Burns injury - PACT - ESICM
Burns injury - PACT - ESICM
Burns injury - PACT - ESICM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
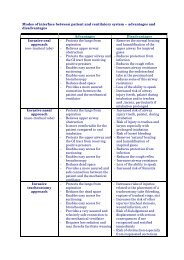
Urine with<br />
rhabdomyolysis<br />
Symptomatic patients (including those with loss of consciousness), those with<br />
abnormal ECG or a history of cardiac disease, and all patients exposed to<br />
intermediate and high voltages require continuous cardiac monitoring for a minimum<br />
of 24 hours post <strong>injury</strong>.<br />
There is no specific therapy for electrical injuries. Management is symptomatic and<br />
supportive.<br />
High voltage electrical <strong>injury</strong> patients need higher volumes of resuscitation<br />
fluid than other burn injuries. The goal of resuscitation is a urine output of >100<br />
mL/h to prevent myoglobin toxicity causing acute renal failure.<br />
Bersten AD, Soni N, editors. Oh’s Intensive Care Manual. 5th edition. Edinburgh:<br />
Butterworth Heinemann; 2003. ISBN 0750651849. pp. 777–782<br />
Koumbourlis AC. Electrical injuries. Crit Care Med 2002; 30(11 Suppl): S424–430.<br />
PMID 12528784<br />
Spies C, Trohman RG. Narrative review. electrocution and life-threatening<br />
electrical injuries. Ann Intern Med 2006; 145(7): 531–537. PMID 17015871<br />
26