Metric Units and Conversions - Unitec
Metric Units and Conversions - Unitec
Metric Units and Conversions - Unitec
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
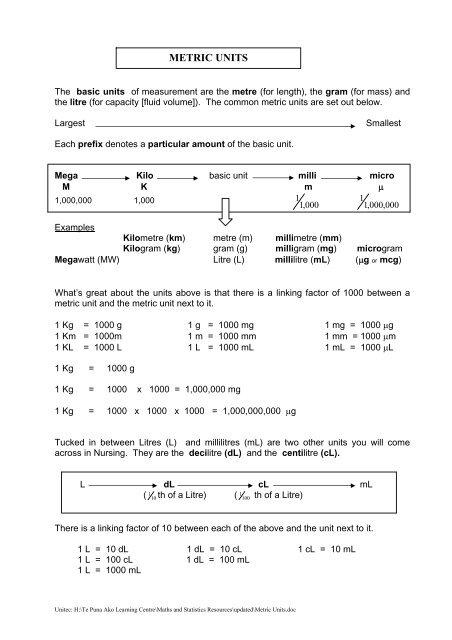
METRIC UNITS<br />
The basic units of measurement are the metre (for length), the gram (for mass) <strong>and</strong><br />
the litre (for capacity [fluid volume]). The common metric units are set out below.<br />
Largest<br />
Smallest<br />
Each prefix denotes a particular amount of the basic unit.<br />
Mega Kilo basic unit milli micro<br />
M K m <br />
1,000,000 1,000<br />
1<br />
1,000<br />
1<br />
1,000,000<br />
Examples<br />
Kilometre (km) metre (m) millimetre (mm)<br />
Kilogram (kg) gram (g) milligram (mg) microgram<br />
Megawatt (MW) Litre (L) millilitre (mL) (g or mcg)<br />
What’s great about the units above is that there is a linking factor of 1000 between a<br />
metric unit <strong>and</strong> the metric unit next to it.<br />
1 Kg = 1000 g 1 g = 1000 mg 1 mg = 1000 g<br />
1 Km = 1000m 1 m = 1000 mm 1 mm = 1000 m<br />
1 KL = 1000 L 1 L = 1000 mL 1 mL = 1000 L<br />
1 Kg = 1000 g<br />
1 Kg = 1000 x 1000 = 1,000,000 mg<br />
1 Kg = 1000 x 1000 x 1000 = 1,000,000,000 g<br />
Tucked in between Litres (L) <strong>and</strong> millilitres (mL) are two other units you will come<br />
across in Nursing. They are the decilitre (dL) <strong>and</strong> the centilitre (cL).<br />
L dL cL mL<br />
(<br />
1 10 th of a Litre) (<br />
1 100 th of a Litre)<br />
There is a linking factor of 10 between each of the above <strong>and</strong> the unit next to it.<br />
1 L = 10 dL 1 dL = 10 cL 1 cL = 10 mL<br />
1 L = 100 cL 1 dL = 100 mL<br />
1 L = 1000 mL<br />
<strong>Unitec</strong>: H:\Te Puna Ako Learning Centre\Maths <strong>and</strong> Statistics Resources\updated\<strong>Metric</strong> <strong>Units</strong>.doc
METRIC UNIT CONVERSIONS<br />
You may need to do metric unit conversions with drug calculations or with rates. In both<br />
cases you need to know :<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
What metric unit you have initially <strong>and</strong> which unit you want to convert to<br />
Whether you are converting from a Bigger unit (B) to a Smaller unit (S)<br />
or the other way round<br />
How many of the smaller units make up the bigger unit<br />
If converting from a Bigger unit to a Smaller unit, you are multiplying so move the decimal<br />
point to the Right by how many zeroes there are in the multiplier, i.e. BSR<br />
If converting from a Smaller unit to a Bigger unit, you are dividing so move the decimal<br />
point to the Left by how many zeroes there are in the divisor, i.e. SBL<br />
EXAMPLES<br />
1. How many micrograms (mcg) in 2.8 mg?<br />
Remember mcg is the same as g<br />
converting from mg to mcg<br />
bigger to smaller so BSR<br />
1 mg = 1000 mcg so move decimal point three places to the right<br />
(since 1000 has three zeroes)<br />
2.8 mg = 2800. g which is 2800 g<br />
2. 965 dL is equivalent to how many mL?<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
converting from dL to mL<br />
bigger to smaller so BSR<br />
1 dL = 100 mL so move the decimal point two places to the right<br />
965 dL = 965. dL = 96500. mL which is 96500 mL<br />
3. How many grams in 750 g ?<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
converting mcg to g<br />
smaller to bigger so SBL<br />
1g = 1,000,000 mcg so move the decimal point six places to the left<br />
750 mcg = 750. mcg = .000750 g<br />
<strong>Unitec</strong>: H:\Te Puna Ako Learning Centre\Maths <strong>and</strong> Statistics Resources\updated\<strong>Metric</strong> <strong>Units</strong>.doc
METRIC CONVERSIONS IN RATES<br />
4. Convert 6.6 L/min to mL/min. (Here you have to convert 6.6 L to mL)<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
converting from L to mL<br />
bigger to smaller so BSR<br />
1 L = 1000 mL so move decimal point three places to the right<br />
6.6 L = 6600. mL = 6600 mL<br />
So 6.6 L/min = 6600 mL/min.<br />
5. Change 350 mcg/dL into mg/dL. (You have to convert 350 mcg to mg)<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
converting from mcg to mg<br />
smaller to bigger so SBL<br />
1 mg = 1000 mcg so move the decimal point three places to the left<br />
350 mcg = 350. mcg = .350 mg (which can be written as 0.35 mg)<br />
So 350 mcg/dL = 0.35 mg/dL<br />
METRIC CONVERSIONS IN DRUG CALCULATIONS<br />
It is easier to convert bigger units to smaller units.<br />
6. 0.5 mg of Neocytamen is prescribed. 250 mcg/mL is available…<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
convert 0.5 mg to mcg<br />
bigger to smaller so BSR<br />
1 mg = 1000 mcg so move the decimal point three places to the right<br />
0.5 mg = 0 500. mcg = 500 mcg. You can now think of the problem as:<br />
“ 500 mcg of Neocytamen is prescribed. 250 mcg/mL is available…”<br />
7. Lasix 1 g is prescribed. 20 mg/mL is available…<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
convert 1 g to mg<br />
bigger to smaller so BSR<br />
1 g = 1000 mg so move the decimal point three places to the right<br />
1. g = 1 000. mg. The problem now becomes:<br />
“ Laxin 1000 mg is prescribed. 20 mg/mL is available…”<br />
<strong>Unitec</strong>: H:\Te Puna Ako Learning Centre\Maths <strong>and</strong> Statistics Resources\updated\<strong>Metric</strong> <strong>Units</strong>.doc
8. How much solute is required to make 1 L of 5% glucose? Remember 5% means<br />
5 g/100mL so we need to convert 1L to mL. After the procedure as before we find<br />
that 1 L = 1000 mL <strong>and</strong> the problem can now be re-phrased more simply as:<br />
“How much (what mass/weight of) solute is required to make 1000 mL of solution if<br />
5 g of solute is required for 100 mL?”<br />
EXERCISE 1<br />
Change to Change to Change to Change to Change to<br />
milligrams grams milligrams millilitres Litres<br />
1 4 g 6000 mg 825 mcg 2 L 4000 mL<br />
2 8.7 g 865 mg 750 mcg 30 L 10000 mL<br />
3 0.69 g 70 mg 65 mcg 1.5 L 625 mL<br />
4 0.02 g 5 mg 95 mcg 4.5 L 359 mL<br />
5 0.035 g 7259 mg 10 mcg 1.6 L 95 mL<br />
6 0.006 g 95 mg 5 mcg 2.24 L 60 mL<br />
7 0.655 g 2 mg 200 mcg 0.8 L 5 mL<br />
8 4.28 g 125 mg 30 mcg 0.75 L 2 mL<br />
EXERCISE 2<br />
Change to<br />
grams<br />
Change to<br />
millilitres<br />
Change to<br />
centilitres<br />
Change to<br />
decilitres<br />
1 3 Kg 3 L 85 mL 8.3 L 2 g<br />
2 6.5 Kg 25 cL 6 dL 0.9 L 2 Kg<br />
Change to<br />
milligrams<br />
3 500 mg 600 dL 0.5 L 63 cL 0.43 g<br />
4 2000 mg 3.1 dL 0.2 mL 0.75 cL 0.825 Kg<br />
5 45 mg 0.45 cL 0.09 dL 806 mL 125 mcg<br />
6 100 mcg 0.25 L 1.8 L 0.1 mL 8 mcg<br />
7 24000 mcg 0.075 cL 512 mL 437 cL 0.035 g<br />
8 6000000 mcg 546 cL 0.04 L 6000 mL 10.4 mcg<br />
ANSWERS<br />
EXERCISE 1 EXERCISE 2<br />
mg g mg mL L g mL cL dL mg<br />
1) 4000 6 0.825 2000 4 1) 3000 3000 8.5 83 2000<br />
2) 8700 0.865 0.75 30000 10 2) 6500 250 60 9 2000000<br />
3) 690 0.07 0.065 1500 0.625 3) 0.5 60000 50 6.3 430<br />
4) 20 0.005 0.095 4500 0.359 4) 2 310 0.02 0.075 825000<br />
5) 35 7.259 0.01 1600 0.095 5) 0.045 4.5 0.9 8.06 0.125<br />
6) 6 0.095 0.005 2240 0.06 6) 0.0001 250 180 0.001 0.008<br />
7) 655 0.002 0.2 800 0.005 7) 0.024 0.75 51.2 43.7 35<br />
8) 4280 0.125 0.03 750 0.002 8) 6 5460 4 60 0.0104<br />
<strong>Unitec</strong>: H:\Te Puna Ako Learning Centre\Maths <strong>and</strong> Statistics Resources\updated\<strong>Metric</strong> <strong>Units</strong>.doc