Microbiology of heat-processed canned foods
Microbiology of heat-processed canned foods
Microbiology of heat-processed canned foods
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Lab.7.<br />
Practical Food <strong>Microbiology</strong><br />
<strong>Microbiology</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>heat</strong>-<strong>processed</strong> <strong>canned</strong> <strong>foods</strong><br />
Introduction:<br />
Canning is a method <strong>of</strong> preserving food in which the food is <strong>processed</strong>, sealed in an airtight<br />
container and <strong>heat</strong>ed to a temperature that destroys microorganisms.<br />
The objective in the thermal canning <strong>of</strong> <strong>foods</strong> is the destruction <strong>of</strong> microorganisms also to<br />
inactivate enzymes that cause spoilage.<br />
These products nevertheless undergo microbial spoilage under certain conditions.<br />
Regardless <strong>of</strong> the safety assured in <strong>canned</strong> <strong>foods</strong>, any damage or defective <strong>canned</strong> products<br />
are a potential public health problem.<br />
Canned food has been involved in enteric infection and food poisoning, including cases <strong>of</strong><br />
typhoid, botulism, salmonellosis and staphylococcal poisoning.<br />
Leakage occurs from can defects, punctures, contaminated cooling water sometimes leaks to<br />
the interior through pinholes or poor seams.<br />
A viable mixed micr<strong>of</strong>lora <strong>of</strong> bacterial rods and cocci is indicative <strong>of</strong> leakage.<br />
Some microorganisms that grow in <strong>canned</strong> <strong>foods</strong>, do not produce gas and therefore cause no<br />
abnormal appearance <strong>of</strong> the can.<br />
Imported <strong>canned</strong> products may need to be examined at point <strong>of</strong> entry to the cities.<br />
Spoilage <strong>of</strong> <strong>canned</strong> Foods<br />
Swollen cans <strong>of</strong>ten indicate a spoiled product.<br />
During spoilage, cans may progress from normal to abnormal appearance, see physical<br />
examination <strong>of</strong> can.<br />
Spoilage is not the only cause <strong>of</strong> abnormal cans. Overfilling or denting may also be<br />
responsible.<br />
The incidence <strong>of</strong> spoilage in <strong>canned</strong> <strong>foods</strong> is low, but when it occurs it must be investigated<br />
properly.<br />
The main reasons for spoilage are preprocess spoilage underprocessing, inadequate cooling,<br />
and contamination <strong>of</strong> the can resulting from leakage through seams.
To determine the type <strong>of</strong> bacteria involved in spoilage it is important to conceder the<br />
following facts:<br />
1- Type <strong>of</strong> food involved ( particularly acidity)<br />
2- Type <strong>of</strong> change in food (acid, gas, purification, blackening...etc)<br />
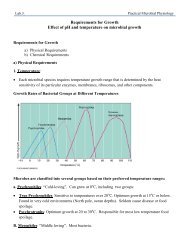
3- Thermophilic or mesophilic character <strong>of</strong> microorganisms<br />
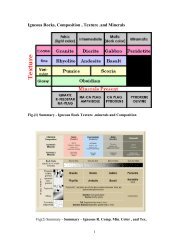
Classification <strong>of</strong> food products according to acidity:<br />
Interpritation <strong>of</strong> the possible causes <strong>of</strong> can spoilage
Physical examination <strong>of</strong> can<br />
Procedure:<br />
Describe internal and external condition <strong>of</strong> can, including evidence <strong>of</strong> leakage, swelling,<br />
corrosion, etc.<br />
Open can in an environment that is as aseptic as possible.<br />
Remove large enough portions from center <strong>of</strong> can.<br />
After removal <strong>of</strong> inoculum, transfer all remaining contents <strong>of</strong> cans to sterile closed containers,<br />
and refrigerate at about 4°C.<br />
Use this material for repeat examination if needed and for possible toxicity tests.<br />
Prepare inoculum for microbiological cultivation.<br />
Cultivation<br />
Total count, Coliform count, Thermophiles, Clostridium<br />
Results:<br />
Condition<br />
<strong>of</strong> can<br />
Can<br />
contents<br />
Odor Appearance Gas pH Culture Diagnose