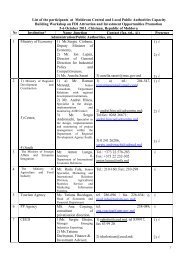
Tradeflow Study - UNDP Black Sea Trade and Investment Promotion ...
Tradeflow Study - UNDP Black Sea Trade and Investment Promotion ...
Tradeflow Study - UNDP Black Sea Trade and Investment Promotion ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
.<br />
country I <strong>and</strong> country j’s capital (or main) cities. Conflict data is obtained from the Heidelberg<br />
Institute for International Conflict Research. With respect to languages, if two countries share<br />
a common main language, a value of 1 is given to the dummy variable; if two countries share<br />
a common language which is the main language of one <strong>and</strong> a second language for the other,<br />
then a value of 0.5 is given; <strong>and</strong> if both countries share a common second language, a value<br />
of 0.25 is given. The data on a country’s latitude is obtained from the CEPII database. The<br />
<strong>Trade</strong>Sim model is described in detail in Helmers <strong>and</strong> Pasteels (2005).<br />
The export potential is calculated using the regressions for all 19 sectors <strong>and</strong> for all BSEC<br />
countries. The following notation is given to indicate the level of trade potential which exists in<br />
each sector between each partner country.<br />
: Very strong untapped trade potential;<br />
: Strong untapped trade potential<br />
: Good fit;<br />
: Good fit or low values<br />
: Very strong current trade;<br />
: Strong current trade<br />
The following abbreviations for countries have been used:<br />
ALB: Albania<br />
ARM: Armenia<br />
AZE: Azerbaijan<br />
BGR: Bulgaria<br />
GEO: Georgia<br />
GRC: Greece<br />
MDA: Republic of Moldova<br />
ROM: Romania<br />
RUS: Russia<br />
S-M: Serbia-Montenegro<br />
TUR: Turkey<br />
UKR: Ukraine<br />
The limitation of the model is that it is based on a conditional general equilibrium framework<br />
which does not capture dynamic effects nor cross country linkages. The static nature of the<br />
equation therefore leads to the omission of second round effects from trade liberalisation. The<br />
omission of countries or variables in the model will have an important effect on the model<br />
results. Moreover, the model fails to capture sufficiently well trade complementarity effects in<br />
weakly diversified economies (which are by their very nature specialized in just a few<br />
commodities <strong>and</strong> therefore appear to over trade in some sectors <strong>and</strong> under trade in other<br />
sectors).<br />
96/135