CASINO manual - Theory of Condensed Matter
CASINO manual - Theory of Condensed Matter
CASINO manual - Theory of Condensed Matter
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
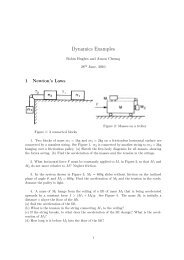
|k| (outermost). Hence one can specify excitations <strong>of</strong> electrons unambiguously. An example <strong>of</strong> the<br />
labelling <strong>of</strong> the {k} for a 2D HEG is shown below. Note that adding and subtracting electrons to<br />
or from particular states in a HEG is achieved by increasing or decreasing the electron number and<br />
making appropriate promotions. Note also that the angular sorting <strong>of</strong> the k vectors is not performed<br />
when the wave function is real, i.e., when complex wf = F.<br />
52<br />
47<br />
51<br />
40<br />
32<br />
27<br />
31<br />
39<br />
41<br />
23<br />
16<br />
11<br />
15<br />
22<br />
38<br />
53<br />
33<br />
17<br />
7<br />
3<br />
6<br />
14<br />
30<br />
50<br />
48<br />
28<br />
12<br />
4<br />
1 2<br />
10<br />
26<br />
46<br />
54<br />
34<br />
18<br />
8<br />
5 9<br />
21<br />
37<br />
57<br />
42<br />
24<br />
19 13 20<br />
25<br />
45<br />
43<br />
35 29 36<br />
44<br />
55 49 56<br />
The labelling <strong>of</strong> the k-vectors in a 2D HEG with a square cell. The filled points indicate the doubly occupied<br />
states in a 74-electron paramagnetic ground state. If one wishes to create an excitation <strong>of</strong> an up-spin electron<br />
from state 25 to state 47 in determinant 1, say, then one should include ‘DET 1 1 PR 1 25 1 47’ in the<br />
excitation specification in the MDET block in correlation.data.<br />
7.4.5 Atomic orbital modification functions<br />
The format <strong>of</strong> the data set used to specify atomic orbital modifications in correlation.data is as<br />
follows:<br />
START ORBMODS<br />
Title<br />
Orbital modification functions for 2s and 2p orbitals <strong>of</strong> neon<br />
Spin-dependence (0->u=d; 1->u/=d)<br />
0<br />
Number <strong>of</strong> modification functions<br />
2<br />
START MODFN 1<br />
Quantum numbers n and l<br />
2 0<br />
Expansion order<br />
3<br />
Parameters in modification function ; Optimizable (0=NO; 1=YES)<br />
END MODFN 1<br />
START MODFN 2<br />
Quantum numbers n and l<br />
2 1<br />
Expansion order<br />
4<br />
Parameters in modification function ; Optimizable (0=NO; 1=YES)<br />
END MODFN 2<br />
END ORBMODS<br />
Notes:<br />
• Atomic orbital modification functions can only be used if atom basis type=‘numerical’ (i.e.,<br />
numerical atomic orbitals are used) and the use orbmods keyword is set to T. When<br />
atom basis type=‘numerical’, the system consists <strong>of</strong> a single, isolated atom, with the nucleus<br />
lying at the origin.<br />
67