalation into<br />
the lungs that could cause additional problems.<br />
• After full delivery of the baby, if no breathing is observed, suction the mouth <strong>and</strong> nostrils<br />
before drying <strong>and</strong> stimulation. Do not suction a baby who is already crying.<br />
<strong>Integrated</strong> maternal <strong>and</strong> newborn care<br />
<strong>Basic</strong> skills course<br />
99