No. 1, 1998 - Tribology in Industry
No. 1, 1998 - Tribology in Industry
No. 1, 1998 - Tribology in Industry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
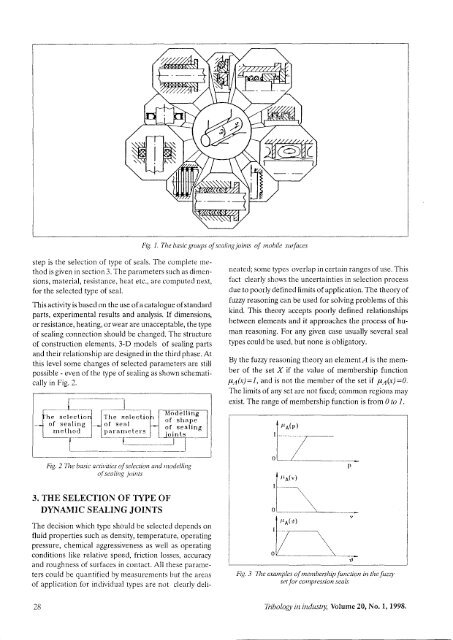
Fig. 1. The basic groups of sealirry jo<strong>in</strong>ts of ntobile surfaccs<br />
step is the selection of type of seals. The cornplete rnethod<br />
is given <strong>in</strong> section 3. The parameters such as dimensions,<br />
material, resistance, heat etc., are computed next,<br />
for the selected type of seal.<br />
This activity is based on the use of a catalogue of standard<br />
parts, experimental results and analysis. If dimensions,<br />
or resistance, heat<strong>in</strong>g, orwear are unacceptable, the type<br />
of seal<strong>in</strong>g connection should be changed. The structure<br />
of construction elements, 3-D models of seal<strong>in</strong>g parts<br />
and their relationship are designed <strong>in</strong> the third phase. At<br />
this level some changes of selected parameters are still<br />
possible - even of the type of seal<strong>in</strong>g as shorvn schematicallv<br />
<strong>in</strong> Fic. 2.<br />
neated; some types overlap <strong>in</strong> certairr ranges of use. This<br />
fact clearly shows the uncertair.rties <strong>in</strong> selection process<br />
due to poorly def<strong>in</strong>ed limits of application. The theory of<br />
fuzzy reason<strong>in</strong>g can be used for solv<strong>in</strong>g problems of this<br />
k<strong>in</strong>d, This theory accepts poorly def<strong>in</strong>ed relationships<br />
between elements and it approaches the process of human<br />
reason<strong>in</strong>g. For any given case usually several seal<br />
types could be used. but none is obligatory.<br />
tsy the fuzzy reason<strong>in</strong>g theory an element,4 is the member<br />
of the set X if the value of membership function<br />
Itaft)= I , and is not the member of the set if pt.a@.) :0 .<br />
The limits of any set are not flxed; cornmon regions may<br />
exist. The range of membership function is from 0 to l.<br />
of shape<br />
of seal<strong>in</strong>g<br />
f ig. 2 Tlrc basic activ'ities of selectiott and nndellittg<br />
o.[ sealittg joitrts<br />
3. THE SELECTION OF Tl?E OF<br />
DYNANIIC SEALING JOINTS<br />
The decision which type should be selected depends on<br />
fluid properties such as density, temperature, operat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
pressure, chemical aggressiveness as well as operat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
conditions like relative speed, friction losses, accuracy<br />
and roughness of surfaces <strong>in</strong> contact. All these parameters<br />
could be quantified by measurenents but the areas<br />
of application for <strong>in</strong>dividual types elre not clearly deli-<br />
/16(d)<br />
Fig. 3 'l-ltc eratnplas of ntenbcnhip funcrion <strong>in</strong> tha fir:1,<br />
set for contprcssion seals<br />
28<br />
Tiibolop irt <strong>in</strong>dustty, V