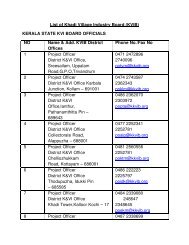
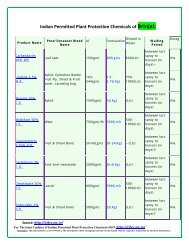
Tripura - Efresh India
Tripura - Efresh India
Tripura - Efresh India
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Tripura</strong><br />
All over <strong>India</strong> the Gomukh is an auspicious emblem. Ancient drinking fountains and clear springs<br />
are often directed to flow through spouts fashioned in the form of a cow's head. <strong>Tripura</strong> is the<br />
gomukh of the north-east. It thrusts out into Bangladesh with only its neck attached to Mizoram<br />
and Assam.<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> is one of the seven states in the north eastern part of <strong>India</strong> located between 22 degree and<br />
56 minutes and 24 degree and 32 minutes north latitude and between 90 degree and 09 minutes<br />
and 92 degree and 20 minutes east latitude. It is bounded on the north, west, south and south-east<br />
by Bangladesh whereas in the east it has a common boundary with Assam and Mizoram.<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> became a Union Territory without legislature with effect from November 1, 1956 and a<br />
popular ministry was installed in <strong>Tripura</strong> on July 1, 1963. On January 21, 1972 <strong>Tripura</strong> attained<br />
statehood.<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> is a hilly and landlocked state endowed with vast green forests and established gas<br />
reserves. The state has a total area of 10492 sq. km. The state has a long border with Bangladesh<br />
of 856 km. After Kerala , <strong>Tripura</strong> is the largest producer of natural rubber and the rubber produced<br />
is of superior quality . The state also has the distinction of being the highest producer of True<br />
Potato Seeds in the country.<br />
As in the other states of the north east , <strong>Tripura</strong>’s economy is primarily agrarian and agriculture<br />
and its allied activities contributes nearly 34 % to the state’s Net Domestic Product . Agriculture in<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> includes traditional Jhum (shifting) cultivation.
Capital: Agartala<br />
Population: 3,199,203<br />
Agricultural Products:<br />
and Rubber<br />
Rice, Sugarcane, Jute, Mesta, Potatoes, Tea<br />
Strategically situated between the river valleys of Myanmar and Bangladesh, <strong>Tripura</strong> has<br />
cultivable area of 2.8 lakh hectares of which about a third or 95,000 hectares is cultivated with 80<br />
% irrigation. It is endowed with abundant resources and the economy is essentially agrarian.<br />
It has all ideal conditions for promotion of a range of food and non food crops including<br />
horticulture in sub tropical clime.<br />
The farming community has taken to cultivation of field crops (paddy, maize, wheat, pulses,<br />
oilseeds jute and mesta), horticulture (mainly fruits and vegetables) and floriculture as also animal<br />
husbandry and pisciculture.<br />
Over half the population depends on agriculture and related activities for livelihood making farm<br />
the largest provider of employment and incomes. Farming is generally in fragmented landholding.<br />
The State's horticulture sector comprises fruits, vegetables, spices, plantation crops, medicinal and<br />
aromatic plants and so on.<br />
Fruits like pineapple, mandarin, banana, litchi, lemon as well as plantation crops such as coconut<br />
and cashew are popular. The strong production base creates opportune conditions for investment in<br />
setting up processing units.<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> cropping pattern is typical of a hilly region. Shifting cultivation in hill regions and settled<br />
farming in the plains.<br />
Weather conditions encourage crop diversification and cultivation of seasonal fruits and<br />
vegetables. Arecanut, oil palm, tea, coffee and rubber hold potential for cultivation. Among spices,<br />
chilli and ginger are grown. A sunrise industry, floriculture is spreading rapidly following demand<br />
for commercially grown flowers like gladioli, marigold and tuberose as also exotic flower<br />
anthurium grown under controlled condition.<br />
<br />
The State Government has placed emphasis on dairy development – milk production and<br />
marketing Fisheries are a vital sector as over 90 per cent of the population eats fish. Fresh water<br />
aquaculture has made progress even as the State government seeks to promote scientific<br />
techniques of fish production. Growing market demand for prawn has resulted in greater attention<br />
to that segment.
It may surprise many that after Kerala, <strong>Tripura</strong> is the second largest producer of 70,000 hectares,<br />
there is scope to reach 1,00,000 hectares of rubber plantation, it is estimated. Tea is also emerging<br />
as an important plantation crop. Organic tea or bio potential.<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> holds great promise for investment in agriculture and allied activities. A large production<br />
base assures steady supplies of raw material. Investment in processing facilities is sure to bring in<br />
good returns.<br />
Area, Production & Average yield per hector of important crops:<br />
Year<br />
Rice Maize Wheat Gram<br />
A P Y A P Y A P Y A P Y<br />
2001-02 246744 587377 2380 2080 2080 1000 1220 2280 1869 399 255 640<br />
2002-03 255270 602370 2375 2305 2200 957 929 1827 1988 323 215 665<br />
2003-04 257450 616830 2396 2240 2150 960 895 1810 2022 344 237 689<br />
2004-05 256078 571659 2232 2790 2967 1063 944 1924 2038 266 187 703<br />
2005-06 256078 606780 2370 2150 2113 983 2610 5259 2015 939 616 656<br />
2006-07 250980 620500 2472 2450 2420 988 984 1827 1857 N.A. N.A. N.A.<br />
(Area in hect., production in tones/bales and yield in kg. per hector, Source: Statistical Abstract of<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> 2007)<br />
Year-wise Area and Production of Fruits and Nuts in <strong>Tripura</strong>:<br />
Year Litchi Mango Pineapple Guava Orange Jackfruit<br />
1995-<br />
96<br />
1996-<br />
97<br />
1997-<br />
98<br />
1998-<br />
99<br />
1999-<br />
00<br />
2000-<br />
01<br />
2001-<br />
02<br />
2002-<br />
03<br />
2003-<br />
04<br />
2004-<br />
05<br />
A P A P A P A P A P A P<br />
3495 2201 5036 41270 3989 35290 - - 4723 23100 8300 219190<br />
4040 2549 5036 41270 4094 36230 - - 5074 24810 8372 221100<br />
4673 2662 5022 23100 4297 36460 - - 5267 25240 8429 221450<br />
4673 2662 5030 23145 4297 36460 - - 5267 25240 8429 22450<br />
4800 2880 5000 22.300 4697 42.273 - - 5427 29.850 8929 250.021<br />
1478 8869 3075 4500 3450 82159 - - 2017 15683 - -<br />
1628 8900 3150 8500 3500 82159 305 579 2107 15800 9000 250000<br />
1738 8950 3175 4600 3705 82600 298 1220 2314 16010 9020 255000<br />
2167 12528 3460 6121 4140 93500 340 1408 2436 16988 9032 270340<br />
2212 12449 3623 9360 4980 105086 353 1490 2698 17044 9032 254945
2005- 2346 14255 3868 12340 5180 106406 356 1560 2811 18150 8645 256280<br />
06<br />
2006- 2476 14400 3700 11358 6184 115829 333 1496 2882 19445 7431 249265<br />
07<br />
Year Banana Lemon Chashwanut Coconut Areconut Other Fruits<br />
A P A P A P A P A P A P<br />
1995- 3914 2673 2735 2730 4868 1480 8770 58.93 1745 3410 -- --<br />
96<br />
1996- 3914 2675 2938 2938 5968 1820 8867 59.58 1757 3450 -- --<br />
97<br />
1997- 4033 27400 3227 3225 6739 1900 9084 61.02 2336 4192 -- --<br />
98<br />
1998- 4065 2770 3240 3238 6739 1900 9084 75.46 2336 4192 -- --<br />
99<br />
1999- 4100 41.000 3227 40.31 7039 2.816 9184 81.08 2436 4.872 -- --<br />
00<br />
2<br />
2000- 4935 63566 - - 3106 1105 3183 69.52 3173 6839 -- --<br />
01<br />
2001- 5000 63600 1400 6300 3220 1200 3333 70.00 3353 6850 695 4170<br />
02<br />
2002- 5011 63732 1500 8200 3245 1300 3493 70.10 3503 6900 844 12027<br />
03<br />
2003- 5423 68994 1891 10510 3706 1502 5101 187.27 4343 8589 926 11474<br />
04<br />
2004- 5374 69330 1982 10170 3814 1542 5201 198.43 4465 9042 1036 12672<br />
05<br />
2005- 5717 79250 2025 11070 3814 1855 5201 2997.00 4465 9580 1120 14245<br />
06<br />
2006-<br />
07<br />
6219 80160 2034 11115 3814 1726 5382 3166.60 4349 9564 2366 18828<br />
(Area in Hectors, Production in M/T, Source: Statistical Abstract of <strong>Tripura</strong> 2007)<br />
Year-wise Area, Production & Average yield of Cereal Crops in <strong>Tripura</strong>.<br />
Year Rice Maize Wheat Gram<br />
1995-<br />
96<br />
1996-<br />
97<br />
1997-<br />
98<br />
1998-<br />
99<br />
1999-<br />
00<br />
2000-<br />
01<br />
2001-<br />
02<br />
2002-<br />
03<br />
2003-<br />
04<br />
2004-<br />
05<br />
A P Y A P Y A P Y A P Y<br />
231536 465550 2010 2280 2000 877 2620 5240 2000 490 305 622<br />
258955 544830 2100 2410 1930 800 1950 3900 2000 615 370 600<br />
257790 535840 2078 2230 1980 890 2310 4400 1905 260 150 577<br />
255490 490110 1918 2315 1730 747 1105 2100 1900 180 110 611<br />
232160 505685 2178 1250 1000 800 1250 2400 1920 213 135 634<br />
241165 513402 2120 1580 1580 1000 1065 2230 2094 340 195 573<br />
246744 587377 2380 2080 2080 1000 1220 2280 1869 399 255 640<br />
255270 602370 2375 2305 2200 957 929 1827 1988 323 215 665<br />
257450 616830 2396 2240 2150 960 895 1810 2022 344 237 689<br />
256078 571659 2232 2790 2967 1063 944 1924 2038 266 187 703
2005-<br />
06 (P)<br />
2006-<br />
07 (P)<br />
256078 606780 2370 2150 2113 983 2610 5259 2015 939 616 656<br />
250980 620500 2472 2450 2420 988 984 1827 1857 N.A. N.A. N.A.<br />
(A in hect., P in tones/bales and Y in kg. per hector, Source: Statistical Abstract of <strong>Tripura</strong> 2007<br />
Year-wise Area, Production & Average yield of Spices in <strong>Tripura</strong>.<br />
Year Chilies Turmeric (Dry) Ginger<br />
A P Y A P Y A P Y<br />
1995-96 1530 830 542 1400 2770 990 1815 1833 1833<br />
1996-97 1600 900 560 1420 2840 1005 1850 1840 1840<br />
1997-98 1850 1045 565 1440 2718 1100 2190 1990 1990<br />
1998-99 2000 1200 600 1500 2800 1200 2400 2000 2000<br />
1999-00 1910 1140 597 1460 2840 1060 2050 1934 1934<br />
2000-01 1845 1025 550 1440 2540 1150 2260 1960 1960<br />
2001-02 1585 2200 1388 1512 6550 1350 2805 2077 2077<br />
2002-03 1680 2405 1432 1480 4290 1330 4140 2030 2030<br />
2003-04 1635 2260 1380 1470 4820 1320 2700 2040 2040<br />
2004-05 1700 16279 9576 1102 3571 1180 2774 2351 2351<br />
2005-06 1940 2910 1500 1108 3750 1364 2895 2122 2122<br />
2006-07 1833 2082 1137 1149 3381 1415 4170 2947 2947<br />
(A in hect., P in tones/bales and Y in kg. per hector, Source: Statistical Abstract of <strong>Tripura</strong> 2007)<br />
Rubber<br />
Rubber plantation has become a much-talked phenomenon in the State of <strong>Tripura</strong>. The State Forest<br />
Department, aiming at soil and moisture conservation, first introduced rubber in <strong>Tripura</strong> in 1963.<br />
With the intervention of the Rubber Board since 1967, rubber then got domesticated and coming<br />
out of the estates, it has reached to the small growers’ yard.<br />
In 1976 <strong>Tripura</strong> Forest Development & Plantation Corporation Ltd. (TFDPC Ltd.) was set up to<br />
bring out more area under rubber cultivation. In 1982, <strong>Tripura</strong> Rehabilitation Plantation<br />
Corporation Ltd. (TRPC Ltd.) was formed with the main objective of economic rehabilitation for<br />
the shifting cultivators and tribal marginal farmers through rubber plantation.<br />
<strong>India</strong> ranks third in terms of production of Natural Rubber in the World after Thailand and<br />
Malayasia. Kerala is the largest and <strong>Tripura</strong> is the second largest producer of natural rubber in the<br />
country.<br />
<br />
In <strong>Tripura</strong> rubber plants (Hevea brasiliensis) were introduced for soil and moisture conservation<br />
by Forest Department in 1963. Rubber is a tropical crop and grows well in <strong>Tripura</strong>. The species<br />
has proved excellent for permanent settlement of tribal jhumias.
Rubber Board started implementing Group and Block plantation schemes from 1992 and thus a<br />
revolution set off. Rubber Board kept on promoting rubber from village to village and a<br />
spectacular progress could be achieved.<br />
Till 2007-08, <strong>Tripura</strong> has about 39,670 hectares of rubber plantation. Total production of rubber in<br />
the State was a 23,087 Mt in 2007-08.<br />
The study conducted by the National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning, as a part of<br />
exploratory study for the World Bank Assistance revealed that approximately 1 lakh hectares of<br />
land is suitable for rubber cultivation in the State.<br />
This offers tremendous scope for expansion of rubber plantation. Apex Bodies of Industries and<br />
Commerce like CII etc. have also realized the importance and the potential of rubber cultivation in<br />
the State. It is also proposed to engage an external agency to study the feasibility to extend rubber<br />
cultivation in an area not exceeding 10 percent of the total geographical area of the State.<br />
The raw rubber now produced is being sent out of the State to neighbouring States for further<br />
value addition. Necessary follow-up action is also being taken to utilize the raw-rubber for value<br />
added finished products within the State.<br />
Recently a Rubber Mission has been set up by Government of <strong>Tripura</strong> for better co-ordination of<br />
all the agencies involved in taking up plantation and marketing of rubber.<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> Forest Development and Plantation Corporation Ltd. (TFDPC Ltd.):<br />
The TFDPC Ltd. is the major producer of rubber in the State and it functions under the<br />
administrative control of State Forest Department. The <strong>Tripura</strong> Rehabilitation Plantation<br />
Corporation Ltd. (TRPC Ltd.) under administrative control of State Tribal Welfare Department is<br />
the 2nd largest producer of rubber in the State. TFDPC Ltd. has so far raised 11,416 hectares of<br />
plantation on forest land over last 26 years. It has so far raised 3127.89 hectares of rubber for<br />
settling the tribal jhumias in the private land owned as well as scheduled caste families.<br />
TFDPC Ltd. markets rubber in the form of ribbed smoke sheet, cenex, crepe rubber and scrap<br />
form. The production of rubber of TFDPC Ltd. in 2006-07 was 3546 MT, which sold for Rs. 27<br />
crores. It created mandays to the tune of 10 lakhs, besides giving regular employment to large<br />
number of permanent labourers for various works in processing, creation of plantations, nurseries<br />
and other related works.<br />
TFDPC Ltd. has taken up the treatment of rubber wood for production of substitute wood to<br />
reduce the demand on forests. Treated rubber wood is similar in properties to natural teak wood<br />
and is in fashion in western world for its shining white cream colour and better properties.<br />
A common facility centre with imported high technology based machines is in final stage of<br />
commissioning. A rubber wood factory has also been setup with a capacity of producing 80 solid<br />
wood boards per annum with finger joining technique. The TFDPC Ltd. has switched over to<br />
RMA system of grading it rubber sheets. Also it is in the process of shifting over to mechanise<br />
processing to ensure higher quality sheets and has started bio-gas plants to reduce the dependence<br />
on fuel wood. A project for door manufacturing unit has been submitted to the Ministry of<br />
Commerce and Industries, Government of <strong>India</strong>. There is a project proposal for setting up of a<br />
Bamboo Board factory with assistance of NMBA.
Year wise acreage of rubber plantation in <strong>Tripura</strong> till 2007-08.<br />
Year<br />
Area (in Ha)<br />
1976-77 574<br />
1981-82 3,590<br />
1986-87 10,085<br />
1991-92 17,860<br />
1996-97 23,936<br />
2001-02 30,575<br />
2006-07 35,760<br />
2007-08 39,670<br />
Source: Economic Review of <strong>Tripura</strong> 2007-08.<br />
Agriculture & Agribusiness Opportunities – <strong>Tripura</strong> State Profile<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> is the remotest state in the northeast region.<br />
Agriculture exhibited an annual compound growth rate of 4.84 percent during the period from<br />
1993-94 to 2008-09.<br />
The total population in Assam state is about 0.32 crore (0.31 % of <strong>India</strong> Population).<br />
Net State Domestic Product in Crores<br />
Per Capita Income<br />
as per sector<br />
Occupational Distribution of Population
Category wise Distribution of workers<br />
Developments in the Agricultural Sector<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong> has net-cropped area of 2.551akh hectares. About 24.3 percent area is devoted to<br />
agriculture use. The principal crops cultivated are paddy, wheat, jute, sugar cane, potato,<br />
turmeric, coconut, oil seeds, pineapple, jackfruit, orange, banana, litchi, potato, tomato,<br />
cauliflower, cabbage, ginger, turmeric, cashew and ginger.<br />
The state is the highest pineapple and jackfruit producing area in the country. Though most of<br />
the crops grown are consumed within and caters to the local market but some vegetable and<br />
horticultural crops like cabbage, cauliflower, potato and pineapple, orange, jackfruit, ginger, etc.<br />
are supplied to the rest of the country.<br />
Due to close proximity of the state to Bangladesh, the producers find it profitable and convenient<br />
to send the produce to that country<br />
Paddy/rice is the main crop grown in the state occupying 70 percent of the gross cropped area.<br />
Other crops having significant share in gross cropped area are fruits and vegetables. Of all the<br />
major crops, production of food grains, tea and spices has increased over the years.<br />
The state government has taken several steps to augment production of diverse crops grown in<br />
<strong>Tripura</strong>. The food grain production was increased from 5.13 lakh tons during 1999-00 to 6.48 lakh<br />
tons during 2009-10. A significant aspect had been the growth in HYV seed replacement rate,<br />
which increased from 2.8 percent in 1999-2000 to 33 percent by 2009-10.<br />
The productivity of jhum paddy has been increased from 409 kg/ha to 1000 kg/ha during the<br />
above mentioned period. As has been observed in many other Northeast states, per hectare use<br />
of chemical fertilizer has remained at a low level of 39 kg/ha.
<strong>Tripura</strong> is also a major producer of horticultural products. Pineapples and oranges from <strong>Tripura</strong><br />
region are renowned for unique flavor and organic nature of produce. There is immense<br />
potential for development of this sector. In order to realize the potential in the horticultural and<br />
food processing sector, the government has established a Food Park at Bodhjungnagar, which has<br />
all the modern facilities like testing laboratories, cold storage, pack house, ware house etc. that<br />
are needed for the growth of food processing industries
Initiatives and Incentives to Promote Agriculture and Agribusiness<br />
The state government has put significant emphasis on the development of agro and food<br />
processing industries with an objective to ensure better returns to the farmers for their products as<br />
well as to create employment opportunities in the rural areas.<br />
The government has also identified the need for infrastructure creation with community<br />
participation for fruit processing and for establishing a fresh fruit marketing chain.<br />
The agro-processing is also thought to be promoted under joint venture or public private<br />
partnership. Along with these, other major thrust areas include, (1) increase in the production of<br />
food grains and certified seeds for High Yielding Varieties, (2) increase in seed replacement rate,<br />
(3) raise fertilizer use rate for both chemicals and bio-fertilizers, and (4) enhance credit to farmers.<br />
Following is the outcome of government's initiatives in this direction.<br />
Since rice is a major crop in the region, the government of <strong>Tripura</strong> also envisages adoption<br />
of best practices through a System of Rice Intensification (SRI). The government has<br />
achieved substantial results from this initiative as the area under SRI has increased<br />
significantly. In the year 2009-10, 59,577 ha was covered under SRI against 39,490<br />
hectares in 2008-09. A target of 85,000 hectares has been fixed for 201011 & 1.00 Lakh<br />
Ha by 2011-12. SRI aims to achieve 15-20 percent increase in yields in paddy cultivation.<br />
The thrust areas for industrial promotion in <strong>Tripura</strong> have been identified as below.<br />
1.Cashew nut processing 2. Fruits & vegetable processing 3. Jackfruit processing 4. Canned fruit<br />
pulps and slices 5. Animal feeds 6. Desiccated coconut 7. Energy food 8. Tapioca starch<br />
9.Pineapple processing 10. Cashew processing 11. Fruit canning 12. Cold storage 13. Spice<br />
powder processing.