Host Intrusion Prevention 7.0.0 for ePO 4.0 Product Guide - McAfee
Host Intrusion Prevention 7.0.0 for ePO 4.0 Product Guide - McAfee
Host Intrusion Prevention 7.0.0 for ePO 4.0 Product Guide - McAfee
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Working with <strong>Host</strong> <strong>Intrusion</strong> <strong>Prevention</strong> Clients<br />
Overview of the Linux client<br />
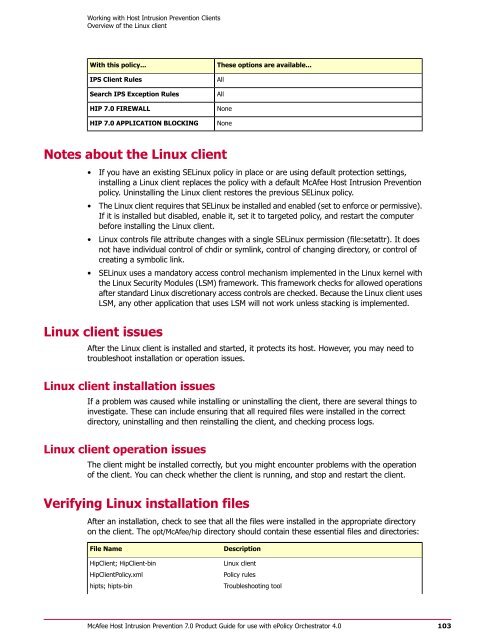
With this policy...<br />
IPS Client Rules<br />
Search IPS Exception Rules<br />
HIP 7.0 FIREWALL<br />
HIP 7.0 APPLICATION BLOCKING<br />
These options are available...<br />
All<br />
All<br />
None<br />
None<br />
Notes about the Linux client<br />
• If you have an existing SELinux policy in place or are using default protection settings,<br />
installing a Linux client replaces the policy with a default <strong>McAfee</strong> <strong>Host</strong> <strong>Intrusion</strong> <strong>Prevention</strong><br />
policy. Uninstalling the Linux client restores the previous SELinux policy.<br />
• The Linux client requires that SELinux be installed and enabled (set to en<strong>for</strong>ce or permissive).<br />
If it is installed but disabled, enable it, set it to targeted policy, and restart the computer<br />
be<strong>for</strong>e installing the Linux client.<br />
• Linux controls file attribute changes with a single SELinux permission (file:setattr). It does<br />
not have individual control of chdir or symlink, control of changing directory, or control of<br />
creating a symbolic link.<br />
• SELinux uses a mandatory access control mechanism implemented in the Linux kernel with<br />
the Linux Security Modules (LSM) framework. This framework checks <strong>for</strong> allowed operations<br />
after standard Linux discretionary access controls are checked. Because the Linux client uses<br />
LSM, any other application that uses LSM will not work unless stacking is implemented.<br />
Linux client issues<br />
After the Linux client is installed and started, it protects its host. However, you may need to<br />
troubleshoot installation or operation issues.<br />
Linux client installation issues<br />
If a problem was caused while installing or uninstalling the client, there are several things to<br />
investigate. These can include ensuring that all required files were installed in the correct<br />
directory, uninstalling and then reinstalling the client, and checking process logs.<br />
Linux client operation issues<br />
The client might be installed correctly, but you might encounter problems with the operation<br />
of the client. You can check whether the client is running, and stop and restart the client.<br />
Verifying Linux installation files<br />
After an installation, check to see that all the files were installed in the appropriate directory<br />
on the client. The opt/<strong>McAfee</strong>/hip directory should contain these essential files and directories:<br />
File Name<br />
HipClient; HipClient-bin<br />
HipClientPolicy.xml<br />
hipts; hipts-bin<br />
Description<br />
Linux client<br />
Policy rules<br />
Troubleshooting tool<br />
<strong>McAfee</strong> <strong>Host</strong> <strong>Intrusion</strong> <strong>Prevention</strong> 7.0 <strong>Product</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>for</strong> use with ePolicy Orchestrator <strong>4.0</strong><br />
103