exotic nuclei structure and reaction noyaux exotiques ... - IPN - IN2P3
exotic nuclei structure and reaction noyaux exotiques ... - IPN - IN2P3
exotic nuclei structure and reaction noyaux exotiques ... - IPN - IN2P3
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
In figure 4 we plot the differential limits <strong>and</strong> the<br />
corresponding integral limits assuming a flux proportional<br />
to E -2 . Also shown is the background contribution<br />
expected to originate from interactions of<br />
CR protons with the CMB. The neutrino background<br />
predicted is smaller if the highest energy<br />
CRs are heavy <strong>nuclei</strong>. shower is directly measured<br />
by the FD elongation rate.<br />
UHECR composition<br />
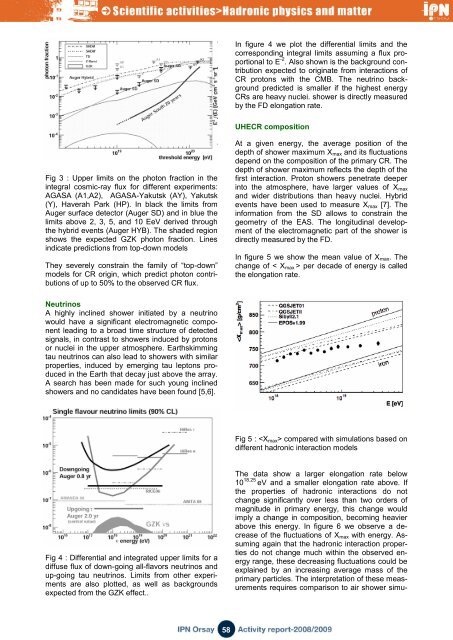
Fig 3 : Upper limits on the photon fraction in the<br />
integral cosmic-ray flux for different experiments:<br />
AGASA (A1,A2), AGASA-Yakutsk (AY), Yakutsk<br />
(Y), Haverah Park (HP). In black the limits from<br />
Auger surface detector (Auger SD) <strong>and</strong> in blue the<br />
limits above 2, 3, 5, <strong>and</strong> 10 EeV derived through<br />
the hybrid events (Auger HYB). The shaded region<br />
shows the expected GZK photon fraction. Lines<br />
indicate predictions from top-down models<br />
They severely constrain the family of “top-down”<br />
models for CR origin, which predict photon contributions<br />
of up to 50% to the observed CR flux.<br />
At a given energy, the average position of the<br />
depth of shower maximum X max <strong>and</strong> its fluctuations<br />
depend on the composition of the primary CR. The<br />
depth of shower maximum reflects the depth of the<br />
first interaction. Proton showers penetrate deeper<br />
into the atmosphere, have larger values of X max<br />
<strong>and</strong> wider distributions than heavy <strong>nuclei</strong>. Hybrid<br />
events have been used to measure X max [7]. The<br />
information from the SD allows to constrain the<br />
geometry of the EAS. The longitudinal development<br />
of the electromagnetic part of the shower is<br />
directly measured by the FD.<br />
In figure 5 we show the mean value of X max . The<br />
change of < X max > per decade of energy is called<br />
the elongation rate.<br />
Neutrinos<br />
A highly inclined shower initiated by a neutrino<br />
would have a significant electromagnetic component<br />
leading to a broad time <strong>structure</strong> of detected<br />
signals, in contrast to showers induced by protons<br />
or <strong>nuclei</strong> in the upper atmosphere. Earthskimming<br />
tau neutrinos can also lead to showers with similar<br />
properties, induced by emerging tau leptons produced<br />
in the Earth that decay just above the array.<br />
A search has been made for such young inclined<br />
showers <strong>and</strong> no c<strong>and</strong>idates have been found [5,6].<br />
Fig 5 : compared with simulations based on<br />
different hadronic interaction models<br />
Fig 4 : Differential <strong>and</strong> integrated upper limits for a<br />
diffuse flux of down-going all-flavors neutrinos <strong>and</strong><br />
up-going tau neutrinos. Limits from other experiments<br />
are also plotted, as well as backgrounds<br />
expected from the GZK effect..<br />
The data show a larger elongation rate below<br />
10 18.25 eV <strong>and</strong> a smaller elongation rate above. If<br />
the properties of hadronic interactions do not<br />
change significantly over less than two orders of<br />
magnitude in primary energy, this change would<br />
imply a change in composition, becoming heavier<br />
above this energy. In figure 6 we observe a decrease<br />
of the fluctuations of X max with energy. Assuming<br />
again that the hadronic interaction properties<br />
do not change much within the observed energy<br />
range, these decreasing fluctuations could be<br />
explained by an increasing average mass of the<br />
primary particles. The interpretation of these measurements<br />
requires comparison to air shower simu-<br />
58