THESE de DOCTORAT - cerfacs
THESE de DOCTORAT - cerfacs
THESE de DOCTORAT - cerfacs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
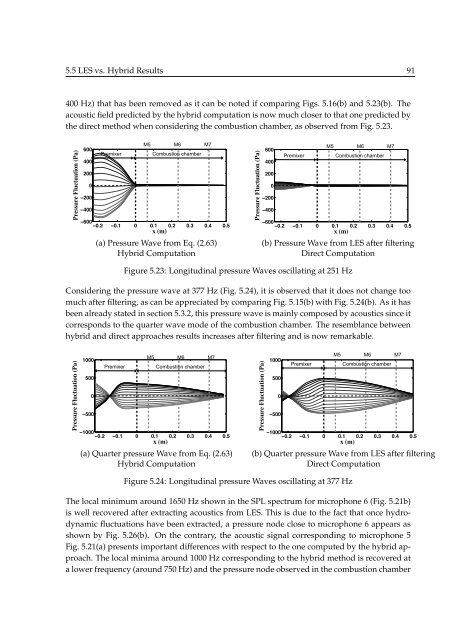
5.5 LES vs. Hybrid Results 91<br />
400 Hz) that has been removed as it can be noted if comparing Figs. 5.16(b) and 5.23(b). The<br />
acoustic field predicted by the hybrid computation is now much closer to that one predicted by<br />
the direct method when consi<strong>de</strong>ring the combustion chamber, as observed from Fig. 5.23.<br />
Pressure Fluctuation (Pa)<br />
M5 M6 M7<br />
600<br />
Premixer<br />
Combustion chamber<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
−200<br />
−400<br />
−600<br />
−0.2 −0.1 0 0.1 0.2<br />
x (m)<br />
0.3 0.4 0.5<br />
(a) Pressure Wave from Eq. (2.63)<br />
Hybrid Computation<br />
Pressure Fluctuation (Pa)<br />
600<br />
M5 M6 M7<br />
Premixer<br />
Combustion chamber<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
−200<br />
−400<br />
−600<br />
−0.2 −0.1 0 0.1 0.2<br />
x (m)<br />
0.3 0.4 0.5<br />
(b) Pressure Wave from LES after filtering<br />
Direct Computation<br />
Figure 5.23: Longitudinal pressure Waves oscillating at 251 Hz<br />
Consi<strong>de</strong>ring the pressure wave at 377 Hz (Fig. 5.24), it is observed that it does not change too<br />
much after filtering, as can be appreciated by comparing Fig. 5.15(b) with Fig. 5.24(b). As it has<br />
been already stated in section 5.3.2, this pressure wave is mainly composed by acoustics since it<br />
corresponds to the quarter wave mo<strong>de</strong> of the combustion chamber. The resemblance between<br />
hybrid and direct approaches results increases after filtering and is now remarkable.<br />
Pressure Fluctuation (Pa)<br />
M5 M6 M7<br />
1000<br />
Premixer<br />
Combustion chamber<br />
500<br />
0<br />
−500<br />
−1000<br />
−0.2 −0.1 0 0.1 0.2<br />
x (m)<br />
0.3 0.4 0.5<br />
(a) Quarter pressure Wave from Eq. (2.63)<br />
Hybrid Computation<br />
Pressure Fluctuation (Pa)<br />
M5 M6 M7<br />
1000<br />
Premixer<br />
Combustion chamber<br />
500<br />
0<br />
−500<br />
−1000<br />
−0.2 −0.1 0 0.1 0.2<br />
x (m)<br />
0.3 0.4 0.5<br />
(b) Quarter pressure Wave from LES after filtering<br />
Direct Computation<br />
Figure 5.24: Longitudinal pressure Waves oscillating at 377 Hz<br />
The local minimum around 1650 Hz shown in the SPL spectrum for microphone 6 (Fig. 5.21b)<br />
is well recovered after extracting acoustics from LES. This is due to the fact that once hydrodynamic<br />
fluctuations have been extracted, a pressure no<strong>de</strong> close to microphone 6 appears as<br />
shown by Fig. 5.26(b). On the contrary, the acoustic signal corresponding to microphone 5<br />
Fig. 5.21(a) presents important differences with respect to the one computed by the hybrid approach.<br />
The local minima around 1000 Hz corresponding to the hybrid method is recovered at<br />
a lower frequency (around 750 Hz) and the pressure no<strong>de</strong> observed in the combustion chamber