Solving equations involving parallel and perpendicular lines examples
Solving equations involving parallel and perpendicular lines examples Solving equations involving parallel and perpendicular lines examples
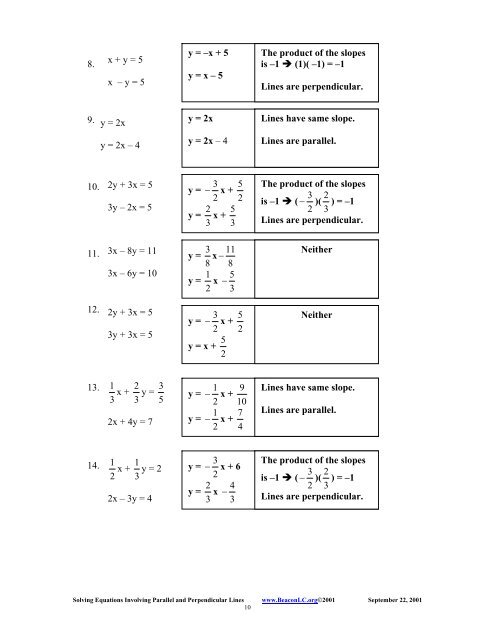
8. x + y = 5 x – y = 5 y = –x + 5 y = x – 5 The product of the slopes is –1 (1)( –1) = –1 Lines are perpendicular. 9. y = 2x y = 2x Lines have same slope. y = 2x – 4 y = 2x – 4 Lines are parallel. 10. 2y + 3x = 5 3y – 2x = 5 3 5 y = − x + 2 2 2 5 y = x + 3 3 The product of the slopes 3 2 is –1 ( − )( ) = –1 2 3 Lines are perpendicular. 11. 3x – 8y = 11 3 11 y = x − 8 8 Neither 3x – 6y = 10 1 5 y = x − 2 3 12. 2y + 3x = 5 3y + 3x = 5 3 5 y = − x + 2 2 5 y = x + 2 Neither 13. 1 2 3 x + y = 3 3 5 2x + 4y = 7 1 9 y = − x + 2 10 1 7 y = − x + 2 4 Lines have same slope. Lines are parallel. 14. 1 1 x + y = 2 2 3 2x – 3y = 4 3 y = − x + 6 2 2 4 y = x − 3 3 The product of the slopes 3 2 is –1 ( − )( ) = –1 2 3 Lines are perpendicular. Solving Equations Involving Parallel and Perpendicular Lines www.BeaconLC.org©2001 September 22, 2001 10
Find an equation of the line that passes through each given point and is parallel to the line with the given equation. 15. (4, 2); y = 2x – 4 Use m = 2 and (4, 2) to find b. 2 = 2(4) + b b = –6 y = mx + b y = 2x – 6 16. (3, 1); y = 3 1 x + 6 Use m = 3 1 and (3, 1) to find b. 1 = 3 1 (3) + b b = 0 y = mx + b y = 3 1 x 17. ( 2 1 , 3 1 ); x + 2y = 5 1 5 x + 2y = 5 y = − x + 2 2 1 1 1 Use m = − and ( , ); to find b. 2 2 3 1 1 1 = − ( ) + b 3 2 2 y = mx + b 7 1 7 b = y = − x + 12 2 12 18. (0, 0); 3x – y = 4 3x – y = 4 y = 3x – 4 Use m = 3 and (0, 0); to find b. 0 = 3 (0) + b b = 0 y = mx + b y = 3x Solving Equations Involving Parallel and Perpendicular Lines www.BeaconLC.org©2001 September 22, 2001 11
- Page 1 and 2: Solving Equations Involving Paralle
- Page 3 and 4: 7. Example - Find an equation of th
- Page 5 and 6: 13. Example - Find an equation of t
- Page 7 and 8: Name:___________________ Date:_____
- Page 9: Name:___________________ Date:_____
- Page 13 and 14: 22. (12, 6); 4 3 x + 2 1 y = 2 3 1
- Page 15 and 16: Student Name: __________________ Da
8.<br />
x + y = 5<br />
x – y = 5<br />
y = –x + 5<br />
y = x – 5<br />
The product of the slopes<br />
is –1 (1)( –1) = –1<br />
Lines are <strong>perpendicular</strong>.<br />
9.<br />
y = 2x<br />
y = 2x<br />
Lines have same slope.<br />
y = 2x – 4<br />
y = 2x – 4<br />
Lines are <strong>parallel</strong>.<br />
10.<br />
2y + 3x = 5<br />
3y – 2x = 5<br />
3 5<br />
y = − x +<br />
2 2<br />
2 5<br />
y = x + 3 3<br />
The product of the slopes<br />
3 2<br />
is –1 ( − )( ) = –1<br />
2 3<br />
Lines are <strong>perpendicular</strong>.<br />
11.<br />
3x – 8y = 11<br />
3 11<br />
y = x − 8 8<br />
Neither<br />
3x – 6y = 10<br />
1 5<br />
y = x − 2 3<br />
12.<br />
2y + 3x = 5<br />
3y + 3x = 5<br />
3 5<br />
y = − x +<br />
2 2<br />
5<br />
y = x + 2<br />
Neither<br />
13.<br />
1 2 3 x + y =<br />
3 3 5<br />
2x + 4y = 7<br />
1 9<br />
y = − x +<br />
2 10<br />
1 7<br />
y = − x +<br />
2 4<br />
Lines have same slope.<br />
Lines are <strong>parallel</strong>.<br />
14.<br />
1 1 x + y = 2<br />
2 3<br />
2x – 3y = 4<br />
3<br />
y = − x + 6<br />
2<br />
2 4<br />
y = x − 3 3<br />
The product of the slopes<br />
3 2<br />
is –1 ( − )( ) = –1<br />
2 3<br />
Lines are <strong>perpendicular</strong>.<br />
<strong>Solving</strong> Equations Involving Parallel <strong>and</strong> Perpendicular Lines www.BeaconLC.org©2001 September 22, 2001<br />
10